Elastic collision of a system demands conservation of both momentum and kinetic energy. To solve problems involving one-dimensional elastic collisions between two objects, the equations for conservation of momentum and conservation of internal kinetic energy can be used. For the two objects, the sum of momentum before the collision equals the total momentum after the collision. An elastic collision conserves internal kinetic energy, and so the sum of kinetic energies before the collision equals the sum after the collision. We can understand this better with the help of a problem.
Let’s try to calculate the velocities of two objects following an elastic collision, given that mA = 0.50 kg, mB = 3.5 kg, vA1x = 4.0 m/s, and vB1x = 0 m/s.
The initial conditions imply that a small object strikes a larger object that is initially at rest. There are two unknowns (the final velocities vA2x and vB2x), which should be found. Because this collision is elastic, the equations for conservation of momentum and conservation of energy can be used. They are given by,
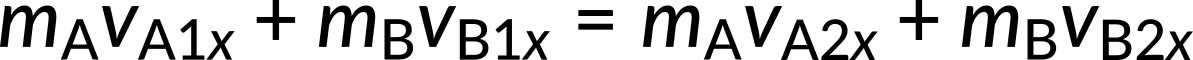
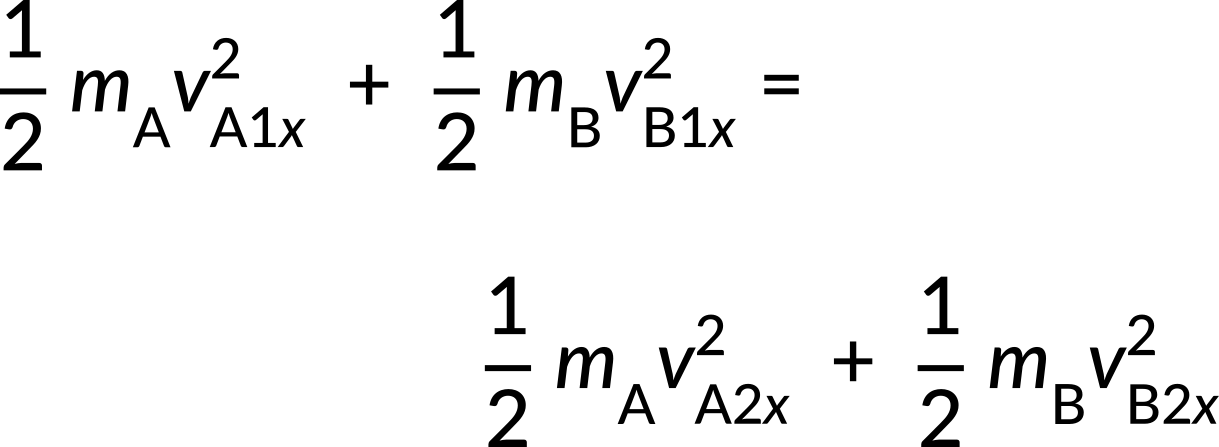
Both can be simplified because object B is initially at rest, and thus vB1x = 0 m/s.
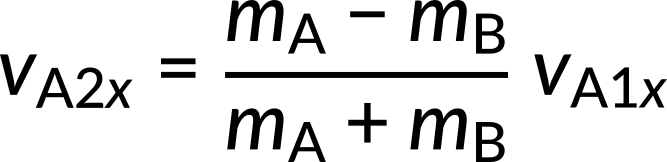
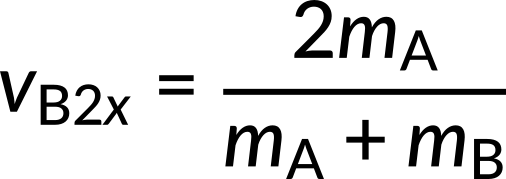
Substituting the known values into these equations, we obtain vA2x = -3 m/s and vB2x= 4 m/s. The negative sign indicates that the first object bounces backward. The result of this example is reasonably intuitive: a small object strikes a larger one at rest and bounces backward. The larger one is knocked forward but with a low speed. This is like a compact car bouncing backward off a full-size SUV that is initially at rest.
This text is adapted from Openstax, University Physics Volume 1, Section 9.4: Types of Collisions.
章から 9:

Now Playing
9.10 : Elastic Collisions: Case Study
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
11.1K 閲覧数

9.1 : Linear Momentum
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
13.1K 閲覧数

9.2 : Force and Momentum
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
13.2K 閲覧数

9.3 : Impulse
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
16.2K 閲覧数

9.4 : Impulse-Momentum Theorem
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
10.6K 閲覧数

9.5 : Conservation of Momentum: Introduction
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
14.0K 閲覧数

9.6 : Conservation of Momentum: Problem Solving
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
9.4K 閲覧数

9.7 : Types Of Collisions - I
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
6.2K 閲覧数

9.8 : Types of Collisions - II
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
6.5K 閲覧数

9.9 : Elastic Collisions: Introduction
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
10.2K 閲覧数

9.11 : Collisions in Multiple Dimensions: Introduction
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
4.2K 閲覧数

9.12 : Collisions in Multiple Dimensions: Problem Solving
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
3.4K 閲覧数

9.13 : Center of Mass: Introduction
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
11.9K 閲覧数

9.14 : Significance of Center of Mass
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
5.9K 閲覧数

9.15 : Gravitational Potential Energy for Extended Objects
Linear Momentum, Impulse and Collisions
1.3K 閲覧数
See More
Copyright © 2023 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved