Marginal Dishonesty: The Adding-to-10 Task
Source: Julian Wills & Jay Van Bavel—New York University
Classical economic theory asserts that people are rational and self-interested. In addition to seeking wealth and status, people are motivated by other goals. As a result, financial motives can sometimes be dwarfed by other internal needs, such as maintaining a positive self-concept or affiliating with other group members.
Ethical dilemmas, such as the temptation to cheat on taxes, can result when these motives are in conflict. On the one hand, people may be tempted to save money by underreporting their taxable income. On the other hand, no one wants to perceive themselves as a dishonest, free-rider. As a result, people are reluctant to fully exploit unethical opportunities because doing so can severely undermine their self-image as morally upstanding individuals. Instead, people cheat to a much smaller degree than they are capable of: just enough to gain additional resources, but not so much as to compromise their self-image.
This tendency for marginal dishonesty, or the "fudge factor," is an important principle in social psychology and can be tested through a variety of techniques. Mazar, Amir, and Ariely originally described six separate experiments involving (dis)honesty and a theory of self-concept maintenance.1 The "Adding-to-10 Task" is one of the experimental techniques discussed and is prevalent in research that involves testing honesty. This video demonstrates how to produce and interpret the Adding-to-10 Task.
1. Participant Recruitment
- Conduct a power analysis and recruit a sufficient number of participants.
- Randomly assign half the participants to the experimental condition and the other half to the control condition.
2. Data Collection
- Give participants a test booklet with twenty matrices from the Adding-to-10 Task.
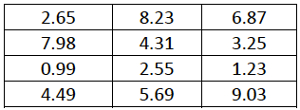
- Each matrix is based on a set of twelve three-digit numbers, two of which sum exactly to 10 (see Figure 1 for exa
This procedure typically results in a considerably higher number of correctly "solved" questions in the experimental condition (Figure 2). This procedure can also dissociate whether this inflated performance is a result of a few individuals cheating a lot or most individuals cheating a little bit. If the former were true, this would result in a mostly overlapping distribution except for a large relative increase of individuals reporting the highest possible score. Instead, typical re
People inherently are torn between achieving gains from cheating versus maintaining a positive self-concept of honesty. By using techniques like the Adding-to-10 Task, modern psychological research concludes that often people, who think highly of themselves in terms of honesty, will rationalize their behavior in such a way to allow them to engage in limited dishonesty while maintaining positive views of themselves. Put another way, there is an acceptable level of dishonesty that is defined by internal reward consideratio
- Mazar, N., Amir, O., & Ariely, D. (2008). The dishonesty of honest people: A theory of self-concept maintenance. Journal of Marketing Research, 45, 633-644.
- Ariely, D. (2012). The (honest) truth about dishonesty: How we lie to everyone-especially ourselves. HarpersCollins. New York.
Vai a...
Video da questa raccolta:

Now Playing
Marginal Dishonesty: The Adding-to-10 Task
Social Psychology
6.3K Visualizzazioni

Analyzing Situations in Helping Behavior
Social Psychology
41.2K Visualizzazioni

Using fMRI to Dissect Moral Judgment
Social Psychology
11.4K Visualizzazioni

Perspectives on Social Psychology
Social Psychology
8.5K Visualizzazioni

Evaluating the Accuracy of Snap Judgments
Social Psychology
21.0K Visualizzazioni

A Minority of One: Conformity to Group Norms
Social Psychology
17.1K Visualizzazioni

Misattribution of Arousal and Cognitive Dissonance
Social Psychology
16.6K Visualizzazioni

Ostracism: Effects of Being Ignored Over the Internet
Social Psychology
10.6K Visualizzazioni

Inducing Emotions
Social Psychology
15.5K Visualizzazioni

Persuasion: Motivational Factors Influencing Attitude Change
Social Psychology
25.6K Visualizzazioni

Creating the Minimal Group Paradigm
Social Psychology
25.4K Visualizzazioni

The Implicit Association Test
Social Psychology
52.0K Visualizzazioni

Nonconscious Mimicry Occurs when Affiliation Goals are Present
Social Psychology
7.9K Visualizzazioni

Effects of Thinking Abstractly or Concretely on Self-control
Social Psychology
6.5K Visualizzazioni

Thinking Too Much Impairs Decision-Making
Social Psychology
10.9K Visualizzazioni