Thyristor Rectifier
Source: Ali Bazzi, Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT.
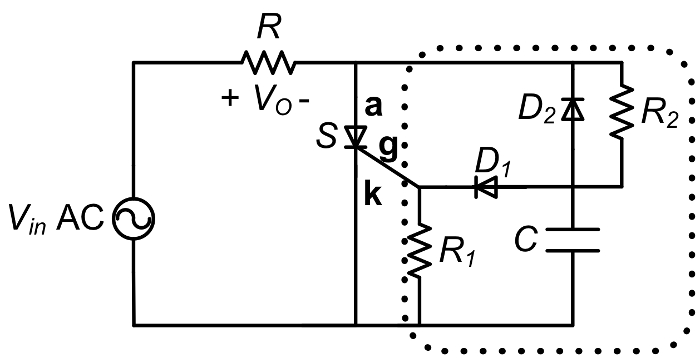
Similar to diodes, thyristors, also called silicon controlled rectifiers (SCRs), pass current in one direction from the anode to cathode, and block current flow in the other direction. However, current passage can be controlled through a "gate" terminal, which requires a small current pulse to turn on the thyristor so it can start conducting.
Thyristors are four-layer devices, composed of alternating layers of n-type and p-type material, thereby forming PNPN structures with three junctions. The thyristor has three terminals; with the anode connected to the p-type material of the PNPN structure, the cathode connected to the n-type layer, and the gate connected to the p-type layer nearest the cathode.
The objective of this experiment is to study a controlled thyristor-based half-wave rectifier at different conditions, and understand how different timings of the gate pulse affect the DC output voltage.
ATTENTION: During this experiment, do not touch any part of the circuit while energized. Do NOT ground the VARIAC.
For this experiment, the variable transformer (VARIAC) at a low frequency of 60 Hz and peak of 35 V is used as the main AC source.
1. Setup
- Before starting, connect the differential probe to one scope channel.
- Set the button on the differential probe to 1/20 (or 20X) attenuation.
- On the sc
The AC input voltage waveform is chopped until the firing angle. Important relationships of the average output voltage and firing angles for different SCR rectifiers with input Vin= V0 cos(ωt) are:
• Single SCR and R load: <Vout>=V0[1+cos(α)]/(2π) (2)
SCR's were common in older DC power supplies that required a variable DC output voltage from an AC input. By adjusting the resistor R2 in the above circuit, it is possible to adjust the average Vout and therefor an adjustable DC power supply results. SCRs are not common any more in DC power supplies as they switch at the input line frequency (typically 50 or 60 Hz), and new power supplies switch at 10 s or 100 s of kHz which makes filtering the output voltage to extract the DC
Vai a...
Video da questa raccolta:

Now Playing
Thyristor Rectifier
Electrical Engineering
17.4K Visualizzazioni

Electrical Safety Precautions and Basic Equipment
Electrical Engineering
144.5K Visualizzazioni

Characterization of Magnetic Components
Electrical Engineering
15.0K Visualizzazioni

Introduction to the Power Pole Board
Electrical Engineering
12.4K Visualizzazioni

DC/DC Boost Converter
Electrical Engineering
56.7K Visualizzazioni

DC/DC Buck Converter
Electrical Engineering
21.1K Visualizzazioni

Flyback Converter
Electrical Engineering
13.2K Visualizzazioni

Single Phase Transformers
Electrical Engineering
20.1K Visualizzazioni

Single Phase Rectifiers
Electrical Engineering
23.4K Visualizzazioni

Single Phase Inverter
Electrical Engineering
17.9K Visualizzazioni

DC Motors
Electrical Engineering
23.3K Visualizzazioni

AC Induction Motor Characterization
Electrical Engineering
11.6K Visualizzazioni

VFD-fed AC Induction Machine
Electrical Engineering
6.9K Visualizzazioni

AC Synchronous Machine Synchronization
Electrical Engineering
21.5K Visualizzazioni

AC Synchronous Machine Characterization
Electrical Engineering
14.2K Visualizzazioni