A rigid body is in static equilibrium when the net force and the net torque acting on the system are equal to zero.
Consider two children sitting on a seesaw, which has negligible mass. The first child has a mass (m1) of 26 kg and sits at point A, which is 1.6 meters (r1) from the pivot point B; the second child has a mass (m2) of 32 kg and sits at point C. How far from the pivot point B should the second child sit (r2) to balance the seesaw?
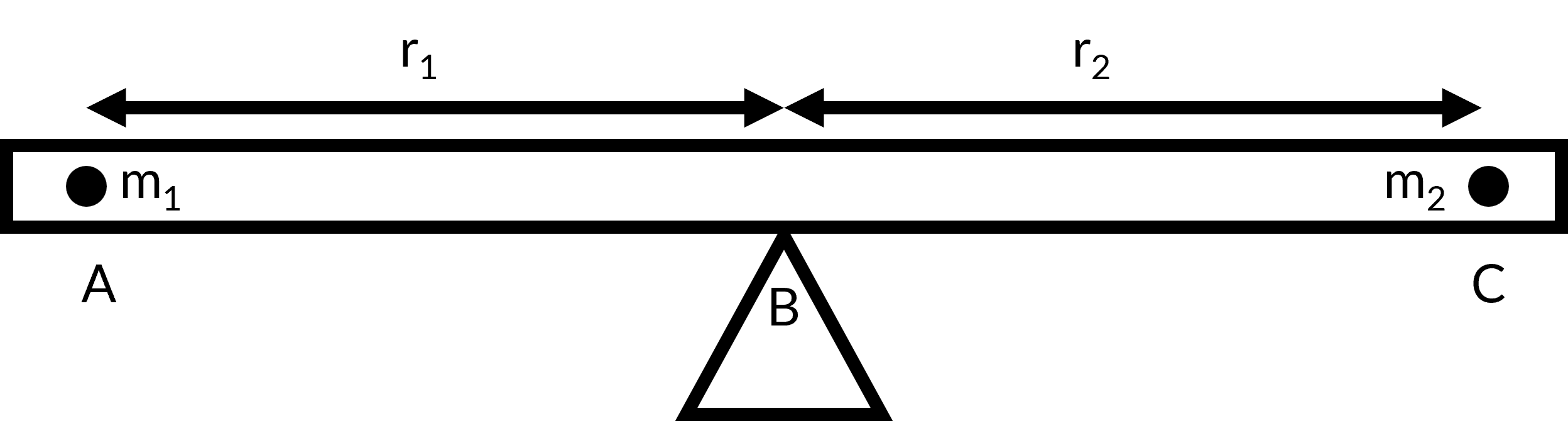
In order to solve the problem, the steps for rigid body equilibrium must be followed:
- Identify the seesaw and two children as the system of interest. Consider the supporting pivot to be the point about which the torques are calculated and all external forces are acting on the system.
- Draw a free-body diagram for the object, including all the forces that act on the system. Here, the three external forces acting on the system are the weights of the two children and the supporting force of the pivot. Now, the torque produced at each point A, C, and B are m1r1, −m2r2, and zero (as the pivot point is the point at which torque is calculated), respectively. The minus sign for m2r2 is due to the torque acting in a clockwise direction.
- Apply the second condition for equilibrium, where the sum of the torques in the system is zero. Substituting the values in the equation, the distance is determined as 1.3 m.
This text is adapted from Openstax, University Physics Volume 1, Section 12.2: Examples of Static Equilibrium.
Etiketler
Bölümden 12:

Now Playing
12.6 : Rigid Body Equilibrium Problems - II
Equilibrium and Elasticity
6.8K Görüntüleme Sayısı

12.1 : Static Equilibrium - I
Equilibrium and Elasticity
10.7K Görüntüleme Sayısı

12.2 : Static Equilibrium - II
Equilibrium and Elasticity
8.1K Görüntüleme Sayısı

12.3 : Center of Gravity
Equilibrium and Elasticity
4.8K Görüntüleme Sayısı

12.4 : Finding the Center of Gravity
Equilibrium and Elasticity
3.3K Görüntüleme Sayısı

12.5 : Rigid Body Equilibrium Problems - I
Equilibrium and Elasticity
4.3K Görüntüleme Sayısı

12.7 : Stress
Equilibrium and Elasticity
5.6K Görüntüleme Sayısı

12.8 : Strain and Elastic Modulus
Equilibrium and Elasticity
3.4K Görüntüleme Sayısı

12.9 : Problem Solving on Stress and Strain
Equilibrium and Elasticity
647 Görüntüleme Sayısı

12.10 : Indeterminate Structure
Equilibrium and Elasticity
456 Görüntüleme Sayısı

12.11 : Elasticity
Equilibrium and Elasticity
3.3K Görüntüleme Sayısı

12.12 : Plasticity
Equilibrium and Elasticity
2.1K Görüntüleme Sayısı
JoVE Hakkında
Telif Hakkı © 2020 MyJove Corporation. Tüm hakları saklıdır