When an object moves with constant acceleration, the velocity of the object changes at a constant rate throughout the motion. The kinematic equations of motions are derived for such cases where the acceleration of the object is constant. The first kinematic equation gives an insight into the relationship between velocity, acceleration, and time. We can see, for example:
- Final velocity depends on how large the acceleration is and how long it lasts
- If the acceleration is zero, then the final velocity equals the initial velocity, as expected (in other words, velocity is constant)
- If acceleration is negative, the final velocity is less than the initial velocity
All these observations fit our intuition. Note that it is always helpful to examine the basic equations in light of our intuition and experience to check that they accurately describe nature.
Consider an airplane landing with an initial velocity of 70 m/s and decelerating at 1.5 m/s2 for 40 seconds. Then, the final velocity of the airplane can be calculated using the first kinematic equation. The known quantities are initial velocity, constant (de)acceleration, and time. By substituting the known values in the equation,
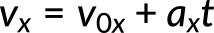
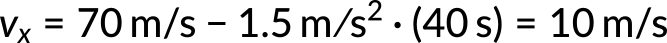
The final velocity of the airplane is 10 m/s.
This text is adapted from Openstax, University Physics Volume 1, Section 3.4: Motion with Constant Acceleration.
Du chapitre 3:

Now Playing
3.7 : Kinematic Equations - I
Motion Along a Straight Line
10.1K Vues

3.1 : Position and Displacement
Motion Along a Straight Line
16.9K Vues

3.2 : Average Velocity
Motion Along a Straight Line
17.8K Vues

3.3 : Instantaneous Velocity - I
Motion Along a Straight Line
12.1K Vues

3.4 : Instantaneous Velocity - II
Motion Along a Straight Line
8.9K Vues

3.5 : Average Acceleration
Motion Along a Straight Line
9.2K Vues

3.6 : Instantaneous Acceleration
Motion Along a Straight Line
7.4K Vues

3.8 : Kinematic Equations - II
Motion Along a Straight Line
9.1K Vues

3.9 : Kinematic Equations - III
Motion Along a Straight Line
7.3K Vues

3.10 : Kinematic Equations: Problem Solving
Motion Along a Straight Line
11.7K Vues

3.11 : Free-falling Bodies: Introduction
Motion Along a Straight Line
7.7K Vues

3.12 : Free-falling Bodies: Example
Motion Along a Straight Line
15.3K Vues

3.13 : Velocity and Position by Graphical Method
Motion Along a Straight Line
7.0K Vues

3.14 : Velocity and Position by Integral Method
Motion Along a Straight Line
5.8K Vues