A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
High-Resolution Respirometry to Assess Mitochondrial Function in Human Spermatozoa
In This Article
Summary
The analysis of sperm mitochondrial function by high-resolution respirometry permits the measurement of the oxygen consumption of freely moving spermatozoa in a closed-chamber system. The technique can be applied to measure respiration in human spermatozoa, which provides information on sperm mitochondrial characteristics and integrity.
Abstract
Semen quality is often studied by routine semen analysis, which is descriptive and often inconclusive. Male infertility is associated with altered sperm mitochondrial activity, so the measurement of sperm mitochondrial function is an indicator of sperm quality. High-resolution respirometry is a method of measuring the oxygen consumption of cells or tissues in a closed-chamber system. This technique can be implemented to measure respiration in human sperm and provides information about the quality and integrity of the sperm mitochondria. High-resolution respirometry allows the cells to move freely, which is an a priori advantage in the case of sperm. This technique can be applied with intact or permeabilized spermatozoa and allows for the study of intact sperm mitochondrial function and the activity of individual respiratory chain complexes. The high-resolution oxygraph instrument uses sensors to measure the oxygen concentration coupled with sensitive software to calculate the oxygen consumption. The data are used to calculate respiratory indices based on the oxygen consumption ratios. Consequently, the indices are the proportions of two oxygen consumption rates and are internally normalized to the cell number or protein mass. The respiratory indices are an indicator of sperm mitochondrial function and dysfunction.
Introduction
Male infertility is estimated to account for 40%-50% of all cases of infertility in couples1. Conventional semen analysis plays a crucial part in determining male fertility; however, approximately 15% of infertile men have normal sperm parameters2. In addition, routine semen analysis provides limited information about sperm function and does not reflect subtle sperm defects3.
Sperm mitochondria have a special structure, as they are arranged as a helical sheath around the flagella. The mitochondrial sheath contains a variable number of mitochondria connected by intermitochondrial linkers and anchored to the cytoskeleton by ordered protein arrangements on the outer mitochondrial membrane4,5. This structure makes it particularly difficult to isolate sperm mitochondria. Therefore, most studies of sperm mitochondrial function use in situ analyses or demembranated sperm6.
Sperm mitochondrial structure and function have been consistently linked to male infertility7,8,9,10,11, suggesting that analysis of the structure and function of these organelles may be a good candidate for inclusion in sperm analysis.
Mitochondria play an important role in cellular energy metabolism, particularly by using oxygen to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). In spermatozoa, in particular, the source of ATP (glycolysis vs. OXPHOS) is disputed, and much of the data remains controversial and depends on different experimental approaches4,12,13. Measurements of respiration by oximetry offer significant insights into the mitochondrial respiratory capacity, mitochondrial integrity, and energy metabolism of the cell14,15,16. Traditionally, this technique has been performed using the Clark oxygen electrode-an instrument that has been used to measure mitochondrial respiration for more than 50 years17,18. In addition, sperm mitochondrial oxygen consumption has been analyzed using the classic Clark oxygen electrode19,20,21. High-resolution respirometry (HRR) using oxygraphs (Oroboros) provides higher sensitivity than using classical respirometry devices22. The oxygraphs are composed of two chambers with injection ports, and each chamber has a polarographic oxygen sensor. With this technique, it is possible to analyze tissue slides, cells, and isolated mitochondrial suspensions. The specimen is continuously stirred in the chamber, and during the experiment, the oxygen consumption is measured, and the oxygen rates are calculated using specific software. The chambers show reduced oxygen leakage, which is an advantage over the conventional oxygen electrode devices14,23.
As with other cells, in the case of spermatozoa, the sensitivity of HRR equipment is higher than for conventional respirometry, meaning that HRR equipment can be used for the analysis of a limited number of intact or permeabilized sperm cells. There are two main strategies for assessing sperm mitochondrial function by HRR: (a) measuring the oxygen consumption in intact cells, which involves reproducing the respiratory function in a medium containing substrates such as glucose, or (b) measuring the oxygen consumption in permeabilized cells using one of the OXPHOS complexes, with the addition of specific substrates to monitor each function separately.
In the present study, we describe the use of HRR to determine mitochondrial respiration in human sperm cells.
Protocol
The experiments were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Facultad de Medicina de la Universidad de la República, Montevideo, Uruguay.
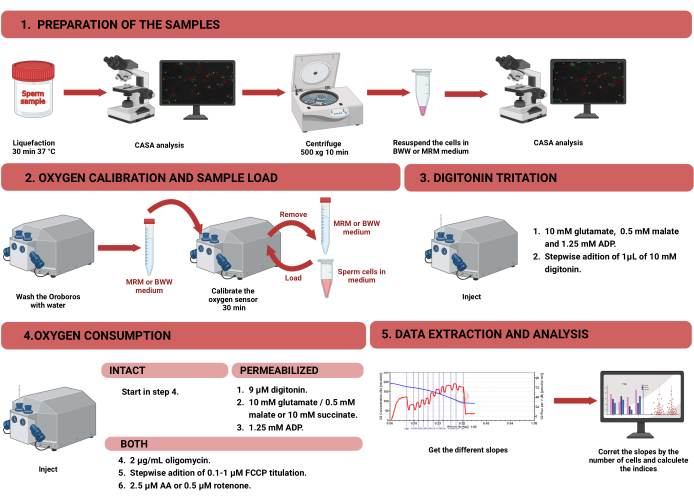
Figure 1: Workflow for high-resolution respirometry to assess mitochondrial function in intact and permeabilized human sperm. The protocol was divided into four different steps: 1) preparation of the sample, 2) oxygen calibration in the Oroboros instrument, 3) oxygen consumption measurement for intact and permeabilized cells, and 4) data extraction from the equipment and analysis. Abbreviations: CASA = computer-assisted sperm analysis; BWW = Biggers Whitten Whittingham medium; MRM = mitochondrial respiration medium; ADP = adenosine diphosphate; FCCP = carbonyl cyanide -p- trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone; AA = antimycin A. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
NOTE: The workflow for measuring the oxygen consumption in sperm cells using HRR is shown in Figure 1. Information on the materials, equipment, and reagents used in the protocol is presented in the Table of Materials.
1. Sample preparation
- Sample collection
- Collect freshly ejaculated human semen by masturbation after a recommended 3 day abstinence in a sterile plastic container. Transport the samples immediately to the laboratory.
- Incubate the samples for 30-60 min at room temperature (RT) to liquefy completely24.
- After liquefaction, store the samples at 37 °C until the experiment begins.
- Sperm evaluation with computer-aided sperm analysis (CASA)
- Mix the sample, and load 7 µL into a pre-warmed sperm counting chamber.
- Place the chamber on the pre-warmed (37 °C) stage of a direct light microscope.
- Open the computerized sperm analysis software and, enter the motility and concentration module (click on Mot).
- Select the configuration that corresponds to human sperm conditions.
NOTE: The configuration must be adapted to the type and depth of the chamber as well as to the sample species and the system CASA. - Randomly analyze 10 different fields per chamber by clicking on the Analyze button.
- Click on Results to obtain the sample concentration and motility.
- Cell preparation
NOTE: If the HRR is not calibrated, start with steps 2.1-2.2 before preparing the cells (step 1.3). It is important to measure the oxygen consumption immediately when the sperm cells are resuspended in the medium.- Centrifuge the samples at 400 x g for 10 min at RT.
- Remove the seminal plasma, and resuspend the spermatozoa in 2 mL of Biggers Whitten Whittingham (BWW) for experiments with intact cells or mitochondrial respiration medium (MRM) for studies with permeabilized cells. The compositions of the media are shown in Table 1.
- Repeat the steps described in step 1.2 for sperm concentration studies.
2. High-resolution respirometry: OXPHOS analysis
NOTE: HRR integrates highly sensitive oxygraphs (Oxygraph-2 K; Oroboros Instruments GmbH, Innsbruck, Austria) with software (DatLab, version 4.2; Oroboros Instruments GmbH). The experimental data are displayed as the oxygen concentration versus time (as pmol of O2/106 cells·min−1) and as real-time transformations of these data, allowing the experimenter to track the respiration (oxygen consumption, oxygen flux) of biological and biochemical samples while the experiment is still running. The HRR can be used to follow the respiration of living and motile cells, which is particularly useful for sperm, whose motility is associated with the sperm quality and fertility potential. The laboratory uses an HRR Oroboros Oxygraph2-k, Oroboros Instruments, with two chambers. The steps described in this protocol must be performed independently for both 2 mL chambers.
- Equipment preparation
- Turn on the HRR, and connect it to the respirometry software (DatLab) for data acquisition and analysis.
- Replace the 70% ethanol in the oxygraph chamber with ddH2O. Stir it continuously with the magnetic stir bar in the chamber at 750 rpm. Let it stand for 10 min, and aspirate the double-distilled (dd) H2O afterward.
- Wash the chamber three times with ddH2O for 5 min each time.
NOTE: This step is necessary to remove the remaining ethanol from the chambers. Sperm cells are very sensitive to ethanol. The recording could be compromised if this step is omitted.
- Calibration of the oxygen sensors
NOTE: The calibration procedure varies slightly depending on the instrument. Perform an air calibration of the polarographic oxygen sensor as described by the manufacturer25. In this section, the calibration protocol is explained briefly.- Remove the ddH2O, and pipette 2 mL of the same medium used for the cell preparation into the chamber. Place the stoppers, leaving an air exchange bubble.
NOTE: It is important to know the volume of the chamber to determine the exact volume of medium needed. - Record the oxygen calibration values (click on Layout > 01 Calibration Exp. Gr3-Temp) to monitor the performance of the sensor membrane by stirring the medium with the stir bar at 750 rpm for at least 30 min at 37 °C. Use the other settings as mentioned: gain for sensor: 2; polarization voltage: 800 mV; data recording interval: 2.0 s.
NOTE: It is expected to obtain an O2 slope uncorrected (red line) within ±2 pmol∙s−1∙mL−1 with a stable signal from the polarographic sensor. - Drag the mouse while holding down the left mouse button and the shift key to select an area where the change in oxygen concentration (Y1 O2 Concentration, blue line) is stable.
- Open the O2 Calibration window (click on Oxygraph > O2 Calibration). In Air Calibration, change the selected mark to the region selected in step 2.2.3. Finish by clicking on Calibrate and Copy to Clipboard.
- Stop the recording, and save by clicking on Oxygraph > Ok Control > Save and Disconnect.
NOTE: This dataset must be saved so that it can be used in all of the day's experiments. The calibration is only performed once per day for each medium.
- Remove the ddH2O, and pipette 2 mL of the same medium used for the cell preparation into the chamber. Place the stoppers, leaving an air exchange bubble.
- Digitonin-permeabilization titration
- Open the chamber, and aspirate the medium inside.
- Load in the chamber at least 24 x 106 and no more than 70 x 106 sperm cells in a final volume of 2 mL of MRM.
NOTE: It is important to measure the number of cells in the chamber in order to adjust the oxygen consumption at the end of the experiment. A lower number of cells than recommended cannot be measured. - Close the chamber by pushing the stoppers all the way in, and aspirate the remaining liquid at the top. Start the experiment with the same settings as for the calibration: stirring speed: 750 rpm; temperature: 37 °C; gain for sensor: 2; polarization voltage: 800 mV; and data recording interval: 2.0 s.
- To load the calibration, double-click on the Pos Calib box in the bottom corner. Open the calibration performed in step 2.2 (click on Oxygraph > O2 Calibration > Copy from File), and click on Calibrate and Copy to Clipboard.
NOTE: The POS Calib box will change from yellow to green. The data are displayed in oxygen flow corrected per volume charts (Layout 05 Flux per Volume uncorrected). Different layouts are available in Oxygraph > Layout. - Add 5 µL of 0.5 M adenosine diphosphate (ADP), 10 µL of 2 M glutamate, and 2.5 µL of 0.4 M malate (final concentrations: 1.25 mM, 10 mM, and 0.5 mM). Measure the oxygen consumption until the signal stabilizes.
NOTE: Precision Hamilton micro-syringes are used for injection through the loading port in the stopper. Use one syringe per drug to avoid cross-contamination. Click on F4 to register, and mark in the oxygen register when a treatment is added.
NOTE: The substrates are prepared in ultrapure water and stored at −20 °C for 3 months. - Tritate by adding 1 µL of 10 mM digitonin in successive steps until the oxygen consumption reaches a maximal level.
NOTE: Thorough washing with water, 70% ethanol, and 100% ethanol is essential if the same chamber is used for two experiments on the same day.
NOTE: Digitonin is prepared in ultrapure water and stored at −20 °C for 3 months.
- Routine respiratory assessment protocol for intact and permeabilized sperm cells (complex I or complex II)
- Open the chamber, and aspirate the medium inside.
- Load in the chamber at least 24 x 106 and no more than 70 x 106 sperm cells in a final volume of 2 mL of BWW (intact cell analysis) or MRM (permeabilized cell analysis).
- Start the experiment with the same settings as for the calibration (this is described in step 2.3.3).
- Load the calibration performed in step 2.2 as described in step 2.3.4.
- Record the respiration of the cells for at least 5 min until a stable signal is obtained. This measurement corresponds to basal respiration in intact cells.
- If the experiment is with intact cells, proceed to step 2.4.9. For permeabilized cells, inject 4.5 µL of 10 mM digitonin (final concentration: 22.5 µM). Permeabilize the cells for 5 min.
- Add the substrates: 10 µL of 2 M glutamate and 2.5 µL of 0.4 M malate (final concentrations: 10 mM and 0.5 mM, respectively) for complex I or 20 µL of 1 M succinate (final concentration: 10 mM) for complex II. Measure the oxygen consumption until the signal increases and stabilizes. This is state 4, which means basal complex I or basal complex II supported respiration in the absence of ADP.
NOTE: The substrates are prepared in ultrapure water and stored at −20 °C for 3 months. - Inject 5 µL of 0.5 M ADP (final concentration: 1.25 mM). Measure the oxygen consumption until the signal increases and stabilizes. The addition of ADP increases the signal corresponding to the maximum oxygen consumption through complex I or complex II (state 3, in permeabilized cells).
- Add 1 µL of 4 mg/mL oligomycin (final concentration: 2 µg/mL), an ATP synthetase inhibitor. Measure the oxygen consumption until the signal decreases and stabilizes.
NOTE: Oligomycin is prepared in ethanol and stored at −20 °C for 3 months. - Titrate by adding 1 µL of 0.1 mM to 1 mM carbonyl cyanide-P- trifluoromethoxy-phenylhydrazone (FCCP) in successive steps until a maximum uncoupled respiration rate is reached. Measure the oxygen consumption until the signal increases and stabilizes.
NOTE: FCCP is prepared in ethanol and stored at −20 °C for 3 months. - The final concentration of FCCP is sample-dependent. Stop injecting the drug when oxygen consumption begins to decrease.
- Finally, inject 1 µL of 5 mM antimycin A (2.5 µM final concentration). This is a complex III inhibitor to discriminate between the mitochondrial and residual oxygen consumption (non-mitochondrial respiration). For the analysis of complex I, add 1 µL of 1 mM rotenone (0.5 µM final concentration), an inhibitor of this complex, instead of AA. Measure the oxygen consumption until the signal decreases and stabilizes.
NOTE: The drugs are prepared in ethanol and stored at −20 °C for 3 months.
3. Data extraction and analysis
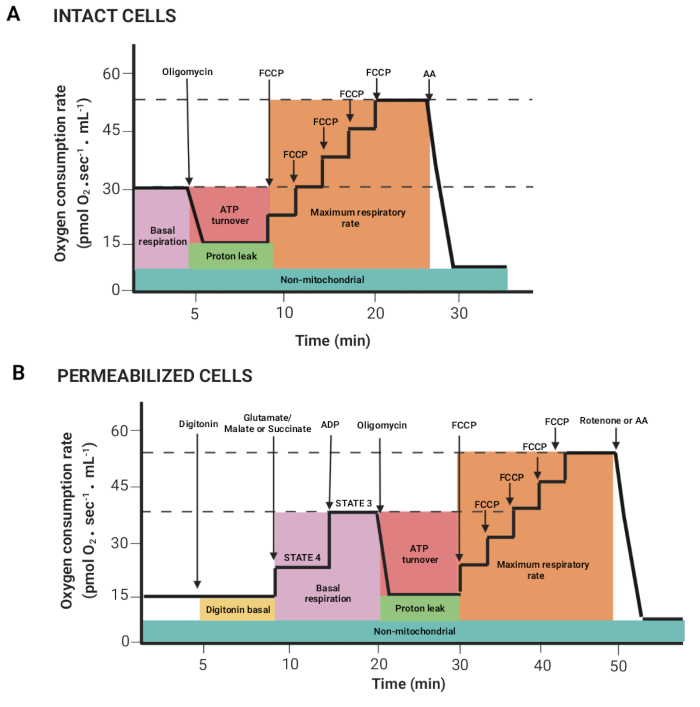
Figure 2: Acquisition of respiratory parameters from a high-resolution respirometry experiment. (A,B) Schematic representations of graphs obtained, as described in Figure 1, for intact and permeabilized cells, respectively. These parameters have been previously described15. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Drag the mouse by pressing the left mouse button and the shift key to select regions where the oxygen flux per volume correlated (Y2 O2 slope uncorr., red line) is stable after the injection of a substrate or inhibitor. Figure 2 shows the different parameters obtained from the register previously described15.
NOTE: The parameters depend on the experiment; all of them are as follows: basal respiration in intact cells and respiration in the presence of glutamate/malate or succinate (state 4), ADP (state 3), oligomycin (proton leak), FCCP (maximum respiration rate), rotenone/AA (non-mitochondrial respiration). In permeabilized cells, basal respiration corresponds to state 3. - Click on the Marks > Statistics windows, and export the data.
- Normalize the data obtained per 1 million sperm cells. The units of the slopes are pmolO2·s−1·mL−1·10−6 cells.
- Subtract the non-mitochondrial oxygen consumption from all the values before calculating the indices.
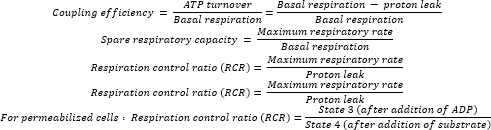
- Calculate the indices using the various equations previously described15:
Results
Determination of the optimal concentration of digitonin in sperm cells
In this protocol, we present the use of HRR to monitor real-time changes in OXPHOS in human sperm cells. Since the method can be used to analyze intact or digitonin-permeabilized sperm, we first present the standardization of digitonin concentration required to permeabilize sperm cells (Figure 3).
Digitonin is used for chemical permeabilization, which allows substrates to...
Discussion
HRR critically depends on several steps: (a) the equipment maintenance, (b) accurate calibration of the oxygen sensors, (c) the uncoupler titration26, and finally, (d) the adequate use of indices representing the mitochondrial function. The equipment maintenance is crucial. It is recommended to replace the membranes of the polarographic oxygen sensor regularly and to correct the instrumental background. Extensive washing after the collection of spermatozoa from the chambers is essential to obtain ...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Fertilab Andrology clinic, especially José María Montes and Andrea Torrents, for allowing us access to donors. Funding: A.C. is supported by grants from Universidad de la República (CSIC_2018, Espacio Interdisciplinario_2021). Additional funding was obtained from the Programa de Desarrollo de Ciencias Básicas (PEDECIBA, Uruguay). P.I. and R.S. are supported by Universidad de la República (I+D, CSIC 2014; I+D, CSIC 2016, Iniciación a la Investigación, CSIC 2019 and FMV_1_2017_1_136490 ANII- Uruguay). P.I. is supported by POS_FMV_2018_1_1007814 and CAP-UDELAR 2020. The figures were illustrated using Biorender.com.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Acid free- Bovine serum albumine | Sigma Aldrich | A8806 | |
| Adenosine 5'-diphosphate monopotassium salt dihydrate | Sigma Aldrich | A5285 | |
| Animycin A from streptomyces sp. | Sigma Aldrich | A8674 | |
| Calcium chloride | Sigma Aldrich | C4901 | |
| carbonyl cyanide-P- trifluoromethoxy-phenylhydrazone | Sigma Aldrich | C2920 | |
| DatLab sofware version 4,2 | Oroboros Instruments GmbH | N/A | |
| D-glucose | Sigma Aldrich | G7021 | |
| Digitonin | Sigma Aldrich | D141 | |
| EGTA | Sigma Aldrich | E4378 | |
| HEPES | Sigma Aldrich | H3375 | |
| L glutamic acid | Sigma Aldrich | G1251 | |
| L malic acid | Sigma Aldrich | M1000 | |
| Magnesium sulphate | Sigma Aldrich | M7506 | |
| Microliter Syringes | Hamilton | 87900 or 80400 | |
| Microscope camera | Basler | acA780-75gc | |
| Microscope Eclipse E200 with phase contrast 10X Ph+ | Nikon | N/A | |
| Monopotassium phosphate | Sigma Aldrich | P5655 | |
| MOPS | Sigma Aldrich | M1254 | |
| Oligomycin A | Sigma Aldrich | 75351 | |
| Oxygraph-2 K | Oroboros Instruments GmbH | N/A | |
| Potassium chloride | Sigma Aldrich | P3911 | |
| Power O2k-Respirometer | Oroboros Intruments | 10033-01 | |
| Rotenone | Sigma Aldrich | R8875 | |
| Saccharose | Sigma Aldrich | S0389 | |
| Sodium bicarbonate | Sigma Aldrich | S5761 | |
| Sodium lactate | Sigma Aldrich | L7022 | |
| Sodium pyruvate | Sigma Aldrich | P2256 | |
| Sperm class analyzer 6.3.0.59 Evolution-SCA Research | Microptic | N/A | |
| Sperm Counting Chamber DRM-600 | Millennium Sciences CELL-VU | N/A | |
| Succinate disodium salt | Sigma Aldrich | W327700 |
References
- Agarwal, A., Mulgund, A., Hamada, A., Chyatte, M. R. A unique view on male infertility around the globe. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology. 13, 37 (2015).
- Guzick, D. S., et al. Sperm morphology, motility, and concentration in fertile and infertile men. The New England Journal of Medicine. 345 (19), 1388-1393 (2001).
- Wang, C., Swerdloff, R. S. Limitations of semen analysis as a test of male fertility and anticipated needs from newer tests. Fertility and Sterility. 102 (6), 1502-1507 (2014).
- Amaral, A. Energy metabolism in mammalian sperm motility. WIREs Mechanisms of Disease. 14 (5), e1569 (2022).
- Leung, M. R., et al. In-cell structures of conserved supramolecular protein arrays at the mitochondria-cytoskeleton interface in mammalian sperm. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 118 (45), e2110996118 (2021).
- Moraes, C. R., Meyers, S. The sperm mitochondrion: Organelle of many functions. Animal Reproduction Science. 194, 71-80 (2018).
- Cassina, A., et al. Defective human sperm cells are associated with mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidant production. Biology of Reproduction. 93 (5), 119 (2015).
- Marchetti, C., Obert, G., Deffosez, A., Formstecher, P., Marchetti, P. Study of mitochondrial membrane potential, reactive oxygen species, DNA fragmentation and cell viability by flow cytometry in human sperm. Human Reproduction. 17 (5), 1257-1265 (2002).
- Amaral, A., Lourenço, B., Marques, M., Ramalho-Santos, J. Mitochondria functionality and sperm quality. Reproduction. 146 (5), R163-R174 (2013).
- Durairajanayagam, D., Singh, D., Agarwal, A., Henkel, R. Causes and consequences of sperm mitochondrial dysfunction. Andrologia. 53 (1), e13666 (2021).
- Uribe, P., et al. Use of the fluorescent dye tetramethylrhodamine methyl ester perchlorate for mitochondrial membrane potential assessment in human spermatozoa. Andrologia. 49 (9), e12753 (2017).
- Storey, B. T. Mammalian sperm metabolism: Oxygen and sugar, friend and foe. The International Journal of Developmental Biology. 52 (5-6), 427-437 (2008).
- Tourmente, M., Sansegundo, E., Rial, E., Roldan, E. R. S. Capacitation promotes a shift in energy metabolism in murine sperm. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 10, 950979 (2022).
- Gnaiger, E., Dykens, J. A., Will, Y. Chapter 12 - Polarographic oxygen sensors, the oxygraph, and high-resolution respirometry to assess mitochondrial function. Drug-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction. , 325-352 (2008).
- Brand, M. D., Nicholls, D. G. Assessing mitochondrial dysfunction in cells. Biochemical Journal. 435 (2), 297-312 (2011).
- Awadhpersad, R., Jackson, C. B. High-resolution respirometry to assess bioenergetics in cells and tissues using chamber- and plate-based respirometers. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (176), e63000 (2021).
- Chance, B., Williams, G. R. A simple and rapid assay of oxidative phosphorylation. Nature. 175 (4469), 1120-1121 (1955).
- Li, Z., Graham, B. H. Measurement of mitochondrial oxygen consumption using a Clark electrode. Methods in Molecular Biology. 837, 63-72 (2012).
- Stendardi, A., et al. Evaluation of mitochondrial respiratory efficiency during in vitro capacitation of human spermatozoa. International Journal of Andrology. 34 (3), 247-255 (2011).
- Ferramosca, A., Focarelli, R., Piomboni, P., Coppola, L., Zara, V. Oxygen uptake by mitochondria in demembranated human spermatozoa: A reliable tool for the evaluation of sperm respiratory efficiency. International Journal of Andrology. 31 (3), 337-345 (2008).
- Ferramosca, A., et al. Modulation of human sperm mitochondrial respiration efficiency by plant polyphenols. Antioxidants. 10 (2), 217 (2021).
- Gnaiger, E., Steinlechner-Maran, R., Méndez, G., Eberl, T., Margreiter, R. Control of mitochondrial and cellular respiration by oxygen. Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes. 27 (6), 583-596 (1995).
- . O2k Quality Control 1: Polarographic oxygen sensors and accuracy of calibration Available from: https://www.bioblst.at/images/archive/7/77/20210819114548%21MiPNet06.03_POS-Calibration-SOP.pdf (2020)
- WHO Laboratory Manual for the Examination and Processing of Human Semen. World Health Organization Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240030787 (2010)
- . O2k-protocols SOP: O2k quality control 1 Available from: https://www.bioblast.at/images/9/9c/MiPNet06.03_POS-Calibration-SOP_DatLab8.pdf (2021)
- Gnaiger, E. . Mitochondrial Pathways and Respiratory Control. , (2012).
- Steinlechner-Maran, R., Eberl, T., Kunc, M., Margreiter, R., Gnaiger, E. Oxygen dependence of respiration in coupled and uncoupled endothelial cells. The American Journal of Physiology. 271, C2053-C2061 (1996).
- Holt, W. V., Van Look, K. J. W. Concepts in sperm heterogeneity, sperm selection and sperm competition as biological foundations for laboratory tests of semen quality. Reproduction. 127 (5), 527-535 (2004).
- Sousa, A. P., et al. Not all sperm are equal: Functional mitochondria characterize a subpopulation of human sperm with better fertilization potential. PloS One. 6 (3), e18112 (2011).
- Moscatelli, N., et al. Single-cell-based evaluation of sperm progressive motility via fluorescent assessment of mitochondria membrane potential. Scientific Reports. 7, 17931 (2017).
- Ferreira, J. J., et al. Increased mitochondrial activity upon CatSper channel activation is required for mouse sperm capacitation. Redox Biology. 48, 102176 (2021).
- Irigoyen, P., et al. Mitochondrial metabolism determines the functional status of human sperm and correlates with semen parameters. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 10, 926684 (2022).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved