A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Methods Article
Image Recognition and Parameter Analysis of Concrete Vibration State Based on Support Vector Machine
In This Article
Summary
The protocol described in this paper utilizes the directional gradient histogram technique to extract the characteristics of concrete image samples under various vibration states. It employs a support vector machine for machine learning, resulting in an image recognition method with minimal training sample requirements and low computer performance demands.
Abstract
In this paper, the directional gradient histogram technology is employed to extract the features of concrete image samples captured under different vibration states. The support vector machine (SVM) is utilized to learn the relationship between image features and vibration state. The machine learning results are subsequently used to assess the feasibility of the concrete vibration state. Simultaneously, the influence mechanism of the calculation parameters of the directional gradient histogram on the recognition accuracy is analyzed. The results demonstrate the feasibility of using the directional gradient histogram-SVM technology to identify the vibration state of concrete. The recognition accuracy initially increases and then decreases as the block size of the directional gradient, or the number of statistical intervals increases. The recognition accuracy also decreases linearly with the increase of the binarization threshold. By using sample images with a resolution of 1024 pixels x 1024 pixels and optimizing the feature extraction parameters, a recognition accuracy of 100% can be attained.
Introduction
Concrete is a fundamental building material extensively used in the construction industry. During pumping, the concrete frequently develops voids that require compaction through vibration. Inadequate vibration may result in a honeycombed concrete surface, while excessive vibration can lead to concrete segregation1,2. The quality of vibration operation significantly impacts the strength3,4,5,6 and durability of the formed concrete structures7,8. Cai et al.9,10 conducted a study that combined experimental research with numerical analysis to investigate the influence mechanism of vibration on aggregate settlement and concrete durability. The findings revealed that vibration time and aggregate particles exert a substantial impact on aggregate settlement, while aggregate density and the plastic viscosity of the cement-based material have minimal effects. Vibration causes aggregate deposition at the bottom of the concrete specimens. Moreover, as the vibration time increases, the chloride ion concentration decreases at the bottom of the concrete specimens while significantly increasing at the top9,10.
Currently, the assessment of concrete vibration state relies predominantly on manual judgment. As the construction industry continues to progress through intelligent reforms, robot operations have emerged as the future direction11,12. Consequently, a crucial challenge in intelligent vibration operations is how to enable robots to identify the vibration state of concrete.
The histogram of the oriented gradient is a technique that utilizes the intensity gradient of pixels or the distribution of edge directions as a descriptor to characterize the representation and shape of objects in images13,14. This approach operates on the local grid cells of the image, providing robust stability in characterizing image changes under various geometric and optical conditions.
Zhou et al.15 proposed a method for directly extracting directional gradient features from Bayer mode images. This approach omits numerous steps in calculating the directional gradient by matching the color filter column with the gradient operator, thereby significantly reducing the computational requirements for directional gradient image recognition. He et al.16 utilized the directional gradient histogram as the underlying feature and employed the mean clustering algorithm to classify rail fasteners and determine whether the fasteners are defective. The recognition results indicated that the histogram of the oriented gradient feature exhibited high sensitivity to fastener defects, meeting the needs of railway maintenance and repair. In another study, Xu et al.17 preprocessed face image features using Gabor wavelet filtering and reduced the dimension of feature vectors through binary coding and the HOG algorithm. The average recognition accuracy of the method is 92.5%.
The support vector machine (SVM)18 is used to map the vector into a high-dimensional space and establishes a separating hyperplane with a suitable direction to maximize the distance between two parallel hyperplanes. This allows for the classification of support vectors19. Scholars have improved and optimized this classification technology, leading to its application in various fields such as image recognition20,21, text classification22, reliability prediction23, and fault diagnosis24.
Li et al.25 developed a two-stage SVM model for seismic failure pattern recognition, focusing on three seismic failure modes. The analysis results indicate that the proposed two-stage SVM method can achieve more than 90% accuracy for the three failure modes. Yang et al.26 integrated an optimization algorithm with the SVM to simulate the relationship between the five ultrasonic parameters and the stress of the loaded concrete. The performance of an unoptimized SVM is unsatisfactory, particularly in the low-stress stage. However, traversing the model optimized by the algorithm yields improved results, albeit with lengthy computation times. In comparison, the particle swarm optimization optimized SVM significantly reduces the calculation time while delivering optimal simulation results. Yan et al.27 employed SVM technology and introduced a precision-insensitive loss function to predict the elastic modulus of high-strength concrete, comparing its prediction accuracy against the traditional regression model and neural network model. The research findings demonstrate that the SVM technology produces a smaller prediction error for elastic modulus compared to other methods.
This paper collects image samples of concrete under various vibration states and describes the concrete's different states using the directional gradient histogram technique. The directional gradient is employed as a feature vector for training the SVM, and the study focuses on the viability of using the directional gradient histogram-SVM technology to identify the vibration state of concrete. Additionally, the paper analyzes the influence mechanism between three key parameters-binarization threshold, directional gradient statistical block size, and directional gradient statistical interval number-in the feature extraction process of the directional gradient histogram and the recognition accuracy of the SVM.
Protocol
1. Concrete sample image acquisition
- Transport concrete to the workplace, where it will be poured by the pump truck.
- To capture images, switch on the shooting equipment by moving the power key switch to the right and turning it to the ON position. Adjust the camera's mode knob to the green automatic mode, ensuring the camera lens is parallel to the concrete surface, and press the Shutter Key. Capture 20 image samples of non-vibrated concrete, saving them in .jpg format with an acquisition resolution of 1024 x 1024 pixels, as illustrated in Figure 1.
- Insert the vibrating part of the concrete vibration equipment (plug-in concrete vibrating rod) into the concrete. Connect the power supply, and then switch on the concrete vibration equipment by setting it to the ON position.
- When there is some collapse on the surface of the concrete (caused by the vibration discharging air inside the concrete, leading to the sinking of surface aggregates to fill the gaps, resulting in concrete collapse) and some cement slurry appears, keep the camera lens parallel to the concrete surface and press the Shutter Key. Collect 20 image samples of vibrating concrete, as shown in Figure 2.
- Continue operating the vibration equipment. When there is no obvious collapse on the concrete surface, no cement slurry appears, and no bubbles are generated, stop the vibration process, and capture 20 image samples of vibrated concrete, as shown in Figure 3.
2. Sample image gray binarization
- Utilize the imread() function of MATLAB software to read the .jpg file as the unit format data of 1024 pixels x 1024 pixels x 3 color channels, representing the red, green, and blue channel values of the image.
- Next, apply the MATLAB function rgb2gray to convert the image to grayscale, denoted by the format gray value = rgb2gray(jpg file name). Calculate the gray value of each pixel according to Equation (1), and save the gray value as the unit8 format data of 1024 x 1024.
GR(i,j) = 0.2989R(i,j) + 0.587G(i,j) + 0.114B(i,j) (1)
where, GR(i,j) is the gray value of the pixel point, R(i,j) is the red channel value of the pixel point, G(i,j) is the green channel value of the pixel point, and B(i,j) is the blue channel value of the pixel point. - Alter the binary value of the gray values greater than the pixel threshold θ to 1 and set the binary value of the gray values less than the θ pixel to 0.
- After obtaining the binarized gray results, save the outcome as 1024 x 1024 logical format data. In this case, θ represents the binarization threshold, and its values are 50, 100, 150, and 200 for different vibration state concrete sample images, as depicted in Figure 5, Figure 6, and Figure 7.
3. Calculation of directional gradient eigenvalue
- Calculate the horizontal and vertical binary gradient of each pixel in the image using the following equation28
Tp = R(x, y + 1) - R(x, y - 1), Th = R(x+1, y) - R(x-1, y)
where Th is the horizontal binarized gradient, Tp is the vertical binarized gradient, R is the binarized logical format data, x is the row number of the binarized matrix, and y is the column number of the binarized matrix. - Calculate the binary gradient direction and size of each point using the following equation29
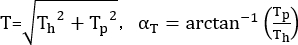
where T is the binary gradient size, αT is the binary gradient direction, Th is the horizontal binary gradient, and Tp is the vertical binary gradient. - Determine the size of the image segmentation block, denoted as n, where the value of n is [ 1,9]. Set the segmentation line for each n pixel in the y direction along the x direction, effectively dividing the image into n x n square blocks based on the segmentation line's position. Any parts of the image that cannot form complete square blocks are then removed.
- Partition binary gradient direction αT (value of the binary gradient direction αT is [ 0°, 360°]) into m parts, resulting in m directional gradient statistical angle intervals. Proceed to calculate the gradient statistical value for each block's gradient statistical angle interval.
- Based on the binary gradient direction of each pixel in the block, classify the pixels into the appropriate gradient statistical angle interval of each direction.
- Sum the binary gradient of the pixels in the gradient statistical angle interval of each direction in the counterclockwise direction to obtain the gradient statistical value of that interval. The obtained results for gradient statistical angle interval directional gradient statistics are depicted in Figure 8, Figure 9, and Figure 10 for block sizes n equal to 8, 128, and 512, respectively .
4. Constructing directional gradient feature vector
- Divide samples into required calculation areas, where each calculation area consists of four adjacent blocks based on the block results obtained in step 3.3. For instance, considering 16 x 16 resolution pixels and a block size of 4 x 4, the image is divided into (16 / 4-1) x ( 16 / 4-1 ) = 9 calculation areas.
- Calculate the statistical value of the directional gradient within angle interval of the gradient statistics of each block in the calculation area. Subsequently, obtain the feature vector with the directional gradient statistics as the component.
- Combine the directional gradient feature vectors from each calculation area to obtain the image's directional gradient feature vector.
5. SVM training
- Randomly select 42 samples from the three vibration states to create the training group, leaving the remaining 18 samples as the test group.
- Utilize the fitcecoc function of MATLAB for SVM training; the format is
SVM = fitcecoc (trainingFeatures, Trainingeigenvalue)
where SVM is the support vector machine to be trained, trainingFeatures is the training group image directional gradient feature vector, and Trainingeigenvalue is the characteristic value of the vibration state of the training group. The characteristic values of the vibration state of the non-vibrated concrete, vibrating concrete, and vibrated concrete samples are 1, 2, and 3, respectively. - Save the trained SVM using the Save function in .mat format.
6. Verification of SVM recognition accuracy
- Using MATLAB's prediction function, input the test group sample image's directional gradient feature vector into the trained SVM to obtain the calculated value of the vibration state feature for each test sample. The format is as follows:
testgroupcalculateseigenvalues = predict (SVM, testFeature)
where testgroupcalculateseigenvalues is the calculated value of the vibration state feature, and SVM is the support vector machine trained in step 5. testFeature is the directional gradient feature vector of the test group sample image. - Determine the test set sample recognition results by feeding the test set into the trained SVM. Count the number of samples for which the test set recognition results match the actual state, and then calculate the recognition accuracy by dividing the number of correct samples by the total number of test set samples.
- If the test recognition accuracy is higher than 94%, consider the SVM recognition as effective. If it is lower than 94%, return to step 1.1 and adjust the binarization threshold, block size n, and the number of directional gradient statistical intervals m.
Results
This protocol aims to analyze how the three-vector calculation parameters of the directional gradient feature affect the accuracy of the SVM in identifying the concrete vibration state. The primary calculation parameters of the directional gradient feature vector include the directional gradient statistical block size, the number of directional gradient statistical angle intervals, and the binary gray threshold. This section uses three main calculation parameters as variables to design the test. The test parameter levels...
Discussion
This paper utilizes the support vector machine (SVM) to learn the image features of various concrete vibration state samples. Based on the machine learning outcomes, a concrete vibration state recognition method based on image recognition is proposed. To enhance the recognition accuracy, it is crucial to control the parameters of the three key steps: image segmentation, image binarization, and directional gradient eigenvalue extraction. According to the test results, a smaller binarization threshold is employed to prepro...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully thank Wuhan Urban Construction Group 2023 Annual Scientific Research Project (NO.7) for funding this work.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| camera | SONY | A6000 | The sensor size is 23.5x15.6mm, the maximum acquisition resolution is 1440 * 1080, and the effective pixel is 24.3 million. |
| concrete | Wuhan Construction Changxin Technology Development Co., Ltd. | C30 pumping concrete | According to the standard of ' concrete strength test and evaluation standard ' ( GB / T 50107-2010 ), the standard value of cubic compressive strength is 30 MPa pumping concrete. |
| Matlab | MathWorks | Matlab R2017a | MATLAB's programming interface provides development tools for improving code quality maintainability and maximizing performance. It provides tools for building applications using custom graphical interfaces. It provides tools for combining MATLAB-based algorithms with external applications and languages |
| Processor | Intel | 12th Gen Intel(R) Core (TM) i7-12700H @ 2.30GHz | 64-bit Win11 processor |
References
- Jiang, L., Tian, Z., Wang, K., Sun, X. Estimating the segregation of concrete under vibration based on electrical method. Concrete. 1, 41-44 (2023).
- Ren, B., Ye, Z., Wang, D., Wu, B., Tan, Y. Evaluation of segregation degree of hardening concrete using improved Mask R-CNN. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering. 41 (5), 93-102 (2022).
- Hu, J., Qin, M., Wang, H., Liu, K. Study on the influence of vibration frequency on the performance of concrete. Highway. 65 (12), 111-114 (2020).
- Bian, C., et al. Experimental study on characterization of evaluation indexes for vibration compaction of fresh concrete. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering. 39 (2), 67-80 (2020).
- Liu, Z., Zhou, M., Bai, J., Mou, S. Influence of vibration time on the strength and homogeneity of rubber concrete. Industrial Construction. 42, 509-512 (2012).
- Cheng, Y., Gou, Z., Wang, Y. Testing Investigation on Effects of Mixing, Vibrating and Curing on Strength of High-Performance Concrete. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science). 31 (12), 1790-1793 (2010).
- Zhao, Y., Chen, S., Liu, Z. Influence mechanism of high-frequency vibration on concrete antifreeze and application in construction of tunnels in cold regions. Industrial Construction. 44 (5), 101-105 (2014).
- Quan, L., Tian, B., Li, S., He, Z., He, K. Evolution characteristics of flexural fatigue performance of dense concrete consolidated with high frequency vibration applied in airport pavement. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering. 20 (2), 34-45 (2020).
- Cai, Y., et al. Influence of coarse aggregate settlement induced by vibration on long-term chloride transport in concrete: a numerical study. Materials and Structures. 55 (9), 1-18 (2022).
- Cai, Y., Liu, Q. F., Yu, L., Meng, Z., Avija, B. An experimental and numerical investigation of coarse aggregate settlement in fresh concrete under vibration. Cement and Concrete Composites. 122 (7), 104153 (2021).
- Wang, X., et al. Development and application of concrete vibrating robot system for high arch dam. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering. 53 (6), 631-654 (2022).
- Chen, C., Li, X., Qiu, Z., Yao, W., Zhu, H. Research Progress of Construction Robots. Journal of Architecture and Civil Engineering. 39 (4), 58-70 (2022).
- Shen, H., Zhang, W., Liu, J., Qiu, K. Development and Prospect of Construction Robots for High Rise Buildings. Construction Technology. 46 (8), 105-108 (2017).
- Dalal, N., Triggs, B. Histograms of Oriented Gradients for Human Detection. IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. , (2005).
- Zhou, W., et al. Gradient-based Feature Extraction From Raw Bayer Pattern Images. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing. (99), 1 (2021).
- He, B., et al. Railway Fastener Defects Detection under Various Illumination Conditions using Fuzzy C-Means Part Model. Transportation Research Record. 2675 (4), 271-280 (2021).
- Xu, X., Quan, C., Ren, F. Facial expression recognition based on Gabor Wavelet transform and Histogram of Oriented Gradients. IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics & Automation. , (2015).
- Cortes, C., Vapnik, V. N. Support Vector Networks. Machine Learning. 20 (3), 273-297 (1995).
- Burges, C. A Tutorial on Support Vector Machines for Pattern Recognition. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery. 2 (2), 121-167 (1998).
- Yang, C., et al. Identification of Pleurotus Ostreatus From Different Producing Areas Based on Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy and Machine Learning. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis. 43 (2), 577-582 (2023).
- Chaabane, S. B., et al. Face recognition based on statistical features and SVM classifier). Multimedia Tools and Applications. 81 (6), 8767-8784 (2022).
- Saleh, M. R., et al. Experiments with SVM to classify opinions in different domains. Expert Systems with Applications. 38 (12), 14799-14804 (2011).
- Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Wang, J. Reliability Prediction of Coal Mine Water Disasters Emergency Rescue System Based on Improved SVM. Journal of Zhengzhou University (Engineering Science). 36 (3), 115-119 (2015).
- Cao, Y., Song, D., Hu, X., Sun, Y. Fault Diagnosis of Railway Point Machine Based on Improved Time-Domain Multiscale Dispersion Entropy and Support Vector Machine. Acta Electronica Sinica. 51 (1), 117-127 (2023).
- Li, Q., Yuze, C., Yu, B., Ning, C. Two-stage support vector machine method for failure mode classification of reinforced concrete columns. Engineering Mechanics. 39 (2), 148-158 (2022).
- Yang, Y., Zhang, W., Yu, H., Chai, W., Liu, D. Analysis on the relationships between ultrasonic parameters and the stress state in loaded concrete based on improved support vector machines). Journal of Vibration and Shock. 42 (2), 175-224 (2023).
- Yan, K., Shi, C. Prediction of elastic modulus of normal and high strength concrete by support vector machine. Construction & Building Materials. 24 (8), 1479-1485 (2010).
- Hussein, I. J., et al. Fully-automatic identification of gynaecological abnormality using a new adaptive frequency filter and histogram of oriented gradients (HOG). Expert Systems. 39 (3), 12789 (2022).
- Chandrakala, M., Devi, P. D. Two-stage classifier for face recognition using HOG features. Materials Today: Proceedings. 47, 5771-5775 (2021).
- Long, C., Yichi, Z., Zhangkai, L., Dandan, D. Low-Light Image Enhancement Based on RAW Domain Image. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics. 35 (2), 303-311 (2023).
- Wang, X., et al. Development and application of concrete vibrating robot system for high arch dam. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering. 53 (6), 631-654 (2022).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved