A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Optimization of Processing Technology for Tiebangchui with Zanba Based on CRITIC Combined with Box-Behnken Response Surface Method
In This Article
Summary
The present protocol describes an efficient and standard detoxification processing method for Zanba-stir-fried Tiebangchui using CRITIC combined with the Box-Behnken response surface method.
Abstract
The dried root of Aconitum pendulum Busch., called Tiebangchui (TBC) in Chinese, is one of the most famous Tibetan medicines. It is a widely used herb in northwest China. However, many cases of poisoning have occurred because of TBC's intense toxicity and because its therapeutic and toxic doses are similar. Therefore, finding a safe and effective method to reduce its toxicity is an urgent task. A search through the Tibetan medicine classics shows that the processing method of TBC stir-fried with Zanba was recorded in the "Processing specification of Tibetan medicine of Qinghai Province (2010)". However, the specific processing parameters are not yet clear. Thus, this study aims to optimize and standardize the processing technology of Zanba-stir-fried TBC.
First, a single-factor experiment was conducted on four factors: the slice thickness of TBC, amount of Zanba, processing temperature, and time. With monoester and diester alkaloid contents in Zanba-stir-fried TBC as indexes, CRITIC combined with the Box-Behnken response surface method was used to optimize the processing technology of Zanba-stir-fried TBC. The optimized processing conditions of Zanba-stir-fried TBC were a TBC slice thickness of 2 cm, three times more Zanba than TBC, a processing temperature of 125 °C, and 60 min of stir-frying. This study determined the optimized and standard processing conditions for the usage of Zanba-stir-fried TBC, thus providing an experimental basis for the safe clinical use and industrial production of Zanba-stir-fried TBC.
Introduction
The dried root of Aconitum pendulum Busch and A. flavum Hand.-Mazz., one of the most famous Tibetan medicines, is called Tiebangchui (TBC) in Chinese1,2. The dried roots of TBC are helpful in dispelling cold and wind, reducing pain, and calming shock. It was recorded in the first volume of "Drug Standards (Tibetan Medicine) of the Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China," which states that the dried roots of TBC are commonly used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, bruises, and other cold diseases3. However, the clinical therapeutic dose of TBC is similar to its toxic dose, and incidents of poisoning or death have been frequently reported due to improper use4. Therefore, reducing the toxicity and preserving the efficacy of TBC has become a research hot spot over the years.
In Tibetan medicine, processing is one of the most effective methods to attenuate the toxicity of TBC. According to "Processing specification of Tibetan medicine of Qinghai Province (2010)", the original herbs (TBC) should be placed in an iron pot and stir-fried with Zanba until the Zanba turns yellow, after which Zanba is removed and the herbs are dried in air5,6. However, no specific process parameters have been documented, which makes controlling the processing technology and the quality of Zanba-stir-fried TBC difficult. The CRITIC method is an objective weight method that can avoid fuzzification and subjectivity, and enhance the objectivity of weighing7. The Box-Behnken response surface method can directly reflect the interaction between each factor through polynomial fitting8. The combination of the Box-Behnken response surface and CRITIC method is commonly used to optimize processing technology to acquire the optimized processing protocol9,10. In this paper, a monoester-diterpenoid alkaloid (MDA) (benzoylaconitine) and two diester-diterpenoid alkaloids (DDAs) (aconitine, 3-deoxyaconitine) were used as evaluation indexes. CRITIC combined with the Box-Behnken response surface method was applied to optimize the processing technology of Zanba-stir-fried TBC and establish a standard processing method for clinical safe use.
Protocol
The Zanba-stir-fried TBC processing method was optimized and standardized by CRITIC combined with the Box-Behnken response surface method. Benzoylaconitine, aconitine, and 3-deoxyaconitine were used as evaluation indexes during this procedure.
1. Sample solution preparation
- Prepare the reference substance stock solution. Weigh precisely 9.94 mg of benzoylaconitine, 8.49 mg of aconitine, and 6.25 mg of 3-deoxyaconitine (Table of Materials) on an electronic analytical balance and place them in a 10 mL volumetric flask. Then, add 0.05% hydrochloric acid methanol solution to dissolve the solids and make up the volume to 10 mL. Finally, shake the mixture well to obtain the reference substance stock solution with mass concentrations of 0.9940 mg/mL benzoylaconitine, 0.8490 mg/mL aconitine, and 0.6250 mg/mL of 3-deoxyaconitine.
CAUTION: Hydrochloric acid is a highly corrosive material11. Use proper protection, such as gloves, a lab coat, goggles, and a fume hood. - Prepare the test sample solution.
- Weigh 2 g of Zanba-stir-fried TBC powder in a conical flask.
- Prepare Zanba-stir-fried TBC by weighing 30 g of TBC (2 cm) and 90 g of Zanba and adding them into the preheated stir-fry machine. Set the time and temperature of the stir-fry machine to 40 min and 140 °C, respectively. Set the machine to complete processing.
- Use a high-speed smashing machine to grind the Zanba-stir-fried TBC separately into powder samples that can pass through a 50 mesh (0.355 mm) sieve.
- Add 3 mL of ammonia solution and 50 mL of a mixed solution of isopropyl alcohol and ethyl acetate (a ratio of 1:1 v/v) into the above conical flask, based on previous studies12,13.
NOTE: To prepare the ammonia solution, add 40 mL of concentrated ammonia solution into a 100 mL volumetric flask and fill with purified water to the measuring line. Take appropriate protective measures when using concentrated ammonia solution as it has a strong smell. - Weigh the above sample and conical flask and record the weight. Ultrasonicate for 30 min (voltage: 220 V, frequency: 40 kHz).
NOTE: Aconitine alkaloids are easily decomposed by heat. Thus, the temperature of ultrasonic extraction must be below 25 °C. - Weigh the sample and conical flask after ultrasonic extraction.
- Make up for the lost weight by adding a mixture of isopropyl alcohol and ethyl acetate (ratio of 1:1 v/v).
- Filter the sample solution. Evaporate 25 mL of the filtrate to dryness using a rotary evaporator at 40 °C.
- Dissolve the residue by adding 5 mL of 0.05% hydrochloric acid methanol solution, filter the solution through a 0.2 µm syringe filter, and analyze it by performing high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
- Weigh 2 g of Zanba-stir-fried TBC powder in a conical flask.
- Prepare a mixed reference solution that contains 0.1988 mg/mL benzoylaconitine, 0.0509 mg/mL aconitine, and 0.0938 mg/mL 3-deoxyaconitine.
NOTE: Each standard (0.9940 mg of benzoylaconitine, 0.2545 mg of aconitine, and 0.4690 mg of 3-deoxyaconitine) is dissolved in a 5 mL volumetric flask in 0.05% hydrochloric acid methanol as the dissolution medium. - Prepare 0.04 M ammonium acetate buffer by dissolving 6.16 g of ammonium acetate (Table of Materials) in 2 L of ultrapure water (mobile phase A). Adjust the pH to 8.50 using ammonia.
CAUTION: Ammonia is a hazardous material. Use proper protection, such as gloves, a lab coat, goggles, and a fume hood. - Filter 2 L of ultrapure 100% acetonitrile (mobile phase B) and degas it.
CAUTION: Acetonitrile is a hazardous material13. Use proper protection, such as gloves, a lab coat, goggles, and a fume hood.
2. Chromatographic condition
- Inject 10 µL of the pretreated sample solutions into an HPLC system with binary pumps. Use an HPLC system employing an ODS-3 column (5 µm x 4.6 mm x 250 mm; working at 30 °C) with mobile phases A and B for the MDA and DDAs separation. Inject each sample three times for technical replication.
- Program the method as shown in Table 1 for the ODS-3 column. Set a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min and the detection wavelength as 235 nm.
- Record the peak areas of every target compound.
NOTE: Details of the instruments can be found in the Table of Materials.
3. System adaptability test
NOTE: Refer to section 2 for the chromatographic conditions to perform steps 3.1-3.5.
- Investigate the linear relationship between the concentration and peak area.
- Prepare various concentrations - 19.88, 39.76, 59.64, 159.04, 198.80, and 497.00 µg/mL - of benzoylaconitine solution.
- Prepare various concentrations - 8.49, 16.98, 25.47, 33.96, 50.94, and 169.80 µg/mL - of aconitine solution.
- Prepare various concentrations - 1.875, 12.50, 37.50, 62.50, 93.75, and 125.00 µg/mL - of 3-deoxyaconitine solution.
- Inject the above reference solutions from low mass concentration to high mass concentration and record the peak areas.
- Obtain three linear regression equations from the plot of the reference solution concentration (µg/L) against the peak area.
NOTE: Ensure that the concentrations of benzoylaconitine, aconitine, and 3-deoxyaconitine fall within the linear range of this standard curve.
- Perform precision testing by continuously injecting six repeats of 10 µL of the sample solution into the HPLC system and run the samples under the same HPLC conditions described in section 2. Record the peak areas of benzoylaconitine, aconitine, and 3-deoxyaconitine.
- Perform stability testing experiments by injecting 10 µL of the prepared sample solution and determine the peak areas after 0 h, 2 h, 4 h, 8 h, 12 h, and 24 h.
NOTE: The peak areas are recorded automatically by the referenced HPLC system. These time points were based on relevant literature15,16,17. - Perform the reproducibility test by taking the same batch of Zanba-stir-fried TBC to prepare six test sample solutions in parallel according to the method in step 1.2. Inject 10 µL of each sample into the HPLC system and run the samples as described in section 2.
NOTE: Reproducibility was assessed by comparing the concentration differences between the six samples. - Perform the recovery experiment by preparing six portions of the same batch of Zanba-stir-fried TBC for the test solution. Then, add ~100% of the reference substance of each index component into six portions of the test solution to calculate the recovery rate. Inject these samples (10 µL) into the HPLC system under the same conditions described in section 2 and calculate the recovery rate using Equation (1):
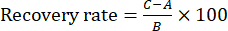 (1)
(1)
NOTE: In Eq. (1), A is the amount of the component to be measured in the test solution, B is the amount of reference substance added, and C is the measured value of the solution that contains the reference substance and the Zanba-stir-fried TBC sample.
4. Single-factor experiments
- Comparison of slice thickness
- Prepare five groups for tests, each with 30 g of TBC, where the thickness of the TBC is 0.5, 1, 2, 3, and 4 cm, respectively. Weigh an amount of Zanba that is three times as much as that of TBC (90 g).
NOTE: TBC is toxic. Use proper protection, such as gloves, a lab coat, goggles, and a fume hood, and be careful during the cutting process. Through the pre-experiment, it was found that three times the amount of Zanba was required for complete contact between TBC and Zanba. Therefore, in the formal experimental design, the study selected three times the amount of Zanba when examining the slice thickness. - Set the temperature and the time of the automatic stir-fry machine to 140 °C and 40 min, respectively.
- Add ~30 g of TBC and 90 g of Zanba into the machine after the automatic stir-fry machine has heated up to the set temperature.
- Prepare the sample solutions by following step 1.2. Calculate the contents of the MDA and DDAs in different processing products according to the standard curve (Table 2). Calculate the comprehensive score based on the results via the CRITIC method in section 6.
- In this way, compare the amounts of Zanba, as well as processing temperatures and times for optimization of the conditions.
- Prepare five groups for tests, each with 30 g of TBC, where the thickness of the TBC is 0.5, 1, 2, 3, and 4 cm, respectively. Weigh an amount of Zanba that is three times as much as that of TBC (90 g).
- Comparison of the amount of Zanba
- Perform five groups of tests, each with 30 g of TBC (2 cm), where the amount of Zanba is one, two, three, four, and five times as much as TBC, respectively.
- Turn on the stir-fry machine for processing. Set the time and the temperature of the stir-fry machine at 40 min and 140 °C.
- Prepare the sample solutions by following step 1.2. Calculate the content of the MDA and DDAs in different processing products according to the standard curve (Table 2). Calculate the comprehensive score based on the results via the CRITIC method in section 6.
- Comparison of processing temperature
- Perform five groups of tests, each with 30 g of TBC (2 cm) and 90 g of Zanba.
- Turn on the stir-fry machine for processing. Set the processing temperature to 100 °C, 120 °C, 140 °C, 160 °C, and 180 °C. Set the processing time as 40 min.
NOTE: Through pre-experiments, it was found that the speed of Zanba yellowing is very low when the processing temperature is below 100 °C, and Zanba is easy to burn and turn black if the temperature is too high (above 180 °C). Therefore, 100 °C and 180 °C were set to be the minimum and maximum values of temperature during processing, respectively. - Prepare the sample solutions by following step 1.2. Record the peak areas of the MDA and DDAs. Calculate the content of the MDA and DDAs in different processing products according to the standard curve (Table 2). Calculate the comprehensive score based on the results via the CRITIC method in section 6.
NOTE: The experiment involves high temperatures of 160 °C and 180 °C. Pay attention to safety during the experiment, according to the safety code of the laboratory.
- Comparison of processing time
- Perform five groups of tests, each with 30 g of TBC (2 cm) and 90 g of Zanba.
- Turn on the stir-fry machine for processing. Set the processing time to 20, 40, 60, 80, and 100 min. Set the temperature to 140 °C.
- Prepare the sample solutions by following the description in step 1.2. Record the peak areas of the MDA and DDAs. Calculate the quality of the MDA and DDAs in different processing products according to the standard curve (Table 2). Calculate the comprehensive score based on the results via the CRITIC method in section 6.
5. Processing technology optimization of Zanba-stir-fried TBC using response surface methodology (RSM)
- Box-Behnken response surface design
- Determine the range of slice thickness (A, 1-3 cm), the amount of Zanba (B, 2-4x), the processing temperature (C, 100-140 °C), and the processing time (D, 40-80 min) by preliminary experiments using single-factor tests (step 4.1-4.4).
NOTE: The coded values of four variables and their levels are shown in Table 3. Three levels of each variable were coded as -1, 0, and 1.
- Determine the range of slice thickness (A, 1-3 cm), the amount of Zanba (B, 2-4x), the processing temperature (C, 100-140 °C), and the processing time (D, 40-80 min) by preliminary experiments using single-factor tests (step 4.1-4.4).
- Use software to generate the matrix and analyze the response surface models.
NOTE: The screenshots for the software usage are shown in Supplementary File 1.- Use a three-level-four-factor Box-Behnken design composed of 24 experiments (as done in this study), and measure five replicates (run order 1, 9, 14, 16, and 25) to calculate the pure error sum of squares (Table 4). Set the comprehensive score (Y) as the response (steps 1-4, Supplementary File 1).
- On the home page, click on New Design (step 1, Supplementary File 1), and in the left panel of the Design page, click on Response Surface | Box-Behnken and set the parameters of the four factors in the table (step 2, Supplementary File 1).
- Click on Next (step 2, Supplementary File 1), set the response names, and click on Finish (step 3, Supplementary File 1).
- Generate the response surface design through the above operation (step 4, Supplementary File 1).
- Use a three-level-four-factor Box-Behnken design composed of 24 experiments (as done in this study), and measure five replicates (run order 1, 9, 14, 16, and 25) to calculate the pure error sum of squares (Table 4). Set the comprehensive score (Y) as the response (steps 1-4, Supplementary File 1).
- Complete the experiment based on the 29 scenarios designed for the response surface.
- Prepare the sample solutions by following step 1.2.
- Record the peak areas of the MDA and DDAs.
NOTE: The peak areas are recorded automatically by the referenced HPLC system. - Calculate the quality of the MDA and DDAs in the different processing products.
- Calculate the comprehensive score based on the results via the CRITIC method in step 6.
NOTE: The specific method is illustrated in step 6. - Input the obtained comprehensive score of 29 trials into the computer and analyze it using the referenced software (step 5, Supplementary File 1).
- Perform the statistical validation of the polynomial equations and response surface analyses plotted in 3D model graphs through the software (steps 6-8, Supplementary File 1).
- In the left Navigation pane, under Analysis (+), click on Y, and then click on Start Analysis in the Configure window (step 6, Supplementary File 1).
- Click on ANOVA in the top menu and observe the table of results displaying variance analysis (step 7, Supplementary File 1).
- In the top menu, click on Model Graphs and then 3D Surface to obtain the response surface plots reflecting the effects of processing parameters on the synthetic scores (step 8, Supplementary File 1).
- Perform the validation of the response surface model in triplicate under the predicted optimum conditions (step 9, Supplementary File 1) to verify the stability of the processing technology. In the left Navigation pane, under Optimization, click on Numerical Then, in the top menu, click on Solutions. Observe the predicted optimal conditions.
6. Model evaluation
NOTE: This step is to be performed after each single-factor experiment or response surface experiment has been completed. After each experiment (e.g., comparison of slice thickness) is completed, the content of the MDA and DDAs in the different samples are measured to obtain five datasets, according to step 1.2 and section 2. The data are shown in Supplementary Table S1.
- Dimensionless processing of the index
NOTE: This step transforms the measured value (Xij) into a dimensionless relative value, so that the value of each index is at the same quantity level. This operation can facilitate comprehensive analysis and comparison of indicators in different units or orders of magnitude18. For the purposes of illustration, slice thickness values have been used for the calculations shown below (Supplementary Table S1).- Standardize the content of the MDA (obtain yMDA; MDA refers to benzoylaconitine) by using the formula in Eq. (2).
NOTE: The index "i" stands for one of four factors, and slice thickness is the first factor investigated. Hence, the value of i is equal to 1. The index "j" stands for each level of factors; thus, when the slice thickness is the first level (0.5 cm), j is equal to 1; When the slice thickness is the fifth level (4 cm), j is equal to 5. The contents of MDA (Xij) in the processed TBC with thicknesses of 0.5, 1, 2, 3, and 4 cm were 0.9693, 1.0876, 1.3940, 1.4185, and 1.3614 mg/g, respectively. Thus, xj, max is 1.4185 and xj, min is 0.9693.
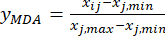 (2)
(2)
Thus,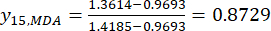
Here, Xij is the measured content of the MDA of the experiment in the i-th factor and at the j-th level; xj, min is the minimum content of the MDA in this group of experiments; and xj, max is the maximum content of the MDA in this group of experiments. Thus, i = 1, 2, …, m, and j = 1, 2, …, n.
NOTE: Thus, the standardized values of the MDA are 0.0000, 0.2634, 0.9455, 1.0000, and 0.8729 using Eq. (2). - Standardize the total content of the DDAs (obtain yDDAs; DDAs refers to aconitine and 3-deoxyaconitine) by using the formula in Eq. (3).
NOTE: i is one of four factors, and j is each level of the factors; Xij is the measured content of the DDAs of the experiment in the i-th factor and at the j-th level; xj, min is the minimum content of the DDAs in this group experiment of data; and xj, max is the maximum content of the DDAs in this group experiment of data. In this way, i = 1, 2, …, m, and j = 1, 2, …, n. The contents of the DDAs (Xij) in the processed TBC with thicknesses of 0.5, 1, 2, 3, and 4 cm were 0.3492, 0.2692, 0.2962, 0.5354, 0.5124 mg/g, respectively. Thus, xj, max is 0.5354 and xj, min is 0.2692.
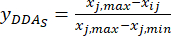 (3)
(3)
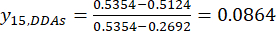
NOTE: The standardized values are 0.6995, 1.0000, 0.8986, 0.0000, and 0.0864 using Eq. (3).
- Standardize the content of the MDA (obtain yMDA; MDA refers to benzoylaconitine) by using the formula in Eq. (2).
- Calculate the corresponding contrast intensity (Si), conflict (δi), information (Ci), and index weight (Wi) according to Eqs. (4) to (7), respectively19,20.
NOTE: i = 1, 2, …, m. yij is the standardized data of the MDA or DDAs content of the experiment in the i-th factor and at the j-th level.- To estimate the contrast intensity, first calculate the average MDA value.
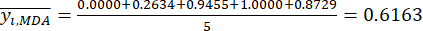
Where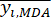 is the average value of the MDA.
is the average value of the MDA.
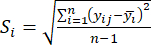 (4)
(4)
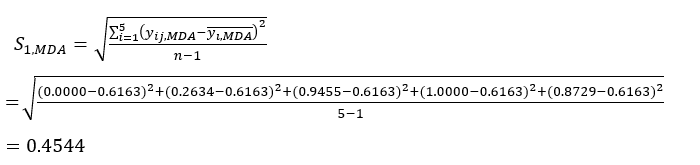
- To calculate the conflict value, first estimate the correlation coefficient γij using the CORREL function in Excel21.
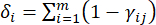 (5)
(5)
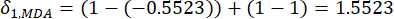
- Calculate information values as follows.
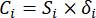 (6)
(6)
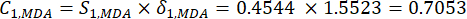
NOTE: Similarly, C1, DDAS = 0.7210 - Calculate the index weight as follows.
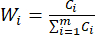 (7)
(7)
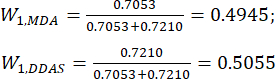
NOTE: Therefore, the weight coefficients of the MDA and DDAs in comparison of slice thickness were established as 0.4945 and 0.5055, respectively.
- To estimate the contrast intensity, first calculate the average MDA value.
- Calculate the comprehensive scores of slice thicknesses.
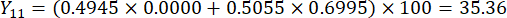
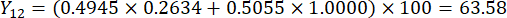
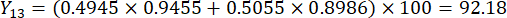
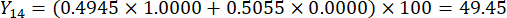
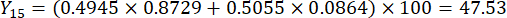
NOTE: Y13 is the maximum value. Therefore, the best parameter of slicing thicknesses is the third level - 2 cm.
Results
In this study, the elution gradient used had a good resolution (Figure 1) for the three index components in Zanba-stir-fried TBC, as determined after repeated debugging. The three index components in Zanba-stir-fried TBC had a good linear relationship within a specific concentration range (Table 2). The precision (Table 5), stability (Table 6), repeatability (Table 7), and sample recovery (Table 8) of Zanba-...
Discussion
TBC is an important Tibetan medicine with the effects of dispelling cold and relieving pain. It has been mostly used to treat traumatic injury and rheumatic arthralgia in China for thousands of years24,25,26. Diterpenoid alkaloids are both active and toxic ingredients of TBC27,28,29. The main toxic effects of the aconitum alkaloids of T...
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82130113), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2021MD703800), the Science Foundation for Youths of Science & Technology Department of Sichuan Province (No. 2022NSFSC1449), and the "Xinglin Scholars" Research Promotion Program of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. BSH2021009).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 3-Deoxyaconitine | Chengdu Desite Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | DST221109-033 | |
| Aconitine | Chengdu Desite Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | DSTDW000602 | |
| Ammonium acetate | Tianjin Kermel Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd | Chromatographic grade | |
| Benzoylaconitine | Chengdu Desite Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | DSTDB005502 | |
| Design-Expert software | Stat-Ease, Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA | version 13.0 | |
| Electronic analytical balance | Shanghai Liangping Instruments Co., Ltd. | FA1004 | |
| High performance liquid chromatography | SHIMADZU Co., Ltd. | LC-20A | |
| High-speed smashing machine | Beijing Zhongxing Weiye Instrument Co., Ltd. | FW-100 | |
| Millipore filter | Tianjin Jinteng Experimental Equipment Co., Ltd | φ13 0.22 Nylon66 | |
| stir-Fry machine | Changzhou Maisi Machinery Co., Ltd | Type 5 | |
| Tiebangchui | Gannan Baicao Biotechnology Development Co., Ltd | 20211012 | |
| Ultra pure water systemic | RephiLe Bioscience, Ltd. | Genie G | |
| Ultrasonic cleansing machine | Ningbo Xinyi Ultrasonic Equipment Co., Ltd | SB2200 | |
| Zanba | 27 Chuanzang Road, Ganzi County | - |
References
- Li, C. Y., et al. Aconitum pendulum and Aconitum flavum: A narrative review on traditional uses, phytochemistry, bioactivities and processing methods. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 292, 115216 (2022).
- Wang, J., Meng, X. H., Chai, T., Yang, J. L., Shi, Y. P. Diterpenoid alkaloids and one lignan from the roots of Aconitum pendulum Busch. Natural Products and Bioprospecting. 9 (6), 419-423 (2019).
- Yu, L., et al. Traditional Tibetan medicine: therapeutic potential in rheumatoid arthritis. Frontiers In Pharmacology. 13, 938915 (2022).
- Zhao, R., et al. One case of ventricular arrhythmia caused by poisoning of traditional Chinese medicine Aconitum pendulum Busch. Journal of People's Military Medical. 61 (4), 346-348 (2018).
- Qinghai Medical Products Administration. Processing specification of Tibetan medicine of Qinghai province. Qinghai Nationalities Publishing House. , 96-97 (2010).
- Li, J., et al. Comparison of three objective weighting methods to optimize the extraction process of Jianwei Chupi granules. Journal of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University. 38 (6), 91-97 (2022).
- Feng, Z. G., et al. Processing methods and the underlying detoxification mechanisms for toxic medicinal materials used by ethnic minorities in China: A review. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 305, 116126 (2023).
- Hsu, Y. T., Su, C. S. Application of Box-Behnken design to investigate the effect of process parameters on the microparticle production of ethenzamide through the rapid expansion of the supercritical solutions process. Pharmaceutics. 12 (1), 42 (2020).
- Cheng, F., et al. Optimization of the baked drying technology of Cinnamomi Ramulus based on CRITIC combined with box-behnken response surface method. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials. 2022 (8), 1838-1842 (2022).
- Huang, X., et al. Optimization of microwave processing technology for carbonized Gardenia jasminoides by Box-Behnken response surface methodology based on CRITIC weighted evaluation. Chinese Herbal Medicines. 48 (6), 1133-1138 (2017).
- Elling, U., et al. Derivation and maintenance of mouse haploid embryonic stem cells. Nature Protocols. 14 (7), 1991-2014 (2019).
- Gu, J., Wang, Y. P., Ma, X. Simultaneous determinnation of three diester diterpenoid alkaloids in the toots of Aconiti flavi et penduli by HPLC method. Chinese Pharmaceutical Affairs. 28 (6), 618-621 (2014).
- Zhang, Y., Fu, X. UPLC simultaneous determination of six esteric alkaloids components in Aconitum Flaram Hand.Mazz. Asia-Pacific Traditional Medicine. 16 (5), 62-65 (2020).
- Rumachik, N. G., Malaker, S. A., Paulk, N. K. VectorMOD: Method for bottom-up proteomic characterization of rAAV capsid post-translational modifications and vector impurities. Frontiers In Immunology. 12, 657795 (2021).
- Wang, Y. J., Tao, P., Wang, Y. Attenuated structural transformation of aconitine during sand frying process and antiarrhythmic effect of its converted products. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2021, 7243052 (2021).
- Wang, H. P., Zhang, Y. B., Yang, X. W., Zhao, D. Q., Wang, Y. P. Rapid characterization of ginsenosides in the roots and rhizomes of Panax ginseng by UPLC-DAD-QTOF-MS/MS and simultaneous determination of 19 ginsenosides by HPLC-ESI-MS. Journal of Ginseng Research. 40 (4), 382-394 (2016).
- vander Leeuw, G., et al. Pain and cognitive function among older adults living in the community. Journals of Gerontology Series A. Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 71 (3), 398-405 (2016).
- Lao, D., Liu, R., Liang, J. Study on plasma metabolomics for HIV/AIDS patients treated by HAART based on LC/MS-MS. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 13, 885386 (2022).
- Li, Y., et al. Evaluation of the effectiveness of VOC-contaminated soil preparation based on AHP-CRITIC-TOPSIS model. Chemosphere. 271, 129571 (2021).
- Zhong, S., Chen, Y., Miao, Y. Using improved CRITIC method to evaluate thermal coal suppliers. Scientific Reports. 13 (1), 195 (2023).
- Lewis, N. S., et al. Magnetically levitated mesenchymal stem cell spheroids cultured with a collagen gel maintain phenotype and quiescence. Journal of Tissue Engineering. 8, (2017).
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Committee. . Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. 4, (2020).
- Li, G., et al. Effect of response surface methodology-optimized ultrasound-assisted pretreatment extraction on the composition of essential oil released from tribute citrus peels. Frontiers in Nutrition. 9, 840780 (2022).
- Liu, X. F., et al. Hezi inhibits Tiebangchui-induced cardiotoxicity and preserves its anti-rheumatoid arthritis effects by regulating the pharmacokinetics of aconitine and deoxyaconitine. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 302, 115915 (2023).
- Smolen, J. S., et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Reviews.Disease Primers. 4, 18001 (2018).
- Wang, F., et al. C19-norditerpenoid alkaloids from Aconitum szechenyianum and their effects on LPS-activated NO production. Molecules. 21 (9), 1175 (2016).
- Wang, B., et al. Study on the alkaloids in Tibetan medicine Aconitum pendulum Busch by HPLC-MSn combined with column chromatography. Journal of Chromatographic Science. 54 (5), 752-758 (2016).
- Liu, S., et al. A review of traditional and current methods used to potentially reduce toxicity of Aconitum roots in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 207, 237-250 (2017).
- Qiu, Z. D., et al. Online discovery of the molecular mechanism for directionally detoxification of Fuzi using real-time extractive electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 277, 114216 (2021).
- El-Shazly, M., et al. Use, history, and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry chemical analysis of Aconitum. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis. 24 (1), 29-45 (2016).
- Chan, T. Y. K. Aconitum alkaloid poisoning because of contamination of herbs by aconite roots. Phytotherapy Research. 30 (1), 3-8 (2016).
- Guo, L., et al. Exploring microbial dynamics associated with flavours production during highland barley wine fermentation. Food Research International. 130, 108971 (2020).
- Guo, T. L., Horvath, C., Chen, L., Chen, J., Zheng, B. Understanding the nutrient composition and nutritional functions of highland barley (Qingke): A review. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 103, 109-117 (2020).
- Wu, H., et al. Anti-myocardial infarction effects of Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata extracts and their influence on small molecules in the heart using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-mass spectrometry imaging. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 20 (19), 4837 (2019).
- Huang, G., et al. Study on cardiotoxicity and mechanism of "Fuzi" extracts based on metabonomics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 19 (11), 3506 (2018).
- Li, S. L., et al. An insight into current advances on pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, toxicity and detoxification of aconitine. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 151, 113115 (2022).
- Xie, Y., et al. Optimization of processing technology of braised Rehmanniae Raidx based on multiple indexes and response surface technology and correlation between components and color. Journal of Chinese Traditional Medicine. 47 (18), 4927-4937 (2022).
- Yang, X. Q., Xu, W., Xiao, C. P., Sun, J., Feng, Y. Z. Study on processing technology of Atractylodes chinensis with rice water and its pharmacodynamics of anti-diarrhea. Chinese Herbal Medicines. 53 (1), 78-86 (2022).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved