Force and momentum are intimately related. Force acting over time can change momentum, and Newton's second law of motion can be stated in its most broadly applicable form in terms of momentum. Momentum can be applied to systems where the mass is changing, such as rockets, as well as to systems of constant mass. Also, momentum continues to be a key concept in the study of atomic and subatomic particles in quantum mechanics. One can consider systems with varying mass in some detail; however, the relationship between momentum and force remains useful when mass is constant, such as in the following example.
During the 2007 French Open, Venus Williams hit the fastest recorded serve in a premier women's match, reaching a speed of 58 m/s (209 km/h). What is the average force exerted on the 0.057 kg tennis ball by Venus Williams'racquet, assuming that the ball's speed just after impact is 58 m/s, that the initial horizontal component of the velocity before impact is negligible, and that the ball remained in contact with the racquet for 5.0 ms (milliseconds)?
To determine the change in momentum, substitute the values for the initial and final velocities into the equation below:
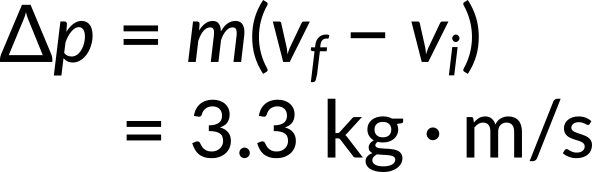
Now, the magnitude of the net external force can be determined by using
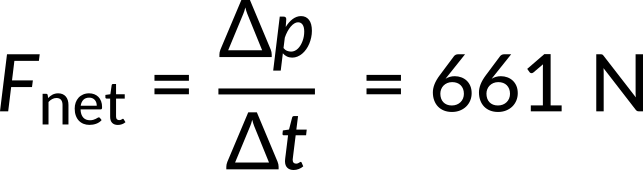
where only two significant figures were retained in the final step.
Du chapitre 9:

Now Playing
9.2 : Force and Momentum
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
12.1K Vues

9.1 : Linear Momentum
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
13.0K Vues

9.3 : Impulse
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
15.1K Vues

9.4 : Impulse-Momentum Theorem
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
10.5K Vues

9.5 : Conservation of Momentum: Introduction
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
13.9K Vues

9.6 : Conservation of Momentum: Problem Solving
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
9.3K Vues

9.7 : Types Of Collisions - I
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
6.1K Vues

9.8 : Types of Collisions - II
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
6.4K Vues

9.9 : Elastic Collisions: Introduction
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
9.2K Vues

9.10 : Elastic Collisions: Case Study
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
10.1K Vues

9.11 : Collisions in Multiple Dimensions: Introduction
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
4.2K Vues

9.12 : Collisions in Multiple Dimensions: Problem Solving
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
3.3K Vues

9.13 : Center of Mass: Introduction
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
10.8K Vues

9.14 : Significance of Center of Mass
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
5.9K Vues

9.15 : Gravitational Potential Energy for Extended Objects
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
1.3K Vues
See More