A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Tuina Intervention in Rabbit Model of Knee Osteoarthritis
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
The protocol describes a method for Tuina intervention in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis.
Abstract
Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is mainly characterized by degenerative changes in the knee joint's cartilage and surrounding soft tissues. The efficacy of Tuina in treating KOA has been confirmed, but the underlying mechanism needs to be investigated. This study aims to establish a scientifically feasible KOA rabbit model treated with Tuina to reveal the underlying mechanisms. For this, 18, 6-month-old normal-grade male New Zealand rabbits were randomly divided into sham, model, and Tuina groups, with 6 rabbits in each group. The KOA model was established by injecting 4% papain solution into the knee joint cavity. The Tuina group was intervened with Tuina combined with the knee joint rotary correction method for 4 weeks. Only the standard grasping and fixation were performed in sham and model groups. At the end of the 1-week intervention, the knee joint range of motion (ROM) was observed, and cartilage hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining was done. The study shows that Tuina could inhibit chondrocyte apoptosis, repair cartilage tissue, and restore knee joint ROM. In conclusion, this study demonstrates the scientific feasibility of Tuina treatment for KOA model rabbits, highlighting its potential application in the study of KOA and similar knee joint-related conditions.
Introduction
Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is a degenerative disease of the knee joint, mainly manifested by knee pain, swelling, deformation, and restricted movement, with a high disability rate and a higher prevalence in women, with 527.81 million patients with osteoarthritis worldwide in 2019 and its global prevalence accounting for 60.6% of the total global prevalence of OA1. Clinically, the treatment of KOA is usually divided into non-surgical and surgical therapies. Non-surgical therapies include physiotherapy, pharmacotherapy, and platelet-rich plasma injection therapy2,3. Tuina is a common, safe, reliable, and effective treatment method in Chinese medicine. This study uses Tuina combined with the knee joint rotary correction method to treat KOA. Tuina techniques such as the rotatory kneading and pressing method can balance muscle tissue, reduce pain, adjust inflammatory factor levels, improve tissue metabolism, and inhibit articular cartilage degeneration4,5. The knee joint rotary correction method can adjust the alignment of lower limb bones and joints, improve the knee joint gap, restore the normal force line, and balance the lower limb biomechanics6,7,8,9. Resistance exercises can enhance muscle mass and strength and promote cartilage tissue renewal10,11. A preliminary study found that this Tuina protocol is significantly more effective than oral glucosamine sulfate capsules in treating KOA, with a faster onset of action and significant inhibition of chondrocyte degeneration and repair of damaged cartilage tissue12. In the treatment of KOA, compared to Tuina therapy, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have adverse effects and unsatisfactory long-term efficacy, relatively high surgical risks and costs, and require certain indications for surgical treatment, with postoperative problems and periprosthetic complications13,14,15. When compared to drug therapy and surgery, Tuina treatment for KOA offers several advantages, including reduced side effects, lower risk, enhanced safety, cost-effectiveness, and longer-lasting efficacy. Additionally, it can effectively alleviate knee joint pain, swelling, popping, and restricted movement6,13,16,17.
However, the mechanism of Tuina for the treatment of KOA needs to be clarified, which limits the improvement and perfection of the treatment protocol for KOA. Therefore, studying the mechanism of Tuina intervention in KOA through animal experiments is an effective method. Rabbits, compared to rats, have a docile temperament and larger knee joints. The anatomical structure and cartilage biochemical indexes are similar to those of humans, so it is a suitable subject for studying the mechanism of knee joint disease by Tuina18. The KOA model established by injecting papain into the knee joint cavity of rabbits has the advantages of short modeling time, reduced trauma, high success rate, high survival rate, and similar pathological mechanism to KOA19. This study aims to establish a scientifically feasible animal experimental protocol for Tuina intervention in KOA and investigate the mechanism of Tuina.
Protocol
The study was approved by the ethics committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (approval number: 2020-29).
1. Experimental animals
- Raise 18, 6-month-old normal-grade male New Zealand rabbits (2.75 ± 0.25 kg) in standard single cages (12 h light/dark cycle, temperature 20-24 °C, air humidity 40%-60%).
2. Grouping method
- Select 6 out of the 18 New Zealand rabbits as the sham group using the random number method and assign the remaining 12 rabbits to the modeling group.
- After successful modeling, divide the modeling group rabbits into the model and Tuina groups according to the random number method, with 6 rabbits in each group.
- Perform the Tuina intervention in the Tuina group. Perform the same grasping and fixation in the sham and model group without Tuina. Operate every other day for 4 weeks (Figure 1).
3. Establishment of the KOA model
- Perform adaptive feeding to rabbits in the standard condition in week 1. Ad libitum access to water and food. Place rabbits on their right sides in the rabbit fixation boxes to calm them down for 15 min a day. Fix their heads on the head-fixing plates. Fix the fastening plates and screws so the rabbits cannot move. Wear protective gloves when grasping and fixing the rabbits (Figure 1).
- On days 1, 4, and 7 of week 2, place all 18 rabbits on their right sides in the rabbit fixation boxes (Figure 1). Perform the below-mentioned operations.
- Inject 3% pentobarbital sodium (1 ml/kg) into the rabbit's marginal ear vein. Shave the rabbit's left knee joint with an animal shaver, resulting in no hair on the exposed skin.
- Disinfect the rabbit's left knee joint from the inside out using medical iodophor and 75% alcohol (Figure 2A).
- Flex the rabbit's left knee joint at 60°. Insert a needle (22G, 0.7 mm x 30 mm) from Waixiyan. Inject 4% papain solution (0.1 mL/kg, 0.275 mL on average for a 2.5 kg animal) into the knee joint cavity of the modeling group. Inject an equal amount of 0.9% sodium chloride solution into the sham group. This injection dose is well-tolerated by the animal without causing evidence of pain or distress (Figure 2B).
NOTE: Waixiyan (EX-LE5) is located in the patellar ligament's lateral recess, and Neixiyan (EX-LE4) is located in the medial recess of the patellar ligament20,21,22. - Press the pinhole for 2 min to avoid solution spillage.
- Place your hands above and below the rabbit's left knee joint. Gently and passively flex the rabbit's knee joint and extend 10 times within the physiological range of motion (ROM) to infiltrate the solution into the knee joint cavity evenly15.Observe the rabbit every 8 h for the duration of the modeling. Administer buprenorphine SR (0.18 mg/kg) when the rabbits show signs of hiding, trembling of limbs, shallow and rapid breathing, or even biting and scratching.
- At week 7, observe the rabbit's left knee in a flexed position as swollen, with increased muscle tone around the knee with nodules and striae, increased local painful irritation response, decreased knee ROM, lame gait, and shift of the center of gravity to the healthy side. This determines the success of the KOA model (Figure 1, Figure 2C)23,24.
4. Tuina manipulation
- Perform training using the Tuina technique parameter determination instrument before Tuina manipulation. Train for 1 h a day for 1 month by the same professional.
- Perform the rotatory kneading and pressing method with the thumb on the Tuina manipulation simulation platform with a force of 5 N and a frequency of 60 times/min (Figure 3A,C).
- Analyze the force in three directions of X, Y, and Z axes by the Tuina manipulation parameter processing software and check the force's magnitude, frequency, and time of action displayed on the screen (Figure 3B, D).
- Evaluate the mechanical parameters of the Tuina manipulation and standardize the Tuina manipulation using the software during training. Maintain the standardized rotatory kneading and pressing method with the thumb with a force of 5 N, a frequency of 60 times/min, and a continuous operating time of 10 min. See the standardized quantitative waveform of the manipulation in Figure 3B,D25,26,27.
- Place the rabbit on its right side in the rabbit fixation box. Gently stroke the rabbit for 10s to soothe and relax the rabbit21. Then perform the Tuina intervention.
- Perform the rotatory kneading method with the thumb on the rabbit's left peri-knee muscles stiffness, tendon knots, and patella, with up and down round-trip manipulation at a force of 5 N and a frequency of 60 times/min for 5 min.
- Use the thumb end to press Yanglingquan (GB 34), Yinlingquan (SP 9), Waixiyan (EX-LE5), Neixiyan (EX-LE4), Heding (EX-LE2), Xuehai (SP 10), Liangqiu (ST 34), and Weizhong (BL 40)20,21,22, with a force of 5 N and a frequency of 60 times/min, and operate on each point for 30 s.
- Perform the rotary correction method on the rabbit knee joint and perform this 3x separately for each animal in the group.
- Fix the femur with one hand. Place the other hand behind the knee joint first, then fix the lateral and medial tibial condyles with the thumb and ring fingers, respectively. Fix the popliteal fossa with the index and middle fingers. Apply traction and twisting force.
- Fix the femur with one hand. Fix the patella's medial and lateral edges with the thumb and little fingers of the other hand. Fix the patellar base with the index, middle, and ring fingers. Apply twisting force.
- Keep the direction of traction force parallel to the long axis of the tibia, and the direction of torsion force in line with the direction of the lower Xiyan. Use fingers to hold the skin in place to avoid friction between the skin and fingers.
5. Measurement of the knee joint ROM
NOTE: Before measurement, calm the rabbit. The measurement statistician and operator are different from one another.
- Measure the mobility of the left knee joint of rabbits of each group at the beginning of the experiment and the end of each week.
- Position the rabbit on its right side in the rabbit fixation box and fix its left femur with one hand.
- Align the center of the circle of the medical arthroscope with the lateral center of the rabbit's left knee joint. Extend the fixation arm such that it is parallel to the line extension connecting the circle's center to the greater trochanter. Extend the mobile arm such that it is parallel to the longitudinal axis of the tibia.
- Place the other hand on the longitudinal axis of the tibia, approximately 9 cm from the knee joint. Manually apply approximately 750-850 g torque at an angular velocity of 3°/s28.
- Perform this till the rabbit's knee joint is no longer moving . Record the number of degrees the goniometer displays when the joint stops moving; this is the knee joint ROM. When reading, ensure the line of sight is perpendicular to the ruler's surface.
- Measure ROM for each knee 3x and take the average value28.
6. Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining
- Sample collection
- At 1 week from the end of the intervention (Figure 1), place the rabbit on its right side in the rabbit fixation box (rabbits are more likely to remain relaxed when lying on their right side). Inject pentobarbitone (100 mg/kg) into the rabbit's ear marginal vein for humane euthanasia29,30.
- Open the left knee cavity quickly with a scalpel, scissors, and hemostatic forceps to remove the soft tissue attached around the cartilage of the distal femur.
- Collect an approximately 1 cm x 1 cm cartilage-bone specimen of the distal femur with biting forceps and place it in saline for cleaning.
- Fixation and decalcification
- Place the cartilage in 4% paraformaldehyde solution and fix it for 72 h.
- Rinse in running water for 12 h. Decalcify in ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) decalcification solution for 6 weeks. Change the EDTA decalcification solution every 3 days. Determine the end point of decalcification when the bone tissue becomes soft and flexible, can be easily bent, and pierced smoothly with a needle31.
- Dehydration of embedded sections
- Place the specimen in an automatic dehydrator for dehydration.
- Place the waxed and trimmed tissue on the bottom of a square container with dissolved paraffin wax for 1 h. Place them in a cooling oven until cooled and solidified into hard blocks. Slice the paraffin-embedded tissue block in a slicer to a thickness of 4 µm.
- Unfold the sections in the bleach machine, then place them on adhesive slides, number them, and dry them with a slice baking machine and oven.
- De-waxing and hydration
- Bake the sections at 65 °C for 60 min.
- Soak the sections in xylene for 7 min, followed by 2 more rounds of soaking in fresh xylene for 7 min each.
- Soak the slice in anhydrous ethanol for 5 min, followed by soaking for 2 min each in 95% ethanol, 85% ethanol, and 75% ethanol.
- Soak sections in distilled water for 2 min.
- Hematoxylin staining: Stain sections with hematoxylin for 20 s. Rinse sections in running water. Soak sections in hydrochloric acid ethanol fractionation for 3 s. Rinse sections in tap water for 5 min.
- Eosin re-staining: Stain sections with eosin for 30 s. Rinse sections with tap water.
- Dehydration for transparency of the sample
- Place sections in 95% ethanol twice for 3 s each, followed by placing in anhydrous ethanol for 3 s.
- Again, place the slices in anhydrous ethanol for 1 min, followed by 2 rounds of xylene wash for 1 min each.
- Sealing of slices: Take out the slices, drop neutral gum sealer, cover with a coverslip, and leave the slices to dry in a fume hood until odorless.
- Photographing the sample: Observe and photograph under the field of view of a light microscope at 100x.
- Evaluation: Evaluate the cartilage tissue by Mankin's score for each group32.
7. Data analysis
- Analyze statistically the experimental data using analysis software. When the data were subjected to a normal distribution, compare two groups of samples by t-test and multiple groups by one-way ANOVA.
- Express results as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Represent results as statistical plots using commercial software. Differences were statistically significant at p < 0.05.
Results
The degree of restricted knee motion and cartilage tissue damage reflects the severity of KOA. The knee joint's ROM reflects the degree of restriction of knee joint motion. The smaller the knee joint ROM, the more serious the limitation of knee joint motion. On the contrary, the bigger the knee joint ROM, the more normal the degree of knee motion. HE staining to observe the morphology and structure of cartilage tissue reflects the degree of cartilage tissue damage. The more irregular the surface of cartilage tissue, ...
Discussion
The design of the experimental protocol is particularly important to investigate the mechanism of Tuina in treating KOA. KOA modeling was performed on rabbits by injection of papain at Waixiyan. Waixiyan is located in the lateral crypt of the patellar ligament, which is easy to locate, and the joint space between the femur and tibia is large here during knee flexion, which makes it easy to inject into the knee joint cavity and prevents damage to the surrounding tissues, so it is easy to establish the KOA model
Disclosures
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Shandong Provincial Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Project (2021Q080) and the Qilu School of Traditional Chinese Medicine Academic School Inheritance Project [Lu-Wei-Letter (2022) 93].
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 0.9 % sodium chloride injection | Sichuan Keren Pharmaceutical Co. | Z22121903 | |
| -20°C refrigerator | Haier | BD-328WL | |
| 4 % fixative solution | Solarbio | P1110 | |
| 4°C refrigerator | Haier | SC-315DS | |
| Anhydrous ethanol | Sinopharm | ||
| Automatic tissue dewatering machine | Dakowei (Shenzhen) Medical Equipment Co. | HP30 | |
| Blast drying oven | Shanghai Yiheng Scientific Instruments Co. | DHG-9070A | |
| Coverslip | Biyuntian | FCGF50 | |
| Electric thermostat water bath | Shanghai Yiheng Scientific Instruments Co. | HWS-26 | |
| Embedding freezing table | Changzhou Paishijie Medical Equipment Co. | BM450 | |
| Embedding machine | Changzhou Paishijie Medical Equipment Co. | BM450A | |
| Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid decalcification solution | Servicebio | G1105-500ML | |
| Fluorescent inverted microscope | Leica | Leica DM IL LED | |
| Hematoxylin-eosin staining kit | Cisco Jet | EE0012 | |
| Hydrochloric acid | Laiyang Economic and Technological Development Zone Fine Chemical Plant | ||
| Medical joint goniometer | KOSLO | ||
| Neutral gum | Cisco Jet | EE0013 | |
| Normal-grade male New Zealand rabbit | Jinan Xilingjiao Breeding and Breeding Center | SCXK (Lu) 2020 0004 | |
| Papain(3000 U/mg) | Bioss | D10366 | |
| Pathological tissue bleaching and drying instrument | Changzhou Paishijie Medical Equipment Co. | PH60 | |
| Pet electric clippers | Codos | CP-3180 | |
| Rabbit fixing box | any brand | ||
| Rotating Slicer | Leica | 531CM-Y43 | |
| Tuina technique parameter determination instrument | Shanghai DuKang Instrument Equipment Co. Ltd. | ZTC-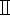 | |
| Ventilator | TALY ELECTRIC | C32 | |
| Xylene | Fuyu Reagent |
References
- Long, H. B., et al. Prevalence trends of site-specific osteoarthritis from 1990 to 2019: findings from the global burden of disease study 2019. Arthritis & Rheumatology. 74 (7), 1172-1183 (2022).
- Tschopp, M., et al. A randomized trial of intra-articular injection therapy for knee osteoarthritis. Investigative Radiology. 58 (5), 355-362 (2023).
- Buchanan, W. W., Kean, C. A., Kean, W. F., Rainsford, K. D. Osteoarthritis. Inflammopharmacology. , (2023).
- Wang, W. Y., et al. A randomized, parallel control and multicenter clinical trial of evidence-based traditional Chinese medicine massage treatment VS External Diclofenac Diethylamine Emulgel for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Trials. 23 (1), 555 (2022).
- Wang, M. N., et al. Mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine in treating knee osteoarthritis. Journal of Pain Research. 13, 1421-1429 (2020).
- Katz, J. N., Arant, K. R., Loeser, R. F. Diagnosis and treatment of hip and knee osteoarthritis: A review. The Journal of the American Medical Association. 325 (6), 568-578 (2021).
- Chang, A., et al. The relationship between toe-out angle during gait and progression of medial tibiofemoral osteoarthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 66, 1271-1275 (2007).
- Jenkyn, T. R., Hunt, M. A., Jones, I. C., Giffin, J. R., Birmingham, T. B. Toe-out gait in patients with knee osteoarthritis partially transforms external knee adduction moment into flexion moment during early stance phase of gait: a tri-planar kinetic mechanism. Journal of Biomechanics. 41 (2), 276-283 (2008).
- Brouwer, G. M., et al. Association between valgus and varus alignment and the development and progression of radiographic osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 56 (4), 1204-1211 (2007).
- Liao, C. D., et al. Effects of protein supplementation combined with resistance exercise training on walking speed recovery in older adults with knee osteoarthritis and sarcopenia. Nutrients. 15 (7), 1552 (2023).
- Thudium, C. S., et al. Cartilage tissue turnover increases with high-compared to low-intensity resistance training in patients with knee OA. Arthritis Research & Therapy. 25 (1), 22 (2023).
- Zheng, L. J., et al. Shutiao Jingjin massage can stabilize intracellular environment of rabbit chondrocytes following knee osteoarthritis-induced cartilage injury. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 27, (2023).
- Liu, K. Q., et al. Efficacy and safety of Tuina (Chinese therapeutic massage) for knee osteoarthritis: A randomized, controlled, and crossover design clinical trial. Frontiers in Medicine. 10, 997116 (2023).
- Wang, Z., et al. Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis of Acupuncture Combined with Massage in Treating Knee Osteoarthritis. BioMed Research International. 2022, 4048550 (2022).
- Li, Y. Y., et al. Therapeutic effect of acupotomy at Sanheyang for cartilage collagen damage in moderate knee osteoarthritis: a rabbit model. Journal of Inflammation Research. 16, 2241-2254 (2023).
- Guo, G. X., et al. Cerebral mechanism of Tuina analgesia in management of knee osteoarthritis using multimodal MRI: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 23 (1), 694 (2022).
- Perlman, A., et al. Efficacy and safety of massage for osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized clinical trial. Journal of General Internal Medicine. 34 (3), 379-386 (2019).
- Chen, B. J., et al. Aerobic exercise combined with glucosamine hydrochloride capsules inhibited the apoptosis of chondrocytes in rabbit knee osteoarthritis by affecting TRPV5 expression. Gene. 830, 146465 (2022).
- Rasheed, M. S., Ansari, S. F., Shahzadi, I. Formulation, characterization of glucosamine loaded transfersomes and in vivo evaluation using papain induced arthritis model. Scientific Reports. 12 (1), 19813 (2002).
- Li, Z. R. Experimental acupuncturology. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2003, 314-319 (2003).
- Hu, Y. L. Manual of practical animal acupuncture. Beijing: China Press of Agriculture. 2003, 286-298 (2014).
- Liu, J., et al. Effects of "knot-loosing" of acupotomy on motor function and morphological changes of knee joint in knee osteoarthritis rabbits. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 46 (2), 129-135 (2021).
- Li, Q., et al. The protective effects and mechanism of Ruyi Zhenbao Pill, a Tibetan medicinal compound, in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 308, 116255 (2023).
- Kwon, M., Nam, D., Kim, J. Pathological characteristics of monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rats. Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. 20 (3), 435-446 (2023).
- Wang, J. G., Tang, C. L. Experimental Tuina science. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Chinese. , (2017).
- Fang, M., Song, B. L. Tuina science. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine. , (2016).
- Jin, X. Y., Yu, Y. Y., Lin, Y. Y., Yang, J. P., Chen, Z. H. Tendon-regulating and bone-setting manipulation promotes the recovery of synovial inflammation in rabbits with knee osteoarthritis via the TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB signaling pathway. Annals of Translational Medicine. 11 (6), 245 (2023).
- Wang, M., Liu, C., Xiao, W. Intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid for the reduction in joint adhesion formation in a rabbit model of knee injury. Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy: Official Journal of the ESSKA. 22 (7), 1536-1540 (2014).
- Xu, C., et al. Bacterial cellulose membranes used as artificial substitutes for dural defection in rabbits. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 15 (6), 10855-10867 (2014).
- Leary, S., et al. AVMA guidelines for the euthanasia of animals: 2020 edition. Schaumburg: American Veterinary Medical Association. 2020, (2020).
- Amirtham, S. M., Ozbey, O., Kachroo, U., Ramasamy, B., Vinod, E. Optimization of immunohistochemical detection of collagen type II in osteochondral sections by comparing decalcification and antigen retrieval agent combinations. Clinical Anatomy. 33 (3), 343-349 (2020).
- Niazvand, F., et al. Curcumin-loaded poly lactic-co-glycolic acid nanoparticles effects on mono-iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rats. Veterinary Research Forum: An International Quarterly Journal. 8 (2), 155-161 (2017).
- Liu, A., et al. Intra-articular injection of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells loaded with graphene oxide granular lubrication ameliorates inflammatory responses and osteoporosis of the subchondral bone in rabbits of modified papain-induced osteoarthritis. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 12, 822294 (2022).
- Hall, M. M. The accuracy and efficacy of palpation versus image-guided peripheral injections in sports medicine. Current Sports Medicine Reports. 12 (5), 296-303 (2013).
- Xing, L., et al. Traditional Chinese medicine ointment combined with Tuina therapy in treatment of pain and swelling after total knee arthroplasty. World Journal of Orthopedics. 13 (10), 932-939 (2022).
- Xu, H., et al. The effectiveness of Tuina in relieving pain, negative emotions, and disability in knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Pain Medicine. 24 (3), 244-257 (2023).
- Ding, N., et al. Mast cells are important regulator of acupoint sensitization via the secretion of tryptase, 5-hydroxytryptamine, and histamine. The Public Library of Science One. 13 (3), e0194022 (2018).
- Cai, F. H., Li, F. L., Zhang, Y. C., Li, P. Q., Xiao, B. Research on electroacupuncture parameters for knee osteoarthritis based on data mining. European Journal of Medical Research. 27 (1), 162 (2022).
- Mei, Z. G., Cheng, C. G., Zheng, J. F. Observations on curative effect of high-frequency electric sparkle and point-injection therapy on knee osteoarthritis. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 31 (4), 311-315 (2011).
- Xiao, G., et al. Effect of manipulation on cartilage in rats with knee osteoarthritis based on the Rho-associated protein kinase/LIM kinase 1/Cofilin signaling pathways. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 42 (2), 194-199 (2022).
- Wu, M. X., et al. Clinical study on the treatment of knee osteoarthritis of Shen-Sui insufficiency syndrome type by electroacupuncture. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine. 16 (4), 291-297 (2010).
- Richards, R. E., Andersen, M. S., Harlaar, J., van den Noort, J. C. Relationship between knee joint contact forces and external knee joint moments in patients with medial knee osteoarthritis: effects of gait modifications. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 26 (9), 1203-1214 (2018).
- Shull, P. B., et al. Toe-in gait reduces the first peak knee adduction moment in patients with medial compartment knee osteoarthritis. Journal of Biomechanics. 46 (1), 122-128 (2013).
- Adouni, M., Shirazi-Adl, A. Partitioning of knee joint internal forces in gait is dictated by the knee adduction angle and not by the knee adduction moment. Journal of Biomechanics. 47 (7), 1696-1703 (2014).
- Kutzner, I., Trepczynski, A., Heller, M. O., Bergmann, G. Knee adduction moment and medial contact force--facts about their correlation during gait. The Public Library of Science One. 8 (12), e81036 (2013).
- Camacho-Cardenosa, A., et al. Resistance circuit training combined with hypoxia stimulates bone system of older adults: a randomized trial. Experimental Gerontology. 169, 111983 (2022).
- Babur, M. N., Siddiqi, F. A., Tassadaq, N., Arshad Tareen, M. A., Osama, M. Effects of glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate supplementation in addition to resistance exercise training and manual therapy in patients with knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. The Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association. 72 (7), 1272-1277 (2022).
- Wang, H. N., et al. Effect of low-load resistance training with different degrees of blood flow restriction in patients with knee osteoarthritis: study protocol for a randomized trial. Trials. 23 (1), 6 (2022).
- Cheon, Y. H., et al. Relationship between decreased lower extremity muscle mass and knee pain severity in both the general population and patients with knee osteoarthritis: Findings from the KNHANES V 1-2. The Public Library of Science One. 12 (3), e0173036 (2017).
- Murton, A. J., Greenhaff, P. L. Resistance exercise and the mechanisms of muscle mass regulation in humans: acute effects on muscle protein turnover and the gaps in our understanding of chronic resistance exercise training adaptation. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology. 45 (10), 2209-2214 (2013).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved