Using a pH Meter
Source: Laboratory of Dr. Zhongqi He - United States Department of Agriculture
Acids and bases are substances capable of donating protons (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-), respectively. They are two extremes that describe chemicals. Mixing acids and bases can cancel out or neutralize their extreme effects. A substance that is neither acidic nor basic is neutral. The values of proton concentration ([H+]) for most solutions are inconveniently small and difficult to compare so that a more practical quantity, pH, has been introduced. pH was originally defined as the decimal logarithm of the reciprocal of the molar concentration of protons 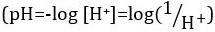 , but was updated to the decimal logarithm of the reciprocal of the hydrogen ion activity
, but was updated to the decimal logarithm of the reciprocal of the hydrogen ion activity 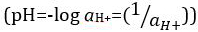 . The former definition is now occasionally expressed as p[H]. The difference between p[H] and pH is quite small. It has been stated that pH = p[H] + 0.04. It is common practice to use the term 'pH' for both types of measurements.
. The former definition is now occasionally expressed as p[H]. The difference between p[H] and pH is quite small. It has been stated that pH = p[H] + 0.04. It is common practice to use the term 'pH' for both types of measurements.
The pH scale typically ranges from 0 to 14. For a 1 M solution of a strong acid, pH=0 and for a 1 M solution of a strong base, pH=14. Thus, measured pH values will lie mostly in the range 0 to 14, though values outside that range are entirely possible. Pure water is neutral with pH=7. A pH less than 7 is acidic, and a pH greater than 7 is basic. As the pH scale is logarithmic, pH is a dimensionless quantity. Each whole pH value below 7 is 10x more acidic than the next integer. For example, a pH of 4 is 10x more acidic than a pH of 5 and 100x (10 x 10) more acidic than a pH of 6. The same holds true for pH values above 7, each of which is 10x more basic (or alkaline) than the next lower whole value. For example, a pH of 10 is 10x more basic than a pH of 9.
1. pH Calibration
- Turn the meter's power on by pressing the "power" button.
- Attach the automatic temperature compensation (ATC) probe if it is available and/or is not with the electrode.
- Check that the measurement mode is pH. If not, press the "MODE" button until "pH" mode appears on the LCD display.
- Consult the quick reference guide at the bottom of the meter or nearby for help if needed.
- Always use fresh, unused, unexpired pH
Figure 1 shows the pH of agricultural soils impacted by cropping management and groundwater irrigation. These soil samples were collected from 5 potato fields under different cropping rotation practices with or without groundwater irrigation. The lowest pH is observed in Field 4 soils in both rainfed and groundwater irrigated series. Groundwater irrigation consistently increased soil pH in all 5 fields. The pH information is essential for recommendation of liming the potato fields appropriately to promote optimal growth.
pH is one of the most commonly measured chemical parameters of aqueous solutions. It is a critical parameter in water and wastewater treatment for municipal and industrial applications, chemical production, agriculture research, and production. It is also critical in environmental monitoring, chemical and life sciences research, biochemical and pharmaceutical research, electronics production, and many more applications. Figure 2 lists pH values of some common substances.
Pure
Vai a...
Video da questa raccolta:

Now Playing
Using a pH Meter
General Chemistry
344.1K Visualizzazioni

Common Lab Glassware and Uses
General Chemistry
652.7K Visualizzazioni

Solutions and Concentrations
General Chemistry
272.6K Visualizzazioni

Determining the Density of a Solid and Liquid
General Chemistry
554.3K Visualizzazioni

Determining the Mass Percent Composition in an Aqueous Solution
General Chemistry
382.9K Visualizzazioni

Determining the Empirical Formula
General Chemistry
179.1K Visualizzazioni

Determining the Solubility Rules of Ionic Compounds
General Chemistry
140.9K Visualizzazioni

Introduction to Titration
General Chemistry
423.0K Visualizzazioni

Ideal Gas Law
General Chemistry
77.8K Visualizzazioni

Spectrophotometric Determination of an Equilibrium Constant
General Chemistry
158.2K Visualizzazioni

Le Châtelier's Principle
General Chemistry
263.7K Visualizzazioni

Freezing-Point Depression to Determine an Unknown Compound
General Chemistry
160.3K Visualizzazioni

Determining Rate Laws and the Order of Reaction
General Chemistry
195.6K Visualizzazioni

Using Differential Scanning Calorimetry to Measure Changes in Enthalpy
General Chemistry
44.4K Visualizzazioni

Coordination Chemistry Complexes
General Chemistry
91.1K Visualizzazioni