Solutions of Gases in Liquids
As for any solution, the solubility of a gas in a liquid is affected by the attractive intermolecular forces between solute and solvent species. Unlike solid and liquid solutes, however, there is no solute-solute intermolecular attraction to overcome when a gaseous solute dissolves in a liquid solvent since the atoms or molecules comprising a gas are far separated and experience negligible interactions. Consequently, solute-solvent interactions are the sole energetic factor affecting solubility. For example, the water solubility of oxygen is approximately three times greater than that of helium (there are greater dispersion forces between water and the larger oxygen molecules) but 100 times less than the solubility of chloromethane, CHCl3 (polar chloromethane molecules experience dipole-dipole attraction to polar water molecules). Likewise, note the solubility of oxygen in hexane, C6H14, is approximately 20 times greater than it is in water because greater dispersion forces exist between oxygen and the larger hexane molecules.
Temperature is another factor affecting solubility, with gas solubility typically decreasing as temperature increases. This inverse relation between temperature and dissolved gas concentration is responsible for one of the major impacts of thermal pollution in natural waters.
The solubility of a gaseous solute is also affected by the partial pressure of solute in the gas to which the solution is exposed. Gas solubility increases as the pressure of the gas increases.
For many gaseous solutes, the relation between solubility, Sgas, and partial pressure, Pgas, is a proportional one:
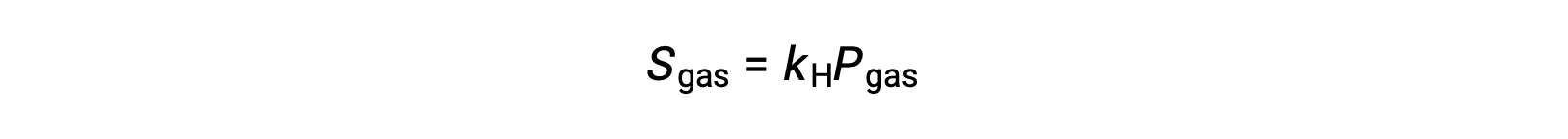
where kH is a proportionality constant that depends on the identities of the gaseous solute and solvent and on the solution temperature. This is a mathematical statement of Henry’s law: The quantity of an ideal gas that dissolves in a definite volume of liquid is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas.
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 11.3: Solubility.
Dal capitolo 12:

Now Playing
12.6 : Physical Properties Affecting Solubility
Solutions and Colloids
21.9K Visualizzazioni

12.1 : Solution Formation
Solutions and Colloids
30.4K Visualizzazioni

12.2 : Intermolecular Forces in Solutions
Solutions and Colloids
32.2K Visualizzazioni

12.3 : Enthalpy of Solution
Solutions and Colloids
24.2K Visualizzazioni

12.4 : Aqueous Solutions and Heats of Hydration
Solutions and Colloids
14.0K Visualizzazioni

12.5 : Solution Equilibrium and Saturation
Solutions and Colloids
17.9K Visualizzazioni

12.7 : Expressing Solution Concentration
Solutions and Colloids
57.6K Visualizzazioni

12.8 : Vapor Pressure Lowering
Solutions and Colloids
25.0K Visualizzazioni

12.9 : Ideal Solutions
Solutions and Colloids
18.5K Visualizzazioni

12.10 : Freezing Point Depression and Boiling Point Elevation
Solutions and Colloids
33.2K Visualizzazioni

12.11 : Osmosis and Osmotic Pressure of Solutions
Solutions and Colloids
38.2K Visualizzazioni

12.12 : Electrolytes: van't Hoff Factor
Solutions and Colloids
32.1K Visualizzazioni

12.13 : Colloids
Solutions and Colloids
17.1K Visualizzazioni