A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Methods Article
Mitochondrial Transformation in Baker's Yeast to Study Translation and Respiratory Complex Assembly
In This Article
Summary
This work explains how to transform yeast mitochondria using a biolistic method. We also show how to select and purify the transformants and how to introduce the desired mutation in the target position within the mitochondrial genome.
Abstract
Baker´s yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has been widely used to understand mitochondrial biology for decades. This model has provided knowledge about essential, conserved mitochondrial pathways among eukaryotes, and fungi or yeast-specific pathways. One of the many abilities of S. cerevisiae is the capacity to manipulate the mitochondrial genome, which so far is only possible in S. cerevisiae and the unicellular algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The biolistic transformation of yeast mitochondria allows us to introduce site-directed mutations, make gene rearrangements, and introduce reporters. These approaches are mainly used to understand the mechanisms of two highly coordinated processes in mitochondria: translation by mitoribosomes and assembly of respiratory complexes and ATP synthase. However, mitochondrial transformation can potentially be used to study other pathways. In the present work, we show how to transform yeast mitochondria by high-velocity microprojectile bombardment, select and purify the intended transformant, and introduce the desired mutation in the mitochondrial genome.
Introduction
The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a widely recognized model used to study mitochondrial biogenesis. Since yeast is an anaerobic, facultative organism, it is possible to extensively study the causes and consequences of introducing mutations that impair respiration. In addition, this organism possesses friendly genetic and biochemical tools to study mitochondrial pathways. However, one of the most powerful resources to explore the mechanisms of respiratory complex assembly and mitochondrial protein synthesis is the ability to transform mitochondria and modify the organelle's genome. Previously, it has been helpful to introduce in the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) point mutations or small deletions/insertions1,2,3,4,5, delete genes6,7, make gene rearrangements7,8, add epitopes to mitochondrial proteins9,10, relocate genes from the nucleus to the mitochondria11,12, and introduce reporter genes like BarStar13, GFP14,15, luciferase16, and the most widely used ARG8m17,18. Mitochondrial genome modifications have allowed us to dissect and identify mechanisms that otherwise would have been difficult to comprehend. For example, the ARG8m reporter gene inserted at the COX1 locus in the mitochondrial DNA was crucial to understanding that Mss51 has a dual role in Cox1 biogenesis. First, it is a translational activator of the COX1 mRNA, and second, it is an assembly chaperone for the newly made Cox1 protein7,19. This work presents a detailed method to transform S. cerevisiae mitochondria. Although the mitochondrial transformation protocol was published earlier16,20,21,22,23, a visual approach through a video is essential to thoroughly understand the different stages and details of the method. The method consists of various steps and is divided into four general stages:
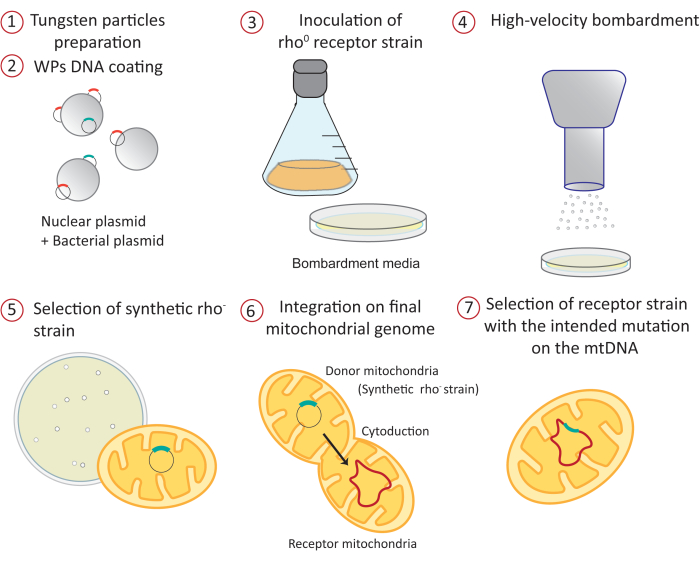
Figure 1: Overview of the mitochondrial transformation procedure by high-velocity microprojectile bombardment: 1) The tungsten particles are sterilized and prepared before DNA coating. 2) Two different plasmids are precipitated on the surface of the WPs. One is a bacterial plasmid containing the construct that will be directed to the mitochondrial matrix. The other is a nuclear yeast expression vector carrying an auxotrophy marker. 3) A receptor yeast strain lacking mitochondrial DNA (rho0) is grown on a fermentative carbon source like galactose or raffinose, which does not exert any glucose repression of mitochondrial gene expression34,35. The culture is spread on petri dishes containing the bombardment medium. 4) WPs coated with plasmids are shot to the receptor strain by high-velocity microprojectile bombardment. 5) Positive synthetic rho- colonies containing the mitochondrial plasmid are selected by mating to a tester strain. 6) The mitochondrial construct is integrated into the mitochondrial genome at the desired locus by mating the synthetic rho- strain (donor) with the acceptor strain by a process known as cytoduction. 7) The positive receptor, haploid strain carrying the mitochondrial construct is selected and purified in different media. Abbreviations: WPs = tungsten particles; mtDNA = mitochondrial DNA. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Transformation of cells with the DNA construct intended to integrate into the mitochondrial genome (Figure 1, steps 1-4)
Although it is possible to directly transform a yeast containing a complete mitochondrial genome (rho+), the transformation is 10-20x more efficient if the cells lack mitochondrial DNA (rho0)24. Tungsten particles (WPs) are coated with two different plasmids that will be co-transformed. The first one is a yeast 2 µ expression vector carrying an auxotrophy marker, such as LEU2 or URA3 (e.g., YEp351 or YEp352, respectively). If the biolistic introduction of DNA into the yeast cells is successful, the transformants will grow on the auxotrophy medium (i.e., a medium lacking leucine or uracil). This plasmid is helpful in making the first selection of the cells that acquired the nuclear plasmid; otherwise, the number of resulting colonies would saturate the plate. The second plasmid is a bacterial plasmid (such as pBluescript or similar) containing the mitochondrial construction intended to be integrated into the mitochondrial genome. The construct must contain at least 100 nt of 5' and 3' flanking mitochondrial sequences for recombination with the mitochondrial region of interest. In our experience, larger flanking sequences are more likely to successfully recombine with the target locus in the mitochondrial genome.
A specific example is shown in Figure 225. In this example, the aim was to delete the region of the mitochondrial COX1 gene coding for the last 15 amino acids of the corresponding protein (Cox1ΔC15) (Figure 2A). The bacterial plasmid carrying the COX1ΔC15 mutation contained 395 nt and 990 nt of the gene's 5' and 3' untranslated regions, respectively. The plasmid was derived from pBluescript (pXPM61) and, together with the 2 µ plasmid YEp352, they were coprecipitated on the surface of WPs (Figure 2B). The WPs were then introduced by microprojectile bombardment into the selected recipient strain (Figure 2C). This strain, named NAB6926, is a MATa, rho0 strain bearing the kar1-1 and ade2 alleles (the importance of these characteristics is discussed below). The cells were plated on bombardment media lacking uracil to select those that acquired the 2 µ plasmid (Figure 2C). Cells were grown for 5-7 nights at 30 °C.
Selection of the cells that acquired the bacterial plasmid containing the mitochondrial construct and the nuclear 2 µ plasmid carrying the auxotrophy marker (Figure 1, step 5)
The positive colonies will maintain many copies of the bacterial plasmid in their mitochondria22. Since the transformed cells are originally rho0, no mitochondrial sequences support the translation of the mitochondrial construct present in the plasmid; hence, the transformed mitochondrial gene will not be expressed. It is necessary to mate the transformants with a tester strain to detect the yeast colonies that acquired the mitochondrial plasmid. The mitochondrial genome of the tester strain contains a nonfunctional mutated version of the gene of interest. After mating, the mitochondria will fuse, and the mitochondrial sequence included in the transformed plasmid will recombine with the mutated mitochondrial gene from the tester strain; consequently, the recovery of the WT gene will reconstitute function. The resulting diploid will have a detectable positive phenotype (usually the capacity to grow in respiratory medium or a medium lacking arginine). The positive cells carrying the bacterial plasmid in mitochondria are named "synthetic rho- cells". In the specific example of Figure 2D, synthetic rho- cells carrying the COX1ΔC15 construct (named XPM199) were replica-plated on a medium lacking uracil (this is the master plate from which positive colonies were purified). They were also replica-plated on a tester strain L4527 lawn, which contains the nonfunctional mutation cox1D369N. After mating for two nights, the mitochondrial genome of L45 and XPM199 recombined, resulting in a functional COX1 gene; therefore, the diploids recovered the ability to grow on respiratory media. From the master plate, we picked the positive colonies. They were streaked on plates lacking uracil, and the selective tests were repeated to obtain pure synthetic rho- cells (Figure 2E). It is important to note that the testing plate is only for the identification of synthetic rho- colonies, and mutants cannot be recovered from these plates.
Integration of the construct into the mitochondrial genome of the intended strain
This step is achieved by a process called cytoduction28,29 (Figure 1, step 6). In this approach, the synthetic rho- strain (donor strain) is mated to the intended acceptor strain of the opposite mating type. An essential requirement is that at least one of the two mating strains carries the kar1-1 mutation to impede nuclear fusion30. Hence, mating of the two cells produces a binucleated zygote (Figure 3). The mitochondrial network from the parental cells (donor and acceptor) fuse and the mitochondrial DNA molecules recombine. The binucleated zygotes are incubated/recovered to allow budding, which will produce haploid cells. These haploids carry the nuclear background of one of the parental cells. Similarly, haploids can carry the mitochondrial DNA from either the parental cell or the recombined mitochondrial DNA of interest. However, the kar1-1 mutation is not 100% effective, and some true diploids will be formed during the mating28,29. The synthetic rho- strain (donor, XPM199) carried the kar1-1 allele in the example. As a selective marker, it had the ade2 allele, making it an auxotroph for adenine (Figure 4). The acceptor strain was XPM10, a rho+ strain bearing the cox1Δ::ARG8m construct, where the reporter ARG8m replaced the COX1 codons in the mitochondrial genome7. The mixture of both cell cultures was added to a YPD plate as a drop to allow mating. After 3-5 h, the cells were observed under a light microscope to detect the formation of shmoos (Figure 3B), a cell shape associated with mating. After the incubation/recovery time, the binuclear zygotes were plated on a medium lacking adenine to prevent the growth of the donor cells.
Selection of the haploid strain carrying the mitochondrial genome of interest (Figure 1, step 7)
A mixture of donor, acceptor, and diploid cells is present after cytoduction. Therefore, after the incubation/recovery of the binucleated zygotes, cells must be grown in different selective media to identify and purify the haploids of interest. The selective media depends on the genotypes of the donor, acceptor strains, and the intended mitochondrial construction. However, in general, the reasoning for choosing the selective media is: i) after incubation/recovery, the cytoduction mix is grown on selective medium where the donor parental strain cannot grow. In the specific example in Figure 4A,B, the donor (synthetic rho- strain) carries the nonfunctional ade2 allele. Thus, the cytoduction mix must be incubated on a medium plate lacking adenine. This is the master plate. ii) Once the colonies grow, the master plate is replicated again on a medium lacking adenine (to generate a new master plate from where the positive colonies of interest will be purified), and next, on a medium where only diploids can grow. This is necessary to avoid further inadvertent purification of diploid colonies. In the case of the example from Figure 4C, only diploids can grow on media lacking leucine. iii) The master plate is also replicated on media where only those acceptor haploids that incorporated the mitochondrial DNA of interest will grow. In the example of Figure 4C, haploids grow on respiratory media containing ethanol/glycerol as a carbon source since the Cox1ΔC15 protein is functional. The resulting rho+ strain bearing the mtDNA of interest was named XPM20925. The strains used in Figure 2 and Figure 4 are listed in Table 1.
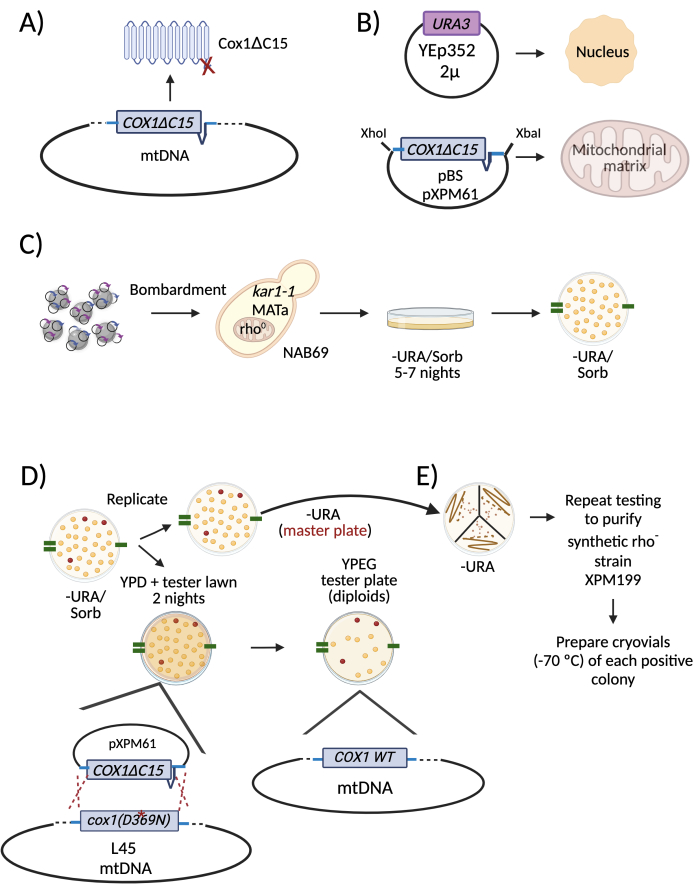
Figure 2: Diagram describing a specific example of mitochondrial transformation and selection of positive rho- cells. (A) The intended modification of the mitochondrial genome was a deletion of the region coding for the last 15 amino acids of the Cox1 subunit (Cox1ΔC15). (B) WPs were coated with two plasmids to transform yeast cells. One was the 2 µ plasmid Yep352 that was directed and expressed in the nucleus. The other was plasmid pXPM61, which contains the COX1ΔC15 allele plus 395 nt and 990 nt of the COX1 5' and 3'-UTRs, respectively. (C) The WPs were introduced into cells from the strain NAB69, which lacks mitochondrial DNA (rho0 strain). Transformant colonies obtained from the bombardment plates were replicated on a medium lacking uracil, the auxotrophic marker of the nuclear plasmid YEp352. (D) To select the positive rho- colonies, the -URA plate was replicated on a media lacking uracil. This was the master plate from which the positive colonies were picked and isolated. It was also replicated on plates with rich media (YPD) and a lawn of a tester strain. During mating, the synthetic rho- mitochondrial DNA was recombined with the mitochondrial DNA from the tester strain, L4527, which carries a mutation in the COX1 gene (D369N). The diploids that grew on respiratory media contained the transformed DNA. The corresponding colonies were picked from the master plate to restreak and purify. To help identify the positive colonies in the master plate throughout all replica plating, marks were made with a permanent marker on the edges of the plates (green lines). (E) The selected positive colonies were restreaked on a medium lacking uracil. This was the new master plate. As in D, two more rounds of testing were carried out to purify the synthetic rho- colonies. Abbreviations: WPs = tungsten particles; mtDNA = mitochondrial DNA; -URA/Sorb = lacking uracil/ containing Sorbitol; WT = wild type. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
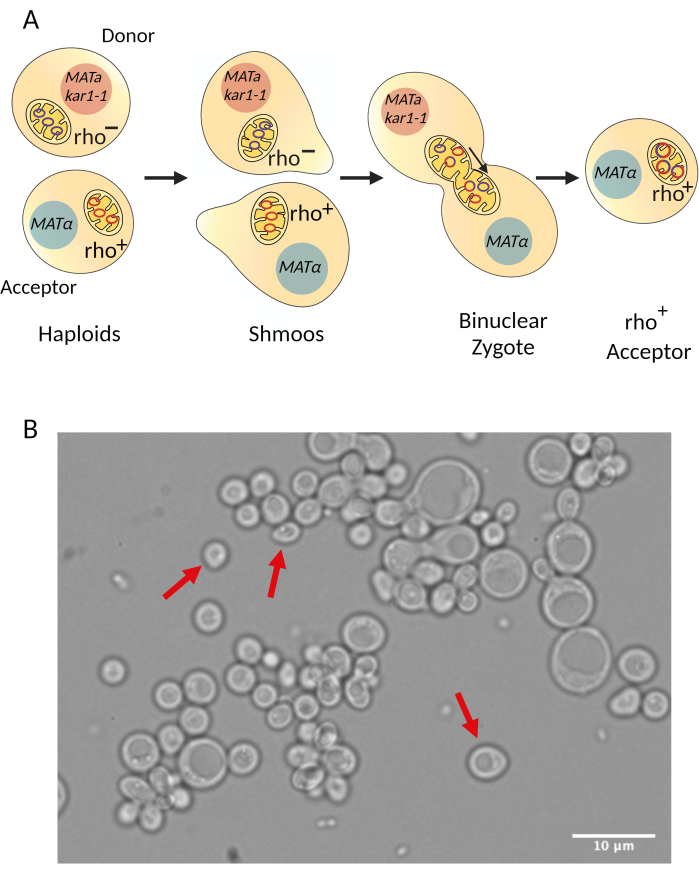
Figure 3: Diagram describing the cytoduction procedure. (A) General overview of how cells mate during cytoduction. During cytoduction, mitochondria from the donor and acceptor strains fuse so mitochondrial DNA from both strains recombine. Since nuclear fusion is reduced due to the kar1-1 mutation30, binuclear zygotes are formed. After some incubation/recovery time, the binuclear zygotes bud and haploid acceptors containing the intended mitochondrial mutation are selected. (B) Mating of the synthetic rho- strain (donor) and the acceptor strain through cytoduction allows the formation of shmoos (red arrows), a characteristic shape of mating yeast. The image was taken under a light microscope with a 100x objective. Scale bar = 10 µm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.

Figure 4: Diagram describing a specific example of cytoduction to integrate the mutation COX1ΔC15 in the mitochondrial genome. (A) Liquid cultures of the synthetic rho- strain (donor, XPM199) and the strain of interest (acceptor, XPM10) were mixed to mate. After shmoo formation, the mix was recovered in a liquid culture for 2-4 h. Next, the cytoduction mix was spread on a plate with a medium lacking adenine to prevent the growth of the donor cells. (B) Schematic representation of the recombination events of the mitochondrial DNA from the donor (XPM199) and the acceptor (XPM10) during cytoduction. (C) The master plate was replicated on different selective media to identify and purify those haploids that integrated the intended mitochondrial gene in the organelle's DNA (XPM209)25. Abbreviations: -ADE = lacking adenine; -LEU = lacking leucine. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Protocol
NOTE: We recommend making six transformations for each construct since mitochondrial transformation efficiency is usually low. The composition of the different growth media is shown in Table 2.
1. Tungsten particle preparation
- Weigh 30 mg of 0.7 µm tungsten particles (WPs, microcarriers) in a microtube. Add 1.5 mL of 70% ethanol (EtOH) to sterilize. Vortex the WPs and let them rest for 10 min at room temperature.
- Centrifuge at 13,200 x g for 15 min at room temperature. Wash the WPs by adding 1.5 mL of sterile water to the particles, vortexing them, and centrifuging at 13,200 × g for 15 min at room temperature. Discard the supernatant.
- Add 500 µL of sterile 50% glycerol (final concentration is 60 µg of WPs/µL).
NOTE: WPs can be stored at -20 °C for at least 6 months. From this stock, take the required amount for six transformations (100 µL).
2. WPs DNA coating
- Add 5 µg of the 2 µ plasmid and 15 µg of the bacterial plasmid containing the mitochondrial sequence to a microtube on ice.
NOTE: The final volume must not exceed 50 µL to avoid further diluting the reagents needed for DNA coating. - Add 100 µL of the WP suspension and vortex for 5 s (6 mg of WPs).
- Add 4 µL of 1 M spermidine. Briefly vortex.
- Add 100 µL of ice-cold 2.5 M CaCl2, briefly vortex. Incubate on ice for 10 min; briefly vortex the mix every 3 min.
NOTE: The CaCl2 solution is filter-sterilized and must not be autoclaved. - Centrifuge the WPs for 30 s at 13,200 × g at 4 °C and discard the supernatant. Wash the particles by gently resuspending them in 200 µL of 100% EtOH at -20 °C.
- Centrifuge the WPs for 30 s at 13,200 × g at 4 °C and discard the supernatant. Repeat the wash.
- Resuspend the WPs in 60-70 µL of room temperature 100% EtOH using a pipette tip; do not vortex.
NOTE: To ensure the quality of the plasmids, DNA coating should be performed on the same day as biolistic transformation.
3. Biolistic material preparation
- Before bombardment, sterilize six macrocarrier holders (Figure 5) in an autoclave and thoroughly dry them. Alternatively, soak them in EtOH and sterilize them using a flame with the help of forceps. Place them on a sterile glass plate.
- During DNA precipitation (10 min incubation on ice in step 2.4), insert six macrocarriers (or flying discs) in each one of the six macrocarrier holders with the help of sterile forceps.
NOTE: Do not sterilize the macrocarriers. - Mix the DNA-coated WPs with the pipette. Add 10 µL of the WPs to each macrocarrier surface and distribute over the entire surface with the pipette tip. If necessary, add a few extra microliters of 100% EtOH to the macrocarrier surface to make an even spreading of the WPs. Let the suspension dry at room temperature for ~20 min.
4. Preparation of yeast cells and bombardment plates
- Inoculate the rho0 receptor strain on 2 mL of YPR medium (Table 2). Grow for one night at 30 °C in a rotating wheel.
- Dilute 300 µL of the culture in 30 mL of fresh YPR medium. Grow at 30 °C and 200 rpm on a rotary shaker for two nights until the culture is saturated.
- Centrifuge the yeast cells at 600 × g for 5 min at room temperature. Discard the supernatant and resuspend the yeast cells in 600 µL of YPD medium (Table 2).
- Using a sterile glass handle, spread 100 µL of the yeast cell suspension on a solid bombardment medium plate.
NOTE: The bombardment medium must lack the selection marker of the 2 µ plasmid that will be used for transformation. - Repeat step 4.4 for the other five plates.
- Incubate for 1-3 h at room temperature before bombardment to ensure the liquid medium is completely absorbed on the plate's surface.
5. Generation of a synthetic rho- strain by biolistic transformation
NOTE: Before beginning, be sure to read the user's manual for the biolistic equipment. We will describe the protocol of the referenced equipment (Table of Materials and Figure 5).
- Clean the chamber of the biolistic particle delivery system with 70% ethanol to prevent contamination and let it stand for at least 10 min. Just before bombardment, wipe the surface with a clean paper towel.
- Open the helium tank valves to set around 2,000 psi.
- Power on the equipment and turn on the vacuum source.
- Using forceps, place the macrocarrier facing down on the macrocarrier holder.
NOTE: Do not use the stopping screen that comes with the equipment. - Screw the macrocarrier lid on top of the macrocarrier. All parts together constitute the microcarrier launch system (Figure 5).
- Place the microcarrier launch system inside the vacuum chamber at the fifth level from the bottom.
- Place one of the plates containing the rho0 strain lawn on the second level from the bottom of the chamber. Ensure that the plate faces up and is without the lid.
- Using sterile forceps, put one rupture disk on the retaining cap. Screw the retaining cap on the acceleration tube; make sure that the retaining cap is snug.
NOTE: Do not treat the ruptured discs with isopropanol as suggested in the manual since we have observed that transformation efficiency decreases. - Close the door of the vacuum chamber.
- Put the VAC/VENT/HOLD switch in the VAC position. When 25-28 inHg vacuum is reached, change the VAC/VENT/HOLD switch to the HOLD position.
NOTE: Be aware that achievable vacuum can vary according to sea level. We found success reaching 25 inHg. - Press the FIRE switch to shoot the WPs. Wait for the pressure to build in the acceleration tube until it reaches 1,300 psi when the rupture disk will break, making a pop sound.
- Immediately after the rupture disk breaks, the FIRE switch and the vacuum are released by changing the VAC/VENT/HOLD switch to the VENT position.
- Carefully, with sterile forceps, remove any debris of the rupture disk present on the surface of the plate and cover the plate with its lid.
- Repeat the procedure for the remaining five plates, placing a new rupture disk and macrocarrier in each round.
- At the end, close the main valve of the helium tank.
- Close the chamber and build a vacuum by taking the VAC/VENT/HOLD switch to the VAC position. Release the system from any helium pressure by pressing and releasing the FIRE switch a few times. Repeat with the door open.
- Turn off the vacuum pump and the bombardment equipment.
- Clean the delivery system with 70% EtOH. Wash the macrocarrier supports with a 0.1% SDS solution; rinse with sterile distilled water and 100% EtOH.
6. Synthetic rho- colony selection
- Incubate the bombardment plates for 5-7 nights at 30 °C.
NOTE: It is important to check the plates daily for contamination. If necessary, the contaminated region can be cut out with a sterile spatula to avoid further contamination. - Inoculate the tester strain of the opposite mating type in 2 mL of YPD medium overnight (see the specific example in Figure 2D,E).
- Inoculate 150 µL of the tester strain culture on a YPD plate. Using a sterile glass handle, spread the tester evenly on the plate surface. Let the plate dry for at least 5 min.
- Make replicas of the bombardment plates using velvet replicating pads and a replicator stamp.
- Replicate on a dropout medium plate corresponding to the transformed 2 µ plasmid auxotrophy marker. Growth takes one overnight incubation at 30 °C. Afterward, store at 4 °C until further use. This plate is the master plate.
- Replicate on the YPD plate containing the tester´s lawn from step 6.3. Incubate at 30 °C for two nights. Afterward, replicate this plate on the selective medium to detect the presence of the mitochondrial gene of interest, for example, respiratory medium or a medium lacking arginine, and incubate overnight at 30 °C. Only the cells that harbored the synthetic bacterial plasmid in mitochondria will grow on the selective medium after mating with the tester strain.
- Identify on the master plate (step 6.4.1) the corresponding colonies that grew in step 6.4.2.
NOTE: Since the bombardment plate (and thus, the master plate) is crowded with transformant colonies, it can be difficult to identify those positive colonies observed on the tester's mating plate. For this reason, it is highly recommended to draw a couple of small lines on each side of all plates with a permanent marker. Draw similar lines on the ring of the replicating stamp. These lines will be helpful in orienting and locating positive colonies on the master plate (see the example in Figure 2D). - Purify the positive colonies by streaking them from the master plate to a second selective dropout plate, as in step 6.4.1. Incubate for two nights at 30 °C.
NOTE: It is essential that streaking allows the growth of single colonies to ensure a pure strain. - Repeat the selection process (steps 6.2-6.5) to confirm the presence of the bacterial plasmid in mitochondria.
NOTE: Usually, this process can be repeated two more times to select stable synthetic rho- strains. - Once the synthetic rho- strain stably maintains the plasmid DNA in mitochondria, select 3-5 different positive colonies and inoculate them in 2 mL of YPD. Use this culture to prepare a cryovial stock (by mixing 600 μL of culture and 600 μL of 50% glycerol to preserve at -70 °C) and to insert the plasmid sequence into the mtDNA of interest by cytoduction (step 6.7).
NOTE: Since there is no selective pressure to maintain the transformed plasmid in the mitochondria from the synthetic rho- strain, the plasmid can be easily lost. Therefore, we recommend making the cytoduction as soon as possible.
7. Integration of the construction present in the synthetic rho- strain into the target site in the mitochondrial genome by cytoduction
- Inoculate two tubes with 3 mL of YPD media, one with the donor cells (synthetic rho- cells) and one with the acceptor cells (yeast cell where the final construction is expected). Incubate overnight at 30 °C.
- Mix 750 µL of the donor strain and 250 µL of the receptor strain in a sterile microtube (3:1 ratio).
- Centrifuge the mixture for 1 min at 13,200 × g; discard the supernatant. Using a 1 mL pipette tip with the end cut off, take one drop of the cell pellet and place it on a YPD plate. Incubate at 30 °C for 2-4 h.
NOTE: To avoid cross-contamination, do not put more than two cell suspensions in a single plate (see the example in Figure 4A). - Take a small amount of the cell mixture, resuspend it in 15 µL of sterile water on a slide, and place a cover slip. Check under a light microscope for the presence of shmoos with a 40x or 100x objective; this characteristic shape shows up when two mating types are present (Figure 3B).
- If shmoos are present, resuspend a small amount (~0.5 mm3) of the cell mass in 2 mL of YPD medium. Incubate for 2 h at 30 °C in a rotating wheel to allow the binuclear zygotes to recover.
- Vortex the mix and dilute 10 µL of the cell suspension in 990 µL of sterile water (1:100 dilution). Use glass beads or a sterile glass handle to spread 100 µL of the cell dilution on a dropout medium where only the acceptor strain (and sporadic diploids) grow. Incubate for 2-3 nights at 30 °C.
- Replicate the resulting colonies on the necessary selective media as explained in the introduction (stage 4; see Figure 4C for a specific example).
- After identification of positive colonies, restreak them on the same selective media to purify the haploid strain carrying the mtDNA of interest.
- Select at least two positive colonies and grow them on 2 mL of YPD medium at 30 °C overnight. Make a cryogenic backup by mixing 600 µL of 50% glycerol with 600 µL of the saturated YPD culture. Store at -70 °C.
- Isolate DNA of the resulting strains31,32. Amplify the desired region by PCR and sequence to confirm the presence of the mitochondrial mutation.
NOTE: Each positive colony is a technical replicate that must be confirmed independently to ensure the correct sequence in the mitochondrial genome.
Results
This section presents some representative results from the different stages of mitochondrial transformation. Figure 6 shows a bombardment procedure. The synthetic rho- cells carried a bacterial plasmid with the reporter gene ARG8m, which will replace the coding sequence of a mitochondrial gene (Figure 6A). After bombardment, the plate was replicated on a medium lacking uracil (-URA); this is the master plate (
Discussion
The present work described how to transform mitochondria from the yeast S. cerevisiae successfully. The process, from high-velocity microprojectile bombardment until purification of the intended yeast strain, takes ~8-12 weeks, depending on how many rounds of purification of the synthetic rho- strain are necessary. Some of the critical steps of the method are as follows. First, the larger the flanking regions added around the mutation site in the mitochondrial gene construct, the higher the probabilit...
Disclosures
The authors do not have any conflicts of interest to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This publication was supported by Programa de Apoyo a Proyectos de Investigación e Innovación Tecnológica (PAPIIT), UNAM [IN223623 to XP-M]. UPD is a CONAHCYT fellow (CVU:883299). We want to thank Dr. Ariann Mendoza-Martínez for technical help with the light microscope images. Biorender licenses: DU26OMVLUU (Figure 2); BK26TH9GXH (Figure 3); GD26TH80R5 (Figure 4); PU26THARYD (Figure 7); ML26THAIFG (Figure 9).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 1 mL pipette tips | Axygen | T-1000-B | |
| 1.5 mL Microtube | Axygen | MCT-150-C | |
| 10 μL pipette tips | Axygen | T-10-C | |
| 15 mL conical bottom tube | Axygen | SCT-25ML-25-S | |
| 200 μL pipette tips | Axygen | T-200-Y | |
| 50 mL conical bottom tube | Axygen | SCT-50ML-25-S | |
| AfiII | New England BioLabs | R0520S | |
| Agarose | SeaKem | 50004 | |
| Analytic balance | OHAUS | ARA520 | |
| Autoclave | TOMY | ES-315 | |
| Bacto agar | BD | 214010 | |
| Bacto peptone | BD | 211677 | |
| Biolisitic Macrocarrier holder | BIO-RAD | 1652322 | |
| Bunsen burner | VWR | 89038-528 | |
| Calcium chloride | Fisher Scientific | C79-500 | |
| CSM -ADE | Formedium | DCS0049 | |
| CSM -ARG | Formedium | DCS0059 | |
| CSM -LEU | Formedium | DCS0099 | |
| CSM -URA | Formedium | DCS0169 | |
| Culture glass flask | KIMAX KIMBLE | 25615 | |
| Culture glass tube | Pyrex | 9820 | |
| Dextrose | BD | 215520 | |
| Ethanol | JT Baker | 9000 | |
| Forceps | Millipore | 620006 | |
| Glass beads | Sigma | Z265926 | |
| Glass handle | Sigma | S4647 | |
| Glycerol | JT BAKER | 2136-01 | |
| Helium tank grade 5 (99.99 %) | - | - | |
| HSTaq Kit | PCR BIO | ||
| Microcentrifugue | Eppendorf | 022620100 | |
| NdeI | New England BioLabs | R0111L | |
| Orbital shaker | New Brunswick scientific | NB-G25 | |
| PCR tubes | Axygen | PCR-02-C | |
| PDS-1000/He TM Biolistic Particle Delivery System | BIO-RAD | 165-2257 | |
| Petri dishes (100X10) | BD | 252777 | |
| QIAprep Spin Miniprep | Qiagen | 27106 | |
| Raffinose | Formedium | RAF03 | |
| Replica plater | Scienceware | Z363391 | |
| Rupture discs 1350 Psi | BIO-RAD | 1652330 | |
| Sorbitol | Sigma | S7547 | |
| Spermidine | Sigma | S0266 | |
| T4 DNA Ligase | Thermo Scientific | EL0011 | |
| Tissue Culture Rotator | Thermo Scientific | 88882015 | |
| Tungsten microcarriers M10 | BIO-RAD | 1652266 | |
| Vaccum pump of 100L/min capacity | - | - | |
| Velvet pads | Bel-Art | H37848-0002 | |
| Vortex | Scientifc Industries | SI-0236 | |
| Wood aplicator stick | PROMA | 1820060 | |
| Yeast extract | BD | 212750 | |
| Yeast Nitrogen base without aminoacids | BD | 291920 |
References
- Bonnefoy, N., Fox, T. D. In vivo analysis of mutated initiation codons in the mitochondrial COX2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae fused to the reporter gene ARG8m reveals lack of downstream reinitiation. Mol Gen Genet. 262 (6), 1036-1046 (2000).
- Franco, L. V. R., Su, C. H., McStay, G. P., Yu, G. J., Tzagoloff, A. Cox2p of yeast cytochrome oxidase assembles as a stand-alone subunit with the Cox1p and Cox3p modules. J Biol Chem. 293 (43), 16899-16911 (2018).
- Flores-Mireles, D., et al. The cytochrome b carboxyl terminal region is necessary for mitochondrial complex III assembly. Life Sci Alliance. 6 (7), (2023).
- Rubalcava-Gracia, D., Vázquez-Acevedo, M., Funes, S., Pérez-Martínez, X., González-Halphen, D. Mitochondrial versus nuclear gene expression and membrane protein assembly: the case of subunit 2 of yeast cytochrome. Mol Biol Cell. 29 (7), 820-833 (2018).
- García-Villegas, R., et al. The Cox1 C-terminal domain is a central regulator of cytochrome c oxidase biogenesis in yeast mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 292 (26), 10912-10925 (2017).
- Rak, M., et al. Yeast cells lacking the mitochondrial gene encoding the ATP synthase subunit 6 exhibit a selective loss of complex IV and unusual mitochondrial morphology. J Biol Chem. 282 (15), 10853-10864 (2007).
- Perez-Martinez, X., Broadley, S. A., Fox, T. D. Mss51p promotes mitochondrial Cox1p synthesis and interacts with newly synthesized Cox1p. EMBO J. 22 (21), 5951-5961 (2003).
- Sanchirico, M. E., Fox, T. D., Mason, T. L. Accumulation of mitochondrially synthesized Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cox2p and Cox3p depends on targeting information in untranslated portions of their mRNAs. EMBO J. 17 (19), 5796-5804 (1998).
- Saracco, S. A., Fox, T. D. Cox18p is required for export of the mitochondrially encoded Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cox2p C-tail and interacts with Pnt1p and Mss2p in the inner membrane. Mol Biol Cell. 13 (4), 1122-1131 (2002).
- McStay, G. P., Su, C. H., Thomas, S. M., Xu, J. T., Tzagoloff, A. Characterization of assembly intermediates containing subunit 1 of yeast cytochrome oxidase. J Biol Chem. 288 (37), 26546-26556 (2013).
- Golik, P., Bonnefoy, N., Szczepanek, T., Saint-Georges, Y., Lazowska, J. The Rieske FeS protein encoded and synthesized within mitochondria complements a deficiency in the nuclear gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 100 (15), 8844-8849 (2003).
- Franco, L. V. R., et al. Allotopic expression of COX6 elucidates Atco-driven co-assembly of cytochrome oxidase and ATP synthase. Life Sci Alliance. 6 (11), e202301965 (2023).
- Mireau, H., Arnal, N., Fox, T. D. Expression of Barstar as a selectable marker in yeast mitochondria. Mol Genet Genomics. 270 (1), 1-8 (2003).
- Cohen, J. S., Fox, T. D. Expression of green fluorescent protein from a recoded gene inserted into Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondrial DNA. Mitochondrion. 1 (2), 181-189 (2001).
- Suhm, T., et al. A novel system to monitor mitochondrial translation in yeast. Microb Cell. 5 (3), 158-164 (2018).
- Rzepka, M., Suhm, T., Ott, M. Incorporation of reporter genes into mitochondrial DNA in budding yeast. STAR Protoc. 3 (2), 101359 (2022).
- Steele, D. F., Butler, C. A., Fox, T. D. Expression of a recoded nuclear gene inserted into yeast mitochondrial DNA is limited by mRNA-specific translational activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 93 (11), 5253-5257 (1996).
- Flores-Mireles, D., Camacho-Villasana, Y., Pérez-Martínez, X. The ARG8m reporter for the study of yeast mitochondrial translation. Methods Mol Biol. 2661, 281-301 (2023).
- Perez-Martinez, X., Butler, C. A., Shingu-Vazquez, M., Fox, T. D. Dual functions of Mss51 couple synthesis of Cox1 to assembly of cytochrome c oxidase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria. Mol Biol Cell. 20 (20), 4371-4380 (2009).
- Bonnefoy, N., Remacle, C., Fox, T. D. Genetic transformation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii mitochondria. Methods Cell Biol. 80, 525-548 (2007).
- Veloso Ribeiro Franco, L., Barros, M. H. Biolistic transformation of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondrial DNA. IUBMB Life. 75 (12), 972-982 (2023).
- Bonnefoy, N., Fox, T. D. Directed alteration of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondrial DNA by biolistic transformation and homologous recombination. Methods Mol Biol. 372, 153-166 (2007).
- Butow, R. A., Henke, R. M., Moran, J. V., Belcher, S. M., Perlman, P. S. Transformation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria using the biolistic gun. Methods Enzymol. 264, 265-278 (1996).
- Bonnefoy, N., Fox, T. D. Genetic transformation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria. Methods Cell Biol. 65, 381-396 (2001).
- Shingú-Vázquez, M., et al. The carboxyl-terminal end of Cox1 is required for feedback assembly regulation of Cox1 synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 285 (45), 34382-34389 (2010).
- Bonnefoy, N., Bsat, N., Fox, T. D. Mitochondrial translation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae COX2 mRNA is controlled by the nucleotide sequence specifying the pre-Cox2p leader peptide. Mol Cell Biol. 21 (7), 2359-2372 (2001).
- Meunier, B., Lemarre, P., Colson, A. M. Genetic screening in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for large numbers of mitochondrial point mutations which affect structure and function of catalytic subunits of cytochrome-c oxidase. Eur J Biochem. 213 (1), 129-135 (1993).
- Dorweiler, J. E., Manogaran, A. L. Cytoduction and plasmiduction in yeast. Bio Protoc. 11 (17), 4146 (2021).
- Zakharov, I. A., Yarovoy, B. P. Cytoduction as a new tool in studying the cytoplasmic heredity in yeast. Mol Cell Biochem. 14 (1-3), 15-18 (1977).
- Conde, J., Fink, G. R. A mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae defective for nuclear fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 73 (10), 3651-3655 (1976).
- Burke, D., Dawson, D., Stearns, T. . Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Methods in yeast genetics : a Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory manual. 2000 ed. , (2000).
- Dunham, M. J., Gartenberg, M. R., Brown, G. W. : a. Methods in yeast genetics and genomics : a Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory course manual. 2015 edition. , (2015).
- Ding, M. G., et al. Chapter 27 An improved method for introducing point mutations into the mitochondrial cytochrome B gene to facilitate studying the role of cytochrome B in the formation of reactive oxygen species. Methods Enzymol. 456, 491-506 (2009).
- Klein, C. J. L., Olsson, L., Nielsen, J. Glucose control in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: the role of Mig1 in metabolic functions. Microbiology (Reading). 144, 13-24 (1998).
- Rolland, F., Winderickx, J., Thevelein, J. M. Glucose-sensing and -signalling mechanisms in yeast. FEMS Yeast Res. 2 (2), 183-201 (2002).
- Gruschke, S., et al. The Cbp3-Cbp6 complex coordinates cytochrome b synthesis with bc(1) complex assembly in yeast mitochondria. J Cell Biol. 199 (1), 137-150 (2012).
- Seshadri, S. R., Banarjee, C., Barros, M. H., Fontanesi, F. The translational activator Sov1 coordinates mitochondrial gene expression with mitoribosome biogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 48 (12), 6759-6774 (2020).
- Rak, M., Tzagoloff, A. F1-dependent translation of mitochondrially encoded Atp6p and Atp8p subunits of yeast ATP synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 106 (44), 18509-18514 (2009).
- He, S., Fox, T. D. Mutations affecting a yeast mitochondrial inner membrane protein, pnt1p, block export of a mitochondrially synthesized fusion protein from the matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 19 (10), 6598-6607 (1999).
- Rak, M., et al. Regulation of mitochondrial translation of the ATP8/ATP6 mRNA by Smt1p. Mol Biol Cell. 27 (6), 919-929 (2016).
- Barrera-Paez, J. D., Moraes, C. T. Mitochondrial genome engineering coming-of-age. Trends Genet. 38 (8), 869-880 (2022).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved