Semiconductors
Source: Derek Wilson, Asantha Cooray, PhD, Department of Physics & Astronomy, School of Physical Sciences, University of California, Irvine, CA
Semiconductors are materials whose ability to conduct an electrical current depends strongly on their temperature and level of impurity. The most common type of semiconductor material is crystalline silicon. Most pure semiconductors are not outstanding conductors; to improve conductivity, a pure semiconductor is often combined or "doped" with an impurity. These impurities are either donors, like phosphorus and arsenic, that donate electrons to the silicon, or acceptors, like boron and aluminum, that steal electrons from the silicon. When acceptors take electrons from the silicon, they leave regions of positive charge called "holes" that effectively behave as positively charged electrons.
A p-type semiconductor is formed when doping makes holes that are the dominant charge carrier in the material. An n-type semiconductor is formed when a semiconductor is doped such that the dominant charge carrier is the electron. As one might expect, a p-n junction is formed at the boundary between the p-type semiconductor and n-type semiconductor. The interaction of electrons and holes at the junction gives rise to the remarkable behavior seen in circuit components such as diodes and transistors. This lab will explore the properties of a single p-n junction in the form of a semiconductor diode.
1. Observe the behavior of a p-n junction in the form of a semiconductor diode and measure its current-voltage characteristic curve.
- Obtain a semiconductor diode, an LED (light-emitting diode), a power source, two digital multimeters, a 1 kΩ resistor, some banana cables and connectors, and a thermometer.
- Look at the semiconductor diode. There should be a band on one of its ends. The side with the band is the "cathode". The side without the band is the "anode".
- Make su
Typical results for the circuit measurements are shown in Table 1. The Shockley diode equation describes the current through a diode as a function of the temperature of the diode and the voltage drop across it. For a temperature of 293.0 K, a voltage of 555 mV across the diode, and an arbitrary (but representative) ideality factor of n = 1.5,
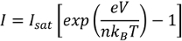
Log in or to access full content. Learn more about your institution’s access to JoVE content here
This lab explored the properties of semiconductors and a p-n junction in the form of a semiconductor diode. A diode is a circuit component composed of one p-n junction. The characteristic curve of the diode was measured, and the diode was observed to conduct an electrical current in only one direction. An LED contains a special type of p-n junction that emits light in addition to conducting unidirectionally.
Semiconductors are used extensively in the electronics industry. Semiconductor diodes
Saltar a...
Vídeos de esta colección:

Now Playing
Semiconductors
Physics II
29.6K Vistas

Electric Fields
Physics II
77.4K Vistas

Electric Potential
Physics II
104.3K Vistas

Magnetic Fields
Physics II
33.3K Vistas

Electric Charge in a Magnetic Field
Physics II
33.6K Vistas

Investigation Ohm's Law for Ohmic and Nonohmic Conductors
Physics II
26.2K Vistas

Series and Parallel Resistors
Physics II
33.1K Vistas

Capacitance
Physics II
43.7K Vistas

Inductance
Physics II
21.5K Vistas

RC/RL/LC Circuits
Physics II
142.7K Vistas

Photoelectric Effect
Physics II
32.6K Vistas

Reflection and Refraction
Physics II
35.7K Vistas

Interference and Diffraction
Physics II
90.8K Vistas

Standing Waves
Physics II
49.7K Vistas

Sound Waves and Doppler Shift
Physics II
23.4K Vistas
ACERCA DE JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos los derechos reservados