A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Spatiotemporal Control of Protein Activity through Optogenetic Allosteric Regulation
In This Article
Summary
This protocol describes the application of an engineered blue-light-activated allosteric switch (LightR) domain for reversible spatiotemporal control of protein activity. Utilizing Src tyrosine kinase as a model, this study offers an elaborate protocol for developing and characterizing light-regulated Src (LightR-Src). It demonstrates the versatility of this approach across enzyme classes.
Abstract
Optogenetics offers the potential for mimicking complex spatiotemporal control of enzyme activity down to a subcellular resolution. However, most optogenetic approaches often face significant challenges in integrating multiple capabilities in a single tool applicable to a wide range of target proteins. Achieving precise control over ON/OFF kinetics, ensuring minimum leakiness in the dark, and demonstrating efficient performance in mammalian cells with subcellular precision are some of the most common challenges faced in this field. A promising solution lies in the application of rationally designed light-sensitive domains to allosterically control protein activity. Using that strategy, we generated an optogenetic method combining all the desired features. The approach involves the incorporation of the Light-regulated allosteric switch module (LightR) in the target protein to regulate enzyme activity using blue (465 nm) light. The LightR domain is generated by linking two Vivid (VVD) photoreceptor domains, creating a light-sensitive clamp that can be incorporated into a small flexible loop within the catalytic domain of an enzyme. In its dark state, LightR clamp is open, thus distorting the enzyme's catalytic domain and inactivating it. Upon exposure to blue light, the LightR domain closes and restores the catalytic domain's structure and enzyme activity. In this manuscript, we discuss design strategies to generate a light-regulated protein kinase and demonstrate its control by blue light, reversibility, kinetics, and precise regulation at the subcellular level, enabling tight spatiotemporal precision. Utilizing Src tyrosine kinase as a model, we showcase a protocol for effectively regulating LightR-Src kinase activity. We also demonstrate LightR applicability across different enzyme classes, expanding the utility of the tool system in addressing mechanistic questions of signaling pathways in different diseases.
Introduction
The ability of the cell to interpret external signals and convert them into specific responses in physiological or pathological contexts is directed by dedicated groups of proteins. The contribution of any protein to such complex responses is often defined by its subcellular location, level of expression, and the timing of transient, sustained, or oscillatory activation. Dissecting the role of these individual parameters in the regulation of signaling demands methods capable of replicating intricate spatiotemporal control of protein activity at the subcellular level. Traditional techniques such as genetic manipulation and small molecule inhibitors fall short in this regard. In contrast, optogenetic techniques promise the potential for the dissection of biological processes by manipulating or mimicking physiological and pathological processes. However, current tools often lack broad applicability or subcellular control. Several existing strategies achieve tight regulation of protein localization and interactions; but lack direct control over enzymatic activity1,2,3,4. Others enable regulation of enzymatic activity but may lack subcellular control or have limited applicability across different enzyme classes5,6,7,8,9. In this protocol paper, we describe a novel protein engineering method that combines the advantages of optogenetics into one tool: tight temporal regulation, tunable kinetics, subcellular control, and broad enzyme applicability10. We engineered a Light-regulated (LightR) domain that functions as an allosteric switch when inserted into the target protein of interest. This strategy enables tight spatiotemporal control of the activation and deactivation of a protein of interest in living cells.
Here, the design and application strategy for the LightR optogenetic tool across several enzyme classes is discussed. This study offers a step-by-step protocol for the development, characterization, and application of light-regulated tyrosine kinase Src (LightR-Src). The study further demonstrates the tunability of LightR switch inactivation kinetics. The slow-inactivating LightR switch can maintain enzyme activity with reduced frequency of illumination, whereas fast cycling version, FastLightR, requires more frequent illumination for activation but shows fast inactivation when illumination is turned off. Activation/inactivation of FastLightR-Src in living cells induces cycles of cell spreading and retraction. FastLightR-Src-induced cell spreading agrees with the physiological role of Src kinase11,12. Due to fast inactivation kinetics, FastLightR-Src can also be regulated at a subcellular level, resulting in stimulation of local protrusions and cell polarization. To demonstrate the applicability of the LightR tool to other types of enzymes, we briefly walk the readers through similar success with engineered light-regulated kinase bRaf (LightR-bRaf, FastLightR-bRaf) and a site-specific DNA recombinase Cre (LightR-Cre). Overall, this approach has the potential to advance our understanding of complex signaling pathways shaping the pathophysiology of diverse diseases.
Protocol
1. Design and development of LightR ( Figure 1)
- Strategic planning
NOTE: The LightR domain is comprised of two tandemly connected Vivid (VVD) photoreceptor domains from Neurospora crassa13,14,15,16. VVDs homodimerize in the presence of light, and such dimerization involves a conformational change that brings the N-terminus of one VVD monomer next to the C-terminus of another VVD monomer (Figure 1A). Connecting two VVD domains with a flexible linker creates a clamp-like domain that will be open in the dark and closed upon illumination with blue light. Integrating this clamp into an enzyme's catalytic domain enables light-mediated regulation of activity. In darkness, the open clamp distorts the domain, deactivating the enzyme; illumination with the blue light causes the clamp to close, restoring enzyme's activity (Figure 1B). This concept can be applied to enzymes from various families, including protein kinases and DNA recombinases10 (Figure 1C).- Design of LightR
- To connect two VVD molecules, use a flexible 22-amino acid linker (GGS)4G(GGS)3 between each monomer.
NOTE: The linker provides sufficient flexibility and length to accommodate the association and dissociation of VVD monomers. - Add GPGGSGG and GSGGPG linkers to the N- and C-termini of the LightR domain, respectively.
NOTE: The length and the composition of the linkers may need to be adjusted for a specific protein. Shorter GSG and single Gly linkers are routinely used when tighter regulation is needed. The size of the insertion loop and its proximity to catalytic residues will also influence the dynamic range of regulation. Shorter loops are more likely to provide tighter regulation of catalytic activity but may result in lower activity after illumination. The sequence of the LightR domain is provided in Supplementary Table 1.
- To connect two VVD molecules, use a flexible 22-amino acid linker (GGS)4G(GGS)3 between each monomer.
- Insertion of LightR
NOTE: A suitable LightR insertion site will enable tight regulation of the targeted domain function without sterically blocking its interactions or causing irreversible structural changes that will affect its biological role. A crystal structure of the target protein is an ideal guide in the identification of such flexible loop regions for the insertion of LightR. If necessary, the crystal structure of a close homolog can suffice. Some general criteria to consider are provided below.- Ensure that the insertion loop is structurally coupled to the critical catalytic elements of the enzyme. Ensure that the selected insertion loop is not an existing binding site for the protein and that the insertion of LightR does not potentially disrupt any functional interactions due to steric effects.
- As an initial strategy, replace one amino acid in the insertion loop when inserting LightR. Target the middle of the insertion loop containing a polar or small amino acid (e.g., Glu, Arg, Lys, Gly) exposed to the solvent and not involved in intramolecular interactions.
NOTE: When one amino acid replacement does not result in a functional protein, optimization of the LightR construct will require the replacement of multiple amino acids or the entire insertion loop. Evaluate the functionality of multiple insertion sites for LightR within the defined loop. - Ensure that the target enzyme operates independently of endogenous regulation. Achieve this by using a constitutively active mutant version of the enzyme for the insertion template.
NOTE: Wild-type enzymes can also be used to generate LightR constructs, but this may result in an AND-gated system that will be regulated by endogenous mechanisms and light. - Positive and negative controls are vital for LightR-enzyme activity analysis. Use constitutively active mutants of endogenous proteins as positive controls and catalytically inactive mutant versions of the targeted LightR enzyme as negative controls.
NOTE: When selecting inactivating mutations, it is crucial to ensure that the mutation is sufficiently spaced from the LightR insertion site to avoid disrupting the irreversibility of LightR-enzyme folding. Based on the above criteria, the LightR insertion site in Src kinase is selected in a flexible loop region that is structurally coupled to the highly conserved GXGXXG motif in the ATP-binding G-loop/glycine-rich loop region via a beta-strand. Importantly, it is positioned away from the ATP binding pocket and substrate binding region10,17 (Figure 1C (i)).
NOTE: Due to structural homology between kinases, the LightR insertion site in bRaf is selected in the same structural loop as the insertion site in Src (Figure 1C (ii)).
NOTE: Based on the principles stated in Section 1.1.2., the LightR insertion site in Cre recombinase, a non-kinase, is picked in one of the flexible loops distant from the catalytic core, i.e., the DNA binding site. However, the insertion loop is still structurally coupled to critical catalytic residues within the DNA binding domain through an α-helix to ensure the success of LightR-Cre functionality (Figure 1C (iii)). All insertion sites with positive and negative controls for different enzymes described in the current protocol are detailed in Supplementary Table 2.
- Development of FastLightR.
NOTE: The introduction of I85V mutation to both VVDs in LightR enables a faster activation-inactivation dynamic, attributed to the rapid conversion of the mutant into the dark state18,19. The generation of FastLightR-Src and FastLightR-bRaf with fast inactivation kinetics enables tight temporal control of activation and inactivation. It allows for achieving subcellular regulation of LightR-Src in living cells.
NOTE: Cre recombinase activity results in irreversible DNA recombination; hence, the reversibility properties of LightR are not applicable.
NOTE: To simplify the detection of the LightR construct, a fluorescent protein or any other suitable tag can be attached to the N- or C- terminus of the target protein. This study used mCherry-myc for LightR-Src, Venus for LightR-bRaf, and miRFP670 for LightR-Cre recombinase.
- Design of LightR
- Cloning Strategy
NOTE: The cloning approach, unlike traditional approaches, is based on site-directed mutagenesis that does not rely on specific restriction sites10,20.- Generation of a "Megaprimer"
- Codon-optimize the LightR genes to ensure stable expression of the two tandem VVD DNA sequences of fungal origin in mammalian cells and to make the sequences as different as possible for errorless cloning using PCR. To perform codon optimization follow steps 1.2.1.2-1.2.1.3.
- Align the amino acid sequence of VVDs and the selected linkers side by side to create the theoretical sequence map of LightR.
- Paste the sequence in any online codon optimization platform that utilizes an advanced algorithm for codon optimization to determine the best sequence option with minimal complexity. Ensure the target organism is selected, the reading frame is maintained, and the VVD sequences are selected for optimization.
- Obtain LightR DNA as a custom synthesized fragment (See Supplementary Table 1) or from a previously published LightR construct10.
- Amplify the LightR gene to generate "Megaprimer" using the previously described20 strategy outlined in Figure 1D. Synthesize the LightR "Megaprimer" via PCR following the manufacturer's recommendations for the specific DNA polymerase and using the following PCR reaction mixture:
5x DNA Polymerase compatible buffer: 10 µL
100 µM Forward megaprimer: 0.5 µL
100 µM Reverse megaprimer: 0.5 µL
10 nM dNTP mix: 2 µL
DNA polymerase (2000 units/mL): 1 µl (0.02 U/µL)
50 ng Template DNA: 1 µL
PCR grade water: 35 µL
NOTE: Here, high fidelity, hot start DNA polymerase with universal primer annealing temperatures are used. - Separate the resulting megaprimer by agarose gel electrophoresis. The product will be approximately 1000 nucleotides in length. Excise the megaprimer from the agarose gel and purify using a gel extraction kit, following the manufacturer's recommendations or using an analogous technique.
- Insertion of LightR gene using site-directed mutagenesis: Insert the LightR, replacing a desired amino acid or a length of amino acids. The template plasmid will be the one where the LightR domain is inserted. Perform PCR reaction as previously described20 using the following mixture.
5x DNA Polymerase compatible buffer: 5 µL
10 nM dNTP mix: 1 µL
DNA polymerase (2000 units/mL): 1 µL (0.02 U/µL)
50 ng Target Template DNA: 1 µL
Extracted Megaprimer (calculated mass): 10 µL
DMSO: 2.5 µL
PCR grade water: 2.5 µL
NOTE: Megaprimer mass (ng) = desired insert/vector molar ratio x mass of vector x ratio of insert to vector lengths. The desired insert/vector molar ratio used is 3/1. - After completion of the PCR reaction, add 1 µL of DpnI (2000 units/mL) enzyme to selectively digest only the excess and methylated DNA and incubate the mixture at 37 °C for 1-1.5 h. This will significantly increase the yield of the modified construct.
- Transform 1-2 µL of the PCR reaction into DH5α competent cells following manufacturer protocols.
- Plate transformed bacteria on Luria Broth (LB)-agar plate with appropriate antibiotic for selection. Incubate plate at 37 °C overnight or at room temperature (RT; 25-30 °C ) for 72 h.
NOTE: LB plates with colonies grown on them can be stored at 4 °C for up to 1 month, and protocol can be paused. - Colony screen PCR
- For PCR-based colony screening, design primers that anneal in the LightR insert and target DNA to generate approximately 400-700 bp fragments.
- Add a small amount of a colony from the LB plate to the PCR mix provided below and proceed to thermocycling following manufacturer's recommendations for the specific DNA polymerase.
2x Taq RED Master Mix: 5 µL
PCR grade water : 5 µL
100 µM Forward primer : 0.5 µL
100 µM Reverse primer: 0.5 µL - Check for positive colonies by agarose gel electrophoresis.
- Pick the colonies that generated the desired PCR product size and inoculate them individually into 3 mL of LB broth with the antibiotic, matching the antibiotic resistance in the plasmid backbone. Then, incubate and shake at 37 °C overnight.
- Extract plasmid DNA from liquid culture following the manufacturer's instructions of the plasmid purification kit for plasmid DNA extraction and verify the presence of the insert by sequencing.
NOTE: Cloning primers are summarized in Supplementary Table 3.
- Generation of a "Megaprimer"
2. Cell plating and biochemical analysis of LightR enzyme activity (Figure 2A)
- For Biochemical analysis of LightR-kinases (LightR Src, FastLightR Src, LightR bRaf), plate 1 x 106 LinXE cells per 3.5 cm cell culture dish for each experimental group. See Supplementary Table 4.
- Incubate cells at 37 °C and 5 % CO2 for 16-18 h.
- The following day, transfect the cells with the selected DNA construct, using a suitable transfection reagent following the manufacturer's recommendations (Supplementary Table 4).
NOTE: The optimal transfection reagent will depend on the construct, vector, and type of cells used. This study used 2 µg of DNA in a 3.5 cm dish using a transfection reagent. Empirical testing should be done to determine the optimal transfection reagent. Since transfected constructs will express proteins regulated by blue light, all subsequent steps handling transfected cells must be performed under red light. Wrap the plates with transfected cells with aluminum foil before placing them in the incubator to prevent accidental illumination. - After 16-18 h of transfection expose the cells to blue light10. To perform this, place a 465 nm light-emitting diode (LED) panel lamp system in the tissue culture incubator. Place a perforated plexiglass panel 10 cm above the lamp to obtain the desired illumination of 3 mW/cm2 (Supplementary File 1). A perforated panel is needed to maintain uninterrupted air circulation in the incubator. Illuminate cells for the desired period.
- For activation of LightR-Src and LightR-bRaf, use continuous illumination. For continuous illumination, turn the LED panel on and off manually.
- For maintaining the activation/inactivation cycle of FastLightR Src, use ON/OFF cycles either controlled manually or by a microcontroller.
NOTE: Several software toolkits that provide an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for writing and uploading the required code can be utilized. These toolkits support C/C++ programming and offer general-purpose input/output (GPIO) access, which is essential for controlling the pulsed illumination. A detailed description of the protocols and code used for these purposes is described in Supplementary File 1. - At the end of the respective time points of the experiment (Supplementary Table 4), harvest the cells under safe red lights. Aspirate the media and wash the cells with cold PBS.
- To isolate protein, lyse cells with 500 µL of 2x Laemmli sample buffer supplemented with 5% v/v 2-Mercaptoethanol. Incubate the lysate at 100 °C for 5 min. Analyze cell lysates by protein gel electrophoresis and Western blotting21.
NOTE: The composition of 2x Laemmli buffer is as follows: For 500 mL: 5.18 g of Tris-HCL, 131.5 mL of glycerol, 52.5 mL of 20% SDS, 0.5 g of bromophenol blue, final pH 6.8. - Assess LightR-Src activity by evaluating the phosphorylation level of endogenous p130cas on Tyr249 and paxillin on TyrY11822,23(Figure 2). Assess LightR-bRaf activity by evaluating the phosphorylation level of MEK1 on Ser217/221 and ERK1/2 on TyrY202/20424,25.
3. Functional analysis of LightR-Cre activity
- For the functional analysis of LightR-Cre activity, plate 1 x 106 LinXE cells per 3.5 cm cell culture dish. Incubate cells at 37 °C and 5% CO2 for 16-18 h.
- Transfect the cells following the protocol outlined in section 2, Figure 2A, and Supplementary Table 5. Co-transfect a total of 2 µg DNA, with a 1:9 ratio of LightR-Cre-iRFP670 and a Reporter plasmid Floxed-STOP-mCherry2.
- Following 16-18 h after transfection, illuminate cells. An efficient LightR-Cre activation needs prolonged illumination. Therefore, to avoid phototoxicity, use pulsed illumination for 8 h with 2 s ON and 20 s OFF cycles utilizing a 465 nm LED panel lamp system controlled by a microcontroller as detailed in section 2 and Supplementary File 1.
- Perform imaging using epifluorescence microscopy with a 20x air objective. For visualization of LightR-Cre-iRFP670, use Cy5 filter set, and for visualization of mCherry from Floxed-mCherry expression, use RFP filter set.
NOTE: For Imaging, an epifluorescence microscope equipped with Cy5/RFP light cubes is used.
4. Preparation of samples for live cell imaging
- Plate 2 x 105 HeLa cells per 35 mm tissue culture dish in cell culture media and incubate for 2 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
- Once the cells have attached and the confluency is approximately 60%-70%, co-transfect the HeLa cells with one of the following mixes: (i) 0.85 µg of FastLightR-Src-mCherry-myc/0.15 µg of Stargazin-iRFP, or (ii) 0.75 µg of FastLightR-bRaf-Venus/0.25 µg of mCherry-ERK2
NOTE: In FastLightR-Src experiments, the Stargazin-iRFP is used to label plasma membrane for cell spreading analysis. If higher FastLightR-Src expression is desired, stargazin-iRFP can be omitted, and 1 µg of FastLightR-Src can be used instead. In these cases, a membrane dye should be used to visualize the cells. Plasma membrane stains are routinely used for labeling cell membranes. - Cover the dish with aluminum foil to avoid accidental illumination of the cells and incubate for 16-18 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
- Complete all the following steps under red light illumination to avoid inadvertent activation of the constructs. Exposure to white light will induce the activation of LightR-kinases and could affect subsequent results.
- On the same day, coat 3 round glass coverslips (25 mm diameter, 0.17 mm thickness) overnight with 5 mg/L fibronectin in PBS at 37 °C.
- Rinse the coverslips with PBS 16-18 h after transfection and plate ~1 x 105 transfected HeLa cells onto each coverslip. Incubate in cell culture media for 2 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
NOTE: The low seeding density is necessary to ensure that cells in the field of view are not touching each other. - Prepare the imaging media by adding FBS to Levobitz's L-15 imaging media to a final concentration of 5%. Filter the solution through a 0.22 µm filter and warm it to 37 °C.
- Prewarm mineral oil to 37 °C.
- Wash the coverslips containing the cells with PBS two times. If using a membrane dye, stain the cells following the manufacturer's instructions before washing the coverslips.
- Carefully place the coverslip into a live cell imaging chamber. Add 1 mL of L-15 imaging media to the chamber.
- Add 1 mL of mineral oil on top of the media to prevent evaporation during the imaging process.
- Keep the chamber protected from light at 37 °C until prepared to image.
5. Global activation and imaging of FastLightR-Src (Figure 3)
- Attach a blue LED microscopy ring light to the microscope condenser, positioning it approximately 1.5 cm above the sample holder. Connect the AC/DC control relay for the ring light to the microscope computer.
NOTE: For the experiments in this study, the illumination was controlled through a Transistor-Transistor Logic (TTL) interface via the imaging software. Epifluorescent illumination may also be used to globally activate LightR constructs if an external illumination source is not available. GFP excitation wavelengths, such as the 490/20 nm excitation filter, are effective in activating LightR. - Place the chamber onto a microscope stage pre-heated to 37 °C and select cells expressing FastLightR-Src-mCherry and Stargazin-iRFP (Figure 3B) Or FastLightR-bRaf-Venus and mCherry ERK-2 (Figure 5B).
- For the study of global illumination and imaging experiments, use microscope-compatible, high-performance objectives (40x) with apochromatic correction, flat field correction, and high numerical aperture.
- For global illumination-based studies of Src kinase, use 561/10 nm excitation and 595/40 nm emission filters to visualize FastLightR-Src-mCherry and use 640/20 nm excitation and 655LP emission filter to visualize stargazin-iRFP.
- For global illumination-based studies of bRaf kinase, use 514/10 nm excitation and 540/21 nm emission filters to visualize FastLightR-bRaf-Venus and use 561/10 nm excitation and 595/40 nm emission filters to visualize mCherry-ERK-2.
- Use a multiband polychroic mirror in all fluorescent imaging channels.
- Depending on experimental conditions, consider the following recommendations.
- Image the cells for at least 10 min prior to illumination to establish a baseline activity of the cells.
NOTE: This baseline is required to determine whether activation of FastLightR kinase by illumination induces any changes in the cell behavior or protein localization. One can also perform longer periods of basal imaging to provide greater statistical significance. - Due to the rapid inactivation kinetics of FastLightRs, including many cells for imaging may cause the deactivation of Src/bRaf between stage positions and can attenuate its response. To avoid such error, image 4 cells/min while analyzing FastLightR-Kinase activity in the described protocol and image each selected cell every minute for a total of 110 min (Supplementary File 2).
- Use pulsed illumination over continuous illumination to reduce the potential phototoxic effects of blue light. Illumination for 12 s for each of the 4 cells/min is effective (Supplementary File 2, Figure 3A).
NOTE: The illumination cycles should be empirically determined for different constructs and illumination source types. - Turn off the Illumination during cell imaging to avoid bleed-through in the fluorescent channels.
NOTE: Imaging too many cells at once will decrease the total illumination time available for the sample, leading to an attenuated response from insufficient activation.
- Image the cells for at least 10 min prior to illumination to establish a baseline activity of the cells.
- After imaging, save the movies as a .TIF stack file format for analysis.
NOTE: Due to the less uniform illumination with GFP epifluorescence compared to ring light, experiments using GFP epifluorescence will require more frequent illumination. This results in fewer cells being imaged per experiment.
6. Subcellular activation and imaging of FastLightR-Src (Figure 4)
- Place the chamber onto a microscope stage pre-heated to 37 °C and select a single cell expressing both FastLightR-Src-mCherry and Stargazin-iRFP.
- Select the specific regions (ROI) within the cell to illuminate. This study chooses a small area at the periphery of the selected cell.
NOTE: For local illumination, a 445 nm laser focused by a TIRF module in FRAP mode or micro-mirror device controlled through TTL interface via the imaging software is used. Any patterned illumination system will work for these experiments. If a scanning-based system is used, determine the laser intensity and homogeneity for sufficient activation without damage to the cell. - Image the selected cell every minute for 20 min in the basal state before illumination, 50 min while illuminating locally, then 20 min after activation for a total of 90 min (Supplementary File 2).
- For activation and deactivation, provide an appropriate amount of time suitable for the target protein to allow complete deactivation of the LightR protein. For FastLightR-Src, allow at least 10 min of deactivation for residual activity to ablate and allow 20 min deactivation in the demonstrated experimental setup for local illumination.
- After imaging, save the movies as .TIF stack file format for analysis.
7. Cell spreading analysis
- Prepare images for data processing and analysis. Ensure that the images are in a .TIF stack format. Save these directly from the imaging software or convert them using an open-source program.
- Download the CellGeo script package from the supplementary data zipped files26.
NOTE: The CellGeo package contains several different scripts. Choose the desired package from the list based on the type of analysis as covered in protocol sections 7-9. - Open and run the script titled MovThresh to create a mask of the cell.
- Select File > Import (.tif) and select the Stargazin-iRFP images of the cells.
- Scan through the frames using the scroll bar in the bottom left corner. If the suggested threshold is appropriate, go to step 7.4.
- If the suggested threshold does not align with the cell's behavior, choose smoothed or custom curves underneath Curve Selection. Create the custom curve by scrolling through the frames and then adjusting the threshold on the right-hand side of the window.
- Click Re-Threshold.
- Click File > Save as masks, Change the name of the file, and save it using the Save as option.
- Open the newly created stack file in an open-source image analysis program.
- Select Image > Adjust > Threshold > Apply.
- Select Analyze > Analyze particles > Check display results -> OK.
- Calculate the change in area for each cell by dividing the area at any given time by the average area of the same cell prior to blue light irradiation.
- Plot the area change as a line or bar graph.
- Calculate the average value and 90% confidence intervals for each time point of all cells treated under the same conditions.
8. Cell edge dynamics analysis
- Prepare the stack files using the steps described in protocol section 7.
- Open and run the script titled ProActive.
- Select File > Import > Masks (.tif) and select the mask created through the MovThresh script.
- Select the activity of interest in analyzing in the bottom right corner (Protrusive, Retractive, or Total).
- Select the type of normalization. Typically, area normalization is used for these analyses.
- Select the beginning frame of reference using the slider on the left. The lag slider on the right will determine the time lag between twotime points used to measure the area gained and lost by the cell.
- If the selected frame and lag number are additively greater than the number of frames in the movie, the preview image will not display. Reset these values to equal less than the total number of frames.
- Modify the thresholding for protrusion or retraction by checking the box for Smooth Curve under the Results section. This averages the thresholds over a specific window, which can resolve issues where minor fluctuations are detected as activity.
- Select Run the Range to calculate the activity over the time specified by the frame and lag sliders.
- Save the numerical data by selecting File > Save As > Results(.mat) and use it to determine mean protrusive or retractive activity.
- Determine the 90% confidence intervals for each time point.
NOTE: This will save an array of several different values. The "How to use ProActive" text file included with the script provides a detailed description of what each value represents and how they have been determined26. - Save the visual representation of the activity by selecting File > Save As > Images (.tif).
9. Centroid shift analysis
- For centroid shift analysis, use any software that can determine centroid coordinates.
- In the analysis software, open the masked image stack of the cell of interest as described in protocol section 7.
- Select Measure > Integrated Morphometry Analysis and then click Preferences > Draw Centroid Mark > Check, then select Measure.
- Record centroid coordinates before movement (A).
- Record centroid coordinates at the end of the experiment (B).
- Record the coordinates for the center of the illumination pattern (C).
- Now that the three points have been collected, determine the angle
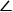 BAC8. θ1 corresponds to the angle
BAC8. θ1 corresponds to the angle 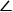 ABC and θ2 corresponds to the angle
ABC and θ2 corresponds to the angle 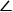 CBA (Figure 4Cii). Do this using the following equation:
CBA (Figure 4Cii). Do this using the following equation:
cosθ = cos(θ1 - θ2) = cosθ1cosθ2 + sinθ1sinθ2
NOTE: A calculator can be used to determine the angles and distances directly from the coordinates for ease of use. - Determine the centroid displacement by multiplying the distance that the cell centroid traveled in pixels by the conversion factor where 1 pixel is equal to 0.4 µm. The specific conversion for pixels to distance will depend on the magnification and camera setup on the system.
- Once the centroid shift angle and distance have been determined, open a graphing software capable of producing images of polar coordinates.
- Insert the centroid shift angle as the θ measurement and the distance traveled as the radius. Utilize ANOVA to test for 95% confidence intervals.
- Plot the results and save the image.
Results
The LightR-Src is designed and generated following the strategy described in Figure 1A,B. Biochemical analysis of LightR-Src accesses the phosphorylation of known endogenous Src substrates, p130Cas (Y249)22 and paxillin (Y118)23 in response to blue light at 60 min of continuous illumination (Figure 2B). Notably, no background activation of Src kinase is observed when LightR-Src is expressed only in...
Discussion
Our study presents an optogenetic approach for the investigation of diverse signaling pathways and demonstrates its wide applicability in addressing different biological questions. The LightR tool system provides several essential advantages: (1) Allosteric regulation of protein activity, (2) Tight temporal control of activity that can be tuned to achieve different kinetics of activation and inactivation, (3) Spatial resolution of activity at the subcellular level, (4) Specificity of signaling modulation and biological a...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Dr. Mark Shaaya for his contribution to the development of LightR enzymes and associated protocols. pCAG-iCre was a gift from Wilson Wong (Addgene plasmid #89573), pcDNA3.1 Floxed-STOP mCherry was a gift from Mositoshi Sato (Addgene plasmid #122963), bRaf-Venus construct bearing V600E mutation was a gift from Dr. John O'Bryan (MUSC); ERK2 gene from pCEFL-ERK2 (a gift from Dr. Channing Der's lab, UNC) was cloned into mCherry-C1 backbone to obtain mCherry-ERK2 plasmid; and pmiRFP670-N1 was a gift from Vladislav Verkhusha (Addgene plasmid # 79987). The work was supported by NIH grants R33CA258012, R35GM145318, and P01HL151327 to AK. This work was further supported by the T32 VBST training fellowship T32HL144459 to NL.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| #1.5 Glass Coverslips 25 mm Round | Warner Instruments | 64-0715 | |
| 1.5 mL Tubes | USA Scientific | cc7682-3394 | |
| 2x Laemmli Buffer | For 500 mL: 5.18 g of Tris-HCL, 131.5 mL of glycerol, 52.5 mL of 20% SDS, 0.5 g of bromophenol blue, final pH 6.8 | ||
| 4-20% Mini-PROTEAN TGX Precast Gel | Biorad | 4561096 | |
| 5x Phusion Plus Buffer | Thermo Scientific | F538L | |
| 60 LED Microscope Ring Light | Boli Optics | ML46241324 | Blue LED, 60 mm diameter, 5 W |
| Agarose | GoldBiotech | A-201 | |
| Anti-Erk 1/2 Antibody | Cell Signaling | 9102 | |
| Anti-GAPDH Antibody | invitrogen | AM4300 | |
| Anti-GFP | Clontech | 632380 | |
| Anti-mCherry Antibody | invitrogen | M11217 | |
| Anti-MEK | Cell Signaling | 9122 | |
| Anti-p130Cas | BD Biosciences | 610271 | |
| Anti-paxillin | Cell Signaling | 2542 | |
| Anti-phospho-Erk 1/2 T202/Y204 Antibody | Cell Signaling | 9101 | |
| Anti-phospho-pY249 p130Cas | Cell Signaling | 4014 | |
| Anti-phospho-Y118 Paxillin | Cell Signaling | 2541 | |
| Anto-phospho-S217/221 MEK | Cell Signaling | 9121 | |
| Arduino Compatable Power Supply | Corporate Computer | LJH -186 | |
| Arduino Uno Rev3 | Arduino | A000066 | |
| Attofluor Cell Chamber | invitrogen | A7816 | |
| Benchmark Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) | Gemini Bio-products | 100-106 | Heat Inactivated Triple 0.1 µm sterile-filtered |
| bRaf-V600E-Venus | Gift from Dr. John O'Bryan, MUSC | ||
| BSA | GoldBiotech | A-420 | |
| Carbenicillin (Disodium) | Gold Biotechnology | C-103-25 | |
| CellMask Deep Red plasma membrane dye | invitrogen | c10046 | |
| Colony Screen MasterMix | Genesee | 42-138 | |
| DH5a competent cells | NEB | C2987H | |
| DMEM | Corning | 15-013-CV | |
| DNA Ladder | GoldBio | D010-500 | |
| dNTPs | NEB | N04475 | |
| Dpn1 Enzyme | NEB | R01765 | |
| DTT | GoldBio | DTT10 | DL-Dithiothreitol, Cleland's Reagents |
| EGTA | Acros | 409910250 | |
| FastLightR-bRaf-mVenus | Addgene | #162155 | |
| Fibronectin from bovine plasma | Sigma | F1141 | |
| FuGENE(R) 6 Transfection Reagent | Promega | E2692 | Transfection reagent |
| Gel Green Nucleic Acid Stain | GoldBio | G-740-500 | |
| Gel Loading Dye Purple 6x | NEB | B7024A | |
| GeneJET Gel extraction Kit | Thermo Scientific | K0692 | Gel Extraction Kit |
| GeneJET Plasmid Miniprep Kit | Thermo Scientific | K0502 | |
| Glutamax | Gibco | 35050-061 | GlutaMAX-l (100x) 100 mL |
| HEK 293T Cells | ATCC | CRL-11268 | |
| HeLa Cells | ATCC | CRM-CCL-2 | |
| HEPES | Fischer | BP310-500 | |
| Iot Relay | Digital Loggers | DLI 705020645490 | AC/DC control relay for illumination |
| Kanamycin Monosulfate | Gold Biotechnology | K-120-25 | |
| KCl | Sigma | P-4504 | |
| L-15 1x | Corning | 10-045-CV | |
| LB Agar | Fisher | BP1425-2 | |
| LED Grow Light System | HQRP | 884667106091218 | LED panel lamp system |
| LightR-bRaf-mVenus | Addgene | #162154 | |
| LightR-iCre-miRFP670 | Addgene | #162158 | |
| MATLAB | Mathworks | R2024a | Software for running CellGEO Scripts |
| Metamorph | Molecular Devices | Imaging Analysis Software | |
| MgCl2 | Fisher Chemical | M33-500 | |
| Mineral Oil | Sigma | M5310 | |
| MiniPrep Kit | Gene Choice | 96-308 | |
| Mini-PROTEAN TGX Precast Gels 12 well | Bio-Rad | 4561085 | |
| Molecular Biology Grade Water | Corning | 46-000-CV | |
| Multiband Polychroic Mirror | 89903BS | Chroma | |
| NaCl | Fisher Chemical | S271-3 | |
| PBS w/o Ca and Mg | Corning | 21-031-CV | |
| pCAG-iCre | Addgene | #89573 | |
| pcDNA3.1_Floxed-STOP mCherry | Addgene | #122963 | |
| pCEFL-ERK2 | Gift from Dr. Channing Der's Lab, UNC | ||
| PCR Tubes | labForce | 1149Z65 | 0.2 mL 8-Strip Tubes and Caps, Rigid Strip Individually Attached Dome Caps |
| Phusion Plus DNA Polymerase | Thermo Scientific | F630S | |
| pmiRFP670-N1 | Addgene | #79987 | |
| Polygon 400 Patterned Illuminator | Mightex | DSI-G-00C | |
| Primers | IDT | ||
| PVDF Membranes | BioRad | 1620219 | Immun-Blot PVDF/Filter Paper Sandwiches |
| T0.25% Trypsin, 2.21 mM, eDTA, 1x [-] sodium | Corning | 25-053-CI | |
| Tris-Acetate-EDTA (TAE) 50x | Fischer | BP1332-1 | For electrophoresis |
| UPlanSApo 40x Microscope Objective | Olympus | 1-U2B828 | |
| USB TTL Box | National Instruments | 6501 | For TTL interface |
| β-Mercaptoethanol | Fisher Chemical | O3446I-100 |
References
- Guntas, G., et al. Engineering an improved light-induced dimer (iLID) for controlling the localization and activity of signaling proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 112 (1), 112-117 (2015).
- Kawano, F., Okazaki, R., Yazawa, M., Sato, M. A photoactivatable Cre-loxP recombination system for optogenetic genome engineering. Nat Chem Biol. 12 (12), 1059-1064 (2016).
- Strickland, D., et al. TULIPs: tunable, light-controlled interacting protein tags for cell biology. Nat Methods. 9 (4), 379-384 (2012).
- Wang, H., et al. LOVTRAP: an optogenetic system for photoinduced protein dissociation. Nat Methods. 13 (9), 755-758 (2016).
- Diaz, J. E., et al. A split-Abl kinase for direct activation in cells. Cell Chem Biol. 24 (10), 1250-1258.e4 (2017).
- Hongdusit, A., Zwart, P. H., Sankaran, B., Fox, J. M. Minimally disruptive optical control of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B. Nat Commun. 11 (1), 788 (2020).
- Wang, J., et al. Time-resolved protein activation by proximal decaging in living systems. Nature. 569 (7757), 509-513 (2019).
- Wu, Y. I., et al. A genetically encoded photoactivatable Rac controls the motility of living cells. Nature. 461 (7260), 104-108 (2009).
- Zhou, X. X., Fan, L. Z., Li, P., Shen, K., Lin, M. Z. Optical control of cell signaling by single-chain photoswitchable kinases. Science. 355 (6327), 836-842 (2017).
- Shaaya, M., et al. Light-regulated allosteric switch enables temporal and subcellular control of enzyme activity. Elife. 9, e60647 (2020).
- Chu, P. H., et al. Engineered kinase activation reveals unique morphodynamic phenotypes and associated trafficking for Src family isoforms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 111 (34), 12420-12425 (2014).
- Kaplan, K. B., Swedlow, J. R., Morgan, D. O., Varmus, H. E. c-Src enhances the spreading of src-/- fibroblasts on fibronectin by a kinase-independent mechanism. Genes Dev. 9 (12), 1505-1517 (1995).
- Nihongaki, Y., Suzuki, H., Kawano, F., Sato, M. Genetically engineered photoinducible homodimerization system with improved dimer-forming efficiency. ACS Chem Biol. 9 (3), 617-621 (2014).
- Vaidya, A. T., Chen, C. H., Dunlap, J. C., Loros, J. J., Crane, B. R. Structure of a light-activated LOV protein dimer that regulates transcription. Sci Signal. 4 (184), ra50 (2011).
- Zoltowski, B. D., Crane, B. R. Light activation of the LOV protein vivid generates a rapidly exchanging dimer. Biochemistry. 47 (27), 7012-7019 (2008).
- Zoltowski, B. D., et al. Conformational switching in the fungal light sensor vivid. Science. 316 (5827), 1054-1057 (2007).
- Karginov, A. V., Ding, F., Kota, P., Dokholyan, N. V., Hahn, K. M. Engineered allosteric activation of kinases in living cells. Nat Biotechnol. 28 (7), 743-747 (2010).
- Zoltowski, B. D., Vaccaro, B., Crane, B. R. Mechanism-based tuning of a LOV domain photoreceptor. Nat Chem Biol. 5 (11), 827-834 (2009).
- Karginov, A. V., Hahn, K. M. Allosteric activation of kinases: Design and application of RapR kinases. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 53 (1), 14.13.1-14.13.16 (2011).
- Kawano, F., Suzuki, H., Furuya, A., Sato, M. Engineered pairs of distinct photoswitches for optogenetic control of cellular proteins. Nat Commun. 6 (1), 6256 (2015).
- Mahmood, T., Yang, P. C. Western blot: technique, theory, and trouble shooting. N Am J Med Sci. 4 (9), 429-434 (2012).
- Cunningham-Edmondson, A. C., Hanks, S. K. p130Cas substrate domain signaling promotes migration, invasion, and survival of estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer. 1, 39-52 (2009).
- Sachdev, S., Bu, Y., Gelman, I. H. Paxillin-Y118 phosphorylation contributes to the control of Src-induced anchorage-independent growth by FAK and adhesion. BMC Cancer. 9, 12 (2009).
- Cope, N., et al. Mechanism of BRAF activation through biochemical characterization of the recombinant full-length protein. ChemBioChem. 19 (18), 1988-1997 (2018).
- Singhal, A., Li, B. T., O'Reilly, E. M. Targeting KRAS in cancer. Nat Med. 30 (4), 969-983 (2024).
- Tsygankov, D., et al. CellGeo: A computational platform for the analysis of shape changes in cells with complex geometries. J Cell Biol. 204 (3), 443-460 (2014).
- Kaimachnikov, N. P., Kholodenko, B. N. Toggle switches, pulses and oscillations are intrinsic properties of the Src activation/deactivation cycle. FEBS J. 276 (15), 4102-4118 (2009).
- Burack, W. R., Shaw, A. S. Live cell imaging of ERK and MEK. J Biol Chem. 280 (5), 3832-3837 (2005).
- Baaske, J., et al. Dual-controlled optogenetic system for the rapid down-regulation of protein levels in mammalian cells. Sci Rep. 8 (1), 15024 (2018).
- Dagliyan, O., et al. Computational design of chemogenetic and optogenetic split proteins. Nat Commun. 9 (1), 4042 (2018).
- Harmer, Z. P., et al. Dynamic multiplexed control and modeling of optogenetic systems using the high-throughput optogenetic platform, Lustro. ACS Synth Biol. 13 (5), 1424-1433 (2024).
- Liu, Q., Tucker, C. L. Engineering genetically-encoded tools for optogenetic control of protein activity. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 40, 17-23 (2017).
- Morikawa, K., et al. Photoactivatable Cre recombinase 3.0 for in vivo mouse applications. Nat Commun. 11 (1), 2141 (2020).
- Shekhawat, S. S., Ghosh, I. Split-protein systems: beyond binary protein-protein interactions. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 15 (6), 789-797 (2011).
- Wu, J., et al. A non-invasive far-red light-induced split-Cre recombinase system for controllable genome engineering in mice. Nat Commun. 11 (1), 3708 (2020).
- Conlon, P., Gelin-Licht, R., Ganesan, A., Zhang, J., Levchenko, A. Single-cell dynamics and variability of MAPK activity in a yeast differentiation pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 113 (40), E5896-E5905 (2016).
- Jacquel, A., et al. Colony-stimulating factor-1-induced oscillations in phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/AKT are required for caspase activation in monocytes undergoing differentiation into macrophages. Blood. 114 (17), 3633-3641 (2009).
- Kholodenko, B. N. Negative feedback and ultrasensitivity can bring about oscillations in the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades. Eur J Biochem. 267 (6), 1583-1588 (2000).
- Kholodenko, B. N. Cell-signalling dynamics in time and space. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7 (3), 165-176 (2006).
- Li, Y., Roberts, J., Aghdam, Z. A., Hao, N. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) dynamics determine cell fate in the yeast mating response. J Biol Chem. 292 (50), 20354 (2017).
- Maeda, M., et al. Periodic signaling controlled by an oscillatory circuit that includes protein kinases ERK2 and PKA. Science. 304 (5672), 875-878 (2004).
- Purvis, J. E., Lahav, G. Encoding and decoding cellular information through signaling dynamics. Cell. 152 (5), 945-956 (2013).
- Roche, S., Fumagalli, S., Courtneidge, S. A. Requirement for Src family protein tyrosine kinases in G2 for fibroblast cell division. Science. 269 (5230), 1567-1569 (1995).
- Klomp, J. E., et al. Mimicking transient activation of protein kinases in living cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 113 (52), 14976-14981 (2016).
- Karginov, A. V., et al. Dissecting motility signaling through activation of specific Src-effector complexes. Nat Chem Biol. 10 (4), 286-290 (2014).
- Cary, L. A., Klinghoffer, R. A., Sachsenmaier, C., Cooper, J. A. Src catalytic but not scaffolding function is needed for integrin-regulated tyrosine phosphorylation, cell migration, and cell spreading. Mol Cell Biol. 22 (8), 2427-2440 (2002).
- Fu, P., et al. Sphingolipids signaling in lamellipodia formation and enhancement of endothelial barrier function. Curr Top Membr. 82, 1-31 (2018).
- Tian, X., Zhou, B. Strategies for site-specific recombination with high efficiency and precise spatiotemporal resolution. J Biol Chem. 296, 100509 (2021).
- Abremski, K., Hoess, R., Sternberg, N. Studies on the properties of P1 site-specific recombination: Evidence for topologically unlinked products following recombination. Cell. 32 (4), 1301-1311 (1983).
- Abremski, K., Hoess, R. Bacteriophage P1 site-specific recombination. Purification and properties of the Cre recombinase protein. J Biol Chem. 259 (3), 1509-1514 (1984).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved